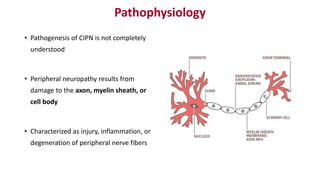
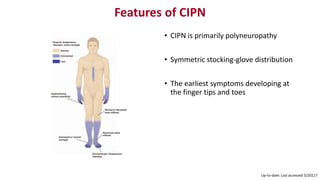
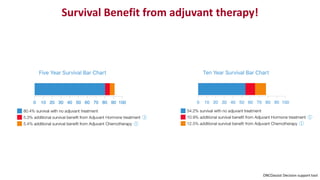
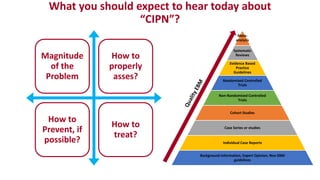
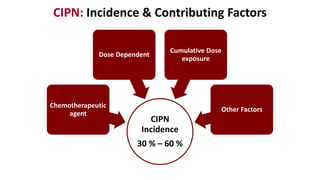
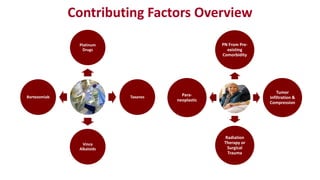
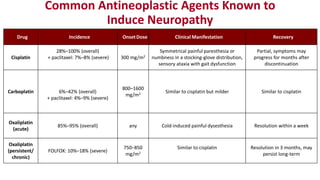
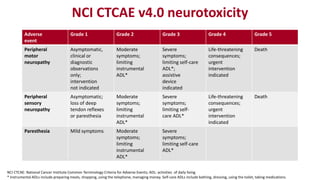
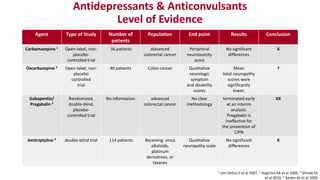
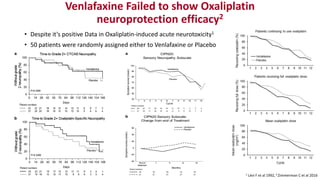
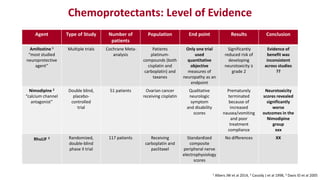
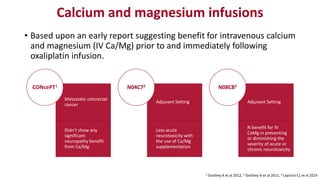
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN) consists of neuromuscular symptoms due to nerve damage from certain chemotherapy agents, significantly affecting patient quality of life. Despite its prevalence, with incidence rates ranging from 30% to 60%, effective prevention and treatment strategies are lacking, and many commonly used interventions lack strong evidence. Clinicians are advised to consider options like duloxetine for treatment, but no established preventative agents are recommended.