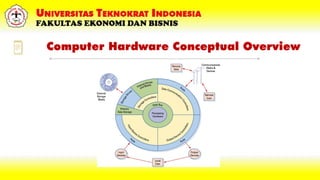
The document is an introduction to information technology focusing on computer hardware, detailing its components, functions, and classifications. It outlines key learning objectives for students, such as identifying hardware parts and understanding their roles in data processing. Additionally, it emphasizes the difference between hardware and software, providing insights into various types of hardware devices and the importance of the motherboard in a computer system.