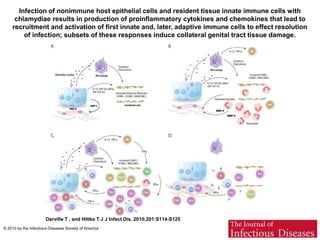
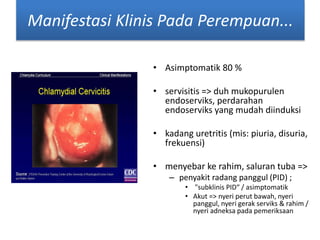
Chlamydia trachomatis adalah infeksi menular seksual yang dapat menyebabkan masalah serius seperti penyakit radang panggul dan infertilitas pada wanita. Gejala infeksi ini bervariasi antara pria dan wanita, dengan sebagian besar wanita tetap asimptomatik. Penularan terjadi melalui kontak seksual dan dapat berdampak pada kesehatan reproduksi.