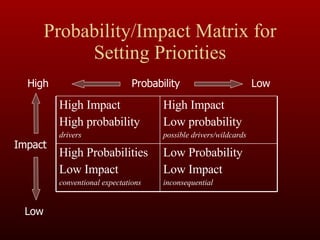
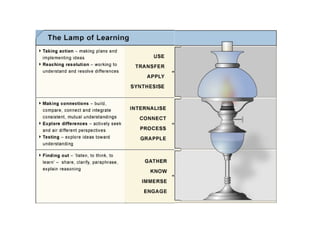
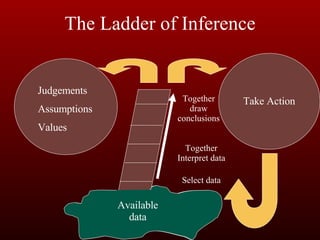
The document outlines an agenda for a leadership development workshop focusing on building sustainable school leadership skills. It discusses principles of sustainability like depth, breadth, and justice. It provides models for quality professional dialogue including quality learning circles and a pedagogy coaching model. It also addresses having tough conversations and developing issue identification and prioritization strategies.