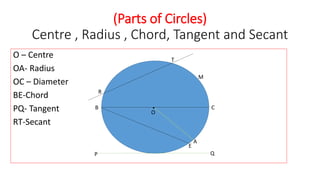
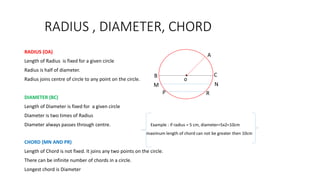
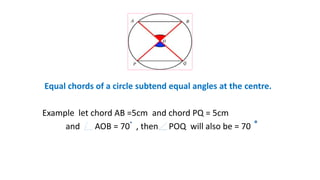
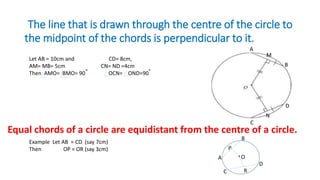
This document defines and describes key parts of a circle including the center, radius, diameter, chord, tangent, and secant. It explains that the radius is half the diameter and connects the center to points on the circle. The diameter passes through the center. A chord connects two points on the circle. A tangent touches at a single point while a secant intersects at two points. Equal chords subtend equal angles at the center and the line through the center to the chord midpoint is perpendicular to the chord. Equal chords are also equidistant from the center.