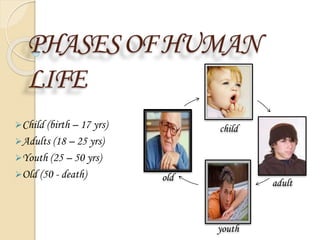
Human beings are the most superior creation, who have remarkable ability to think and progress. There are four phases of human life: child, adult, youth, and old age. Children are considered the purest and most beautiful creation, but many children cannot enjoy basic necessities like good clothes, food, and education due to being forced into child labor instead. Child labor involves children working before the legal minimum age and in harmful conditions that affect them physically, mentally and block their access to education. Poverty, unemployment, population growth, illiteracy, failure of laws, and family traditions are key causes of child labor in Pakistan and other developing nations. Children working in hazardous occupations, commercial sexual exploitation, slavery and illegal activities are