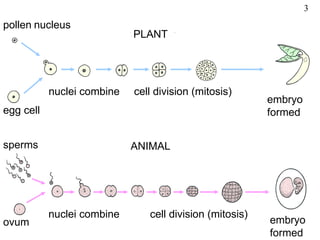
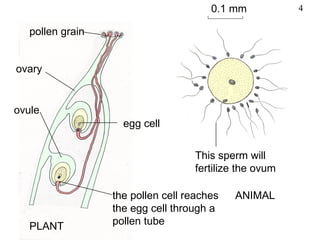
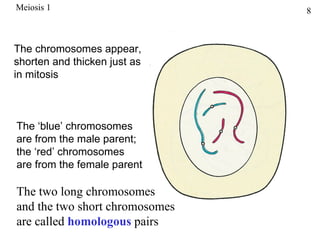
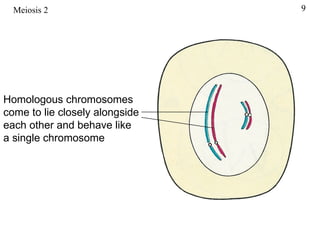
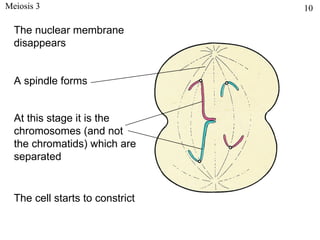
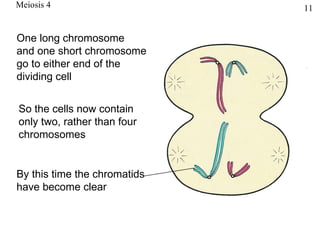
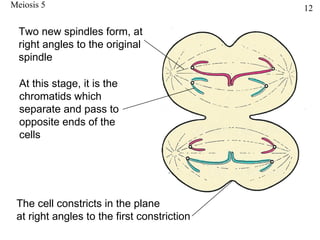
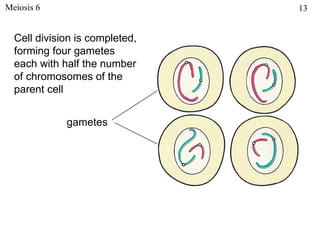
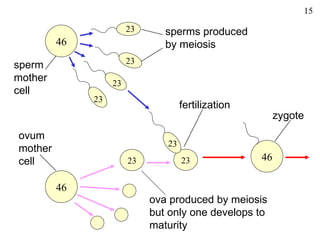
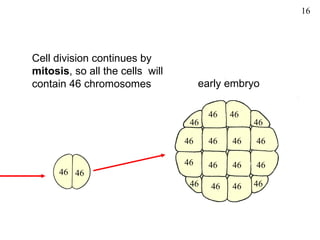
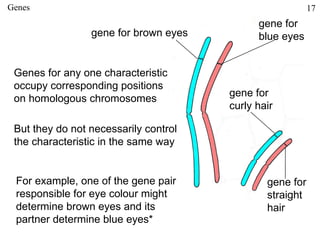
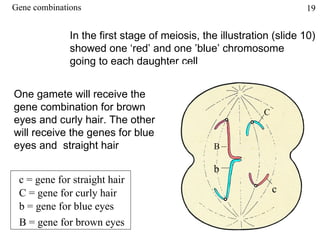
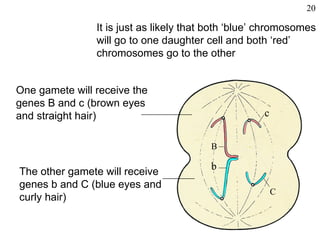
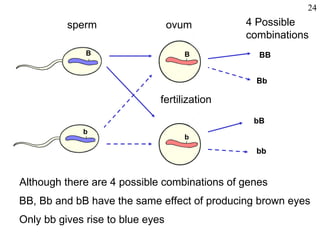
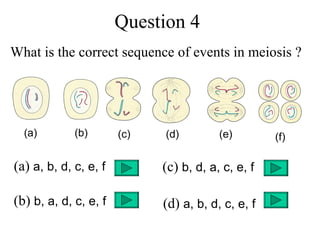
The document discusses fertilization and meiosis. It explains that fertilization occurs when male and female gametes combine, forming a zygote. Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes, ensuring zygotes have the normal number. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate, then chromatids separate, resulting in four haploid gametes. This contributes to genetic variation.