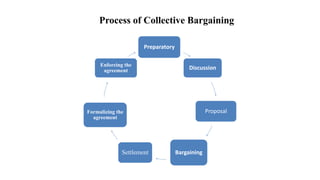
The document discusses collective bargaining in nursing, outlining its definition, objectives, and the processes involved. It highlights the characteristics, merits, and demerits of collective bargaining, as well as types of bargaining such as distributive and integrative. Additionally, it covers the role of healthcare laws, employee unions, and their objectives in safeguarding worker interests and improving conditions.