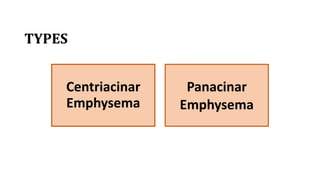
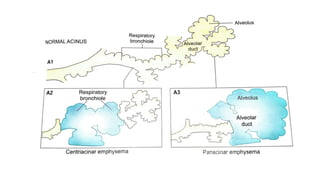
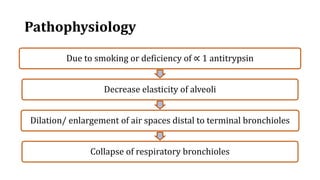
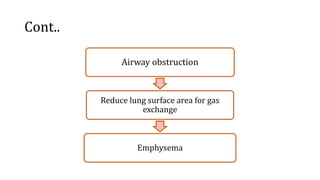
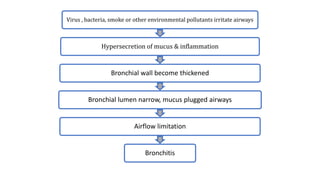
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) encompasses chronic bronchitis and emphysema, primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke. Emphysema involves progressive damage to lung alveoli, leading to airflow obstruction, while chronic bronchitis is characterized by a persistent cough with sputum production. Management strategies include medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes, emphasizing the importance of smoking cessation.