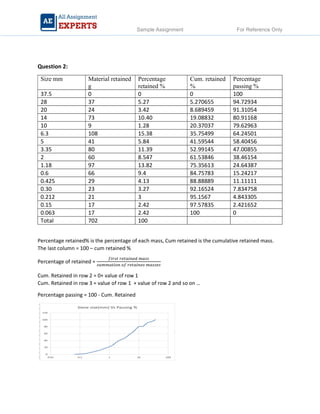
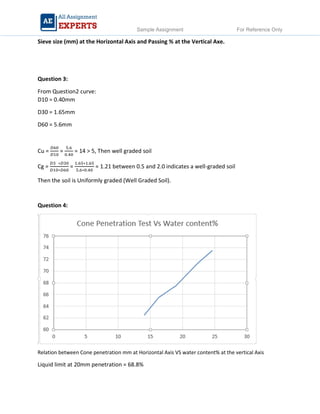
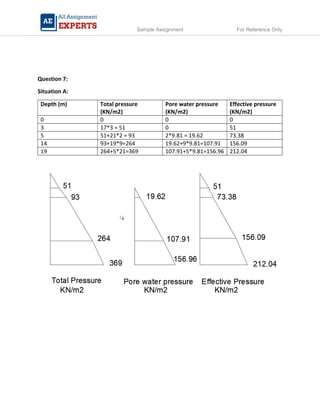
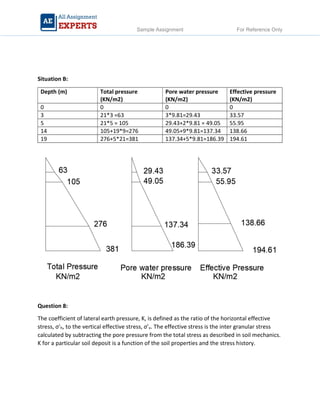
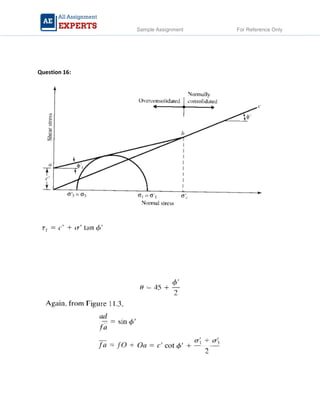
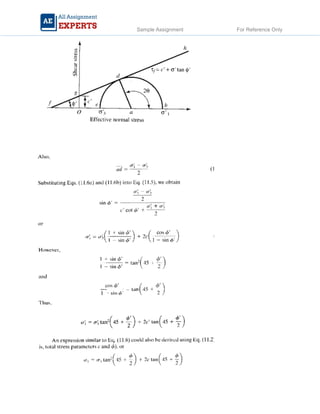
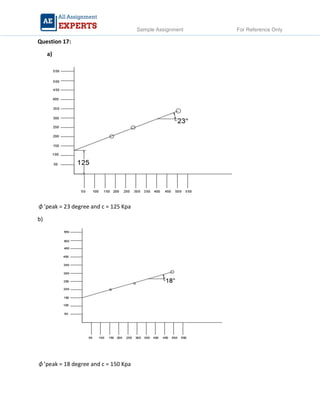
The document contains detailed soil analysis assignments covering various characteristics such as void ratio, specific surface area, and soil classification related to different types of soils. It includes calculations of mass retention, effective pressures, lateral earth pressure, and permeability coefficients in relation to soil mechanics. Additionally, it discusses methods for measuring groundwater flow and shear strength, with parameter comparisons between different soil conditions.