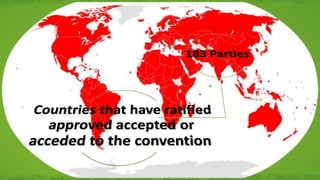
The document discusses the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). CITES aims to ensure international trade in wildlife and plants does not threaten species survival. It protects over 35,000 species and regulates trade through a licensing system. Species are classified into three appendices based on extinction risk, and trade restrictions increase from Appendix I to III. The CITES Secretariat coordinates the convention's implementation and provides services to parties.