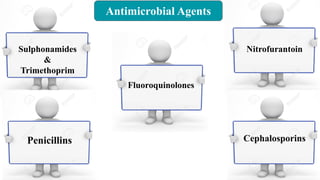
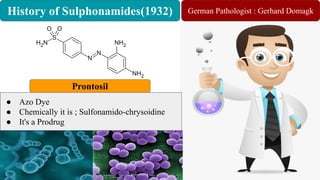
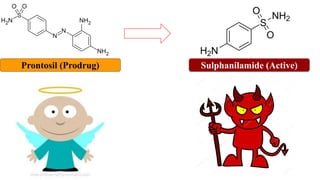
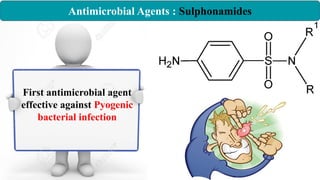
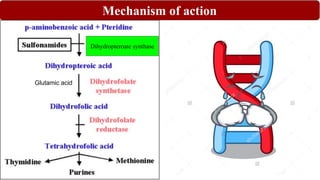
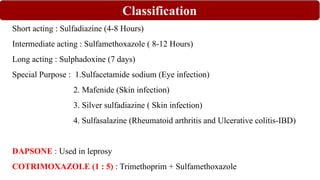
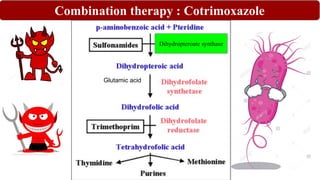
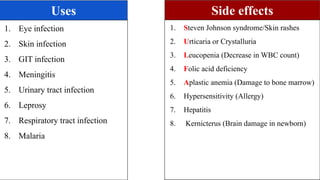
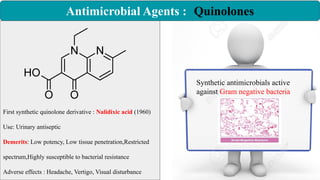
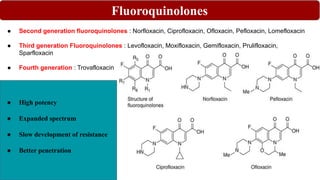
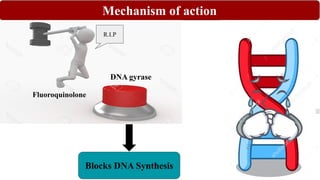
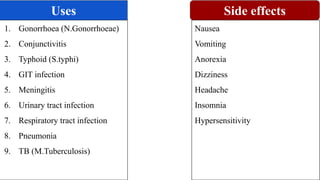
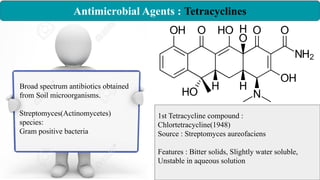
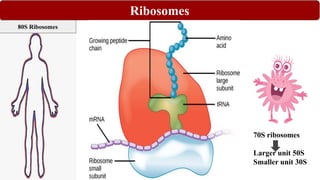
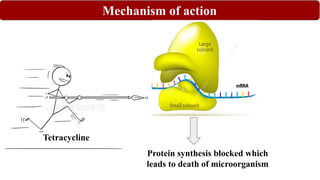
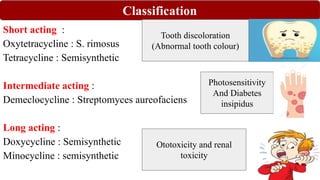
Chemotherapy involves using chemical substances to treat diseases, particularly cancer and microbial infections. The term was coined by Paul Ehrlich, who developed the first effective treatment for syphilis called Salvarsan. Chemotherapeutic agents can be synthetic chemicals or substances produced by microorganisms. Some common classes of antimicrobial agents used in chemotherapy include sulphonamides, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, and others. These work by interfering with bacterial growth and survival through various mechanisms such as inhibiting enzymes or DNA synthesis. While effective against many infections, these agents can sometimes cause side effects and the development of drug resistance remains a concern.