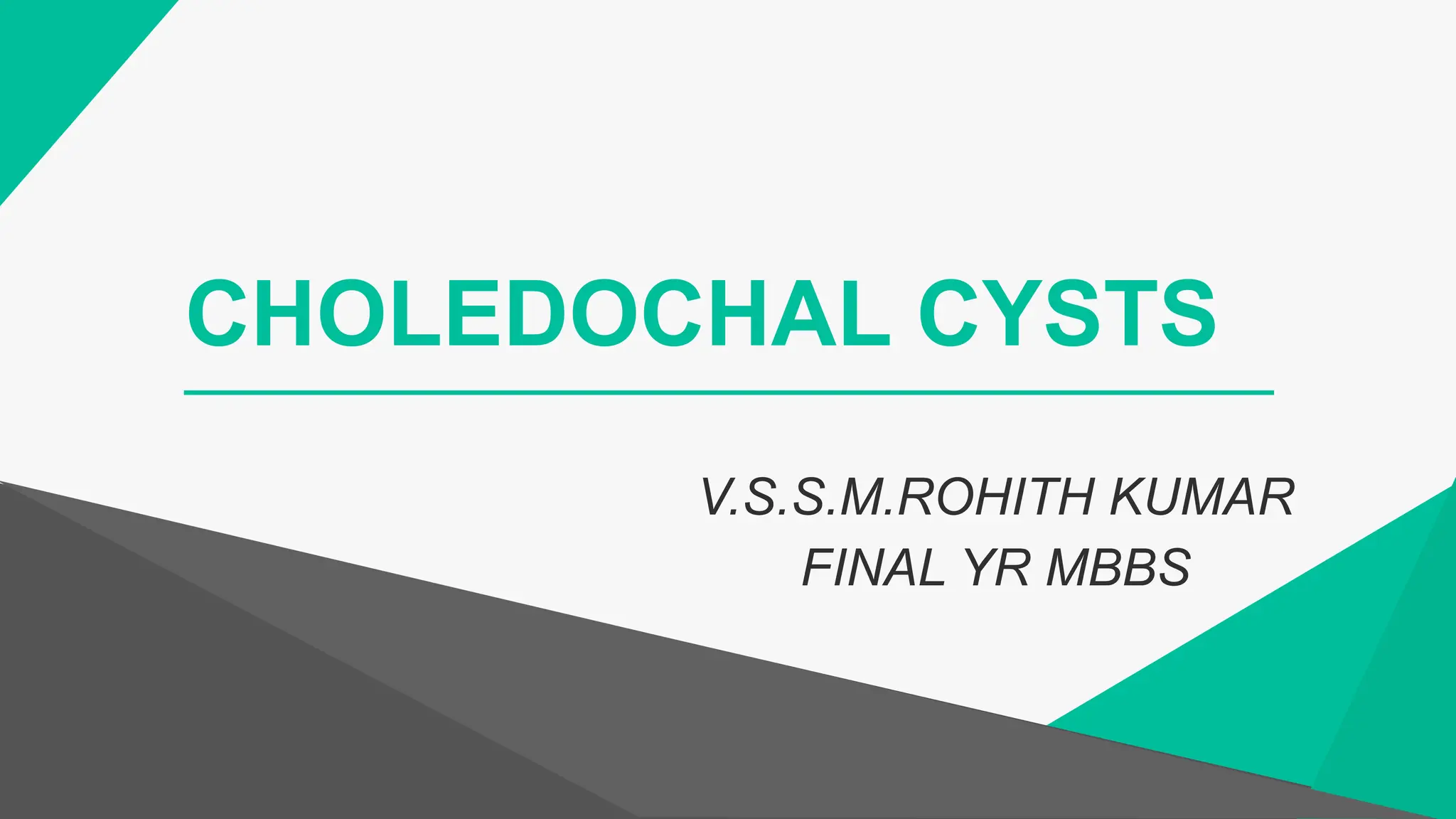
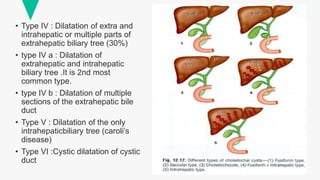
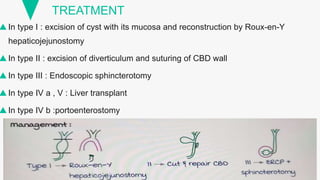
Choledochal cysts are congenital dilations of the biliary tree, more common in Asia with an incidence of 1 in 1000 hospital admissions. They are classified into several types based on their location and characteristics, with presentations including obstructive jaundice, abdominal pain, and complications like pancreatitis and biliary cirrhosis. Treatment varies by type, ranging from cyst excision and reconstruction to liver transplantation.