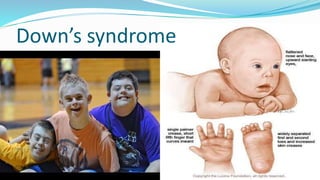
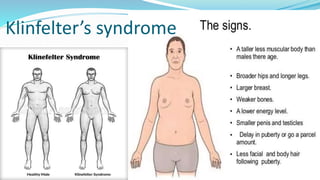
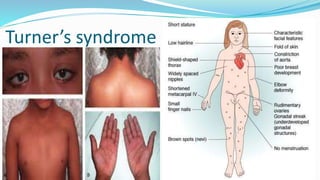
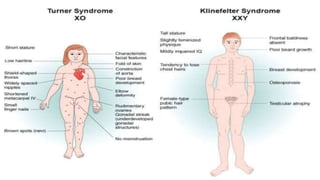
Chromosomal disorders occur due to an abnormal number or structure of chromosomes. There are three main types: changes in number (aneuploidy), changes in structure (translocations or duplications), and changes in both number and structure. Examples of chromosomal disorders include Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY), and Turner syndrome (45,X). Down syndrome is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 and results in intellectual disabilities and characteristic physical features. Klinefelter syndrome affects males and is caused by an extra X chromosome. Turner syndrome only affects females and is caused by the absence of one X chromosome.