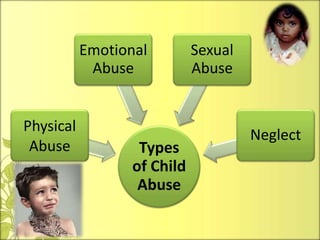
This document discusses child abuse, including its definition, types, causes, symptoms, effects, and prevention. The main types of child abuse are physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, and neglect. Child abuse can cause physical, psychological, behavioral, and societal harm. It is important to prevent child abuse by building children's trust and self-esteem, teaching them about their rights, being supportive listeners, and providing positive feedback. Laws like the Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act provide funding for protecting children from all forms of abuse.