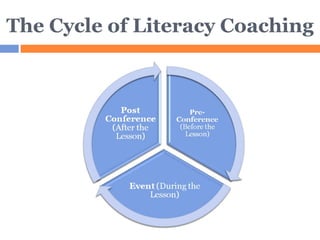
The document discusses the role of literacy coaches and facilitators in developing teachers. It describes three main roles: interventionist, literacy coach, and professional developer. It also outlines the cycle of literacy coaching which involves pre-conferences, classroom observations, and post-conferences between the coach and teacher. The purpose is to jointly analyze teaching and identify improvements to better engage students. Creating professional learning communities is presented as an effective model for ongoing, collaborative professional development.