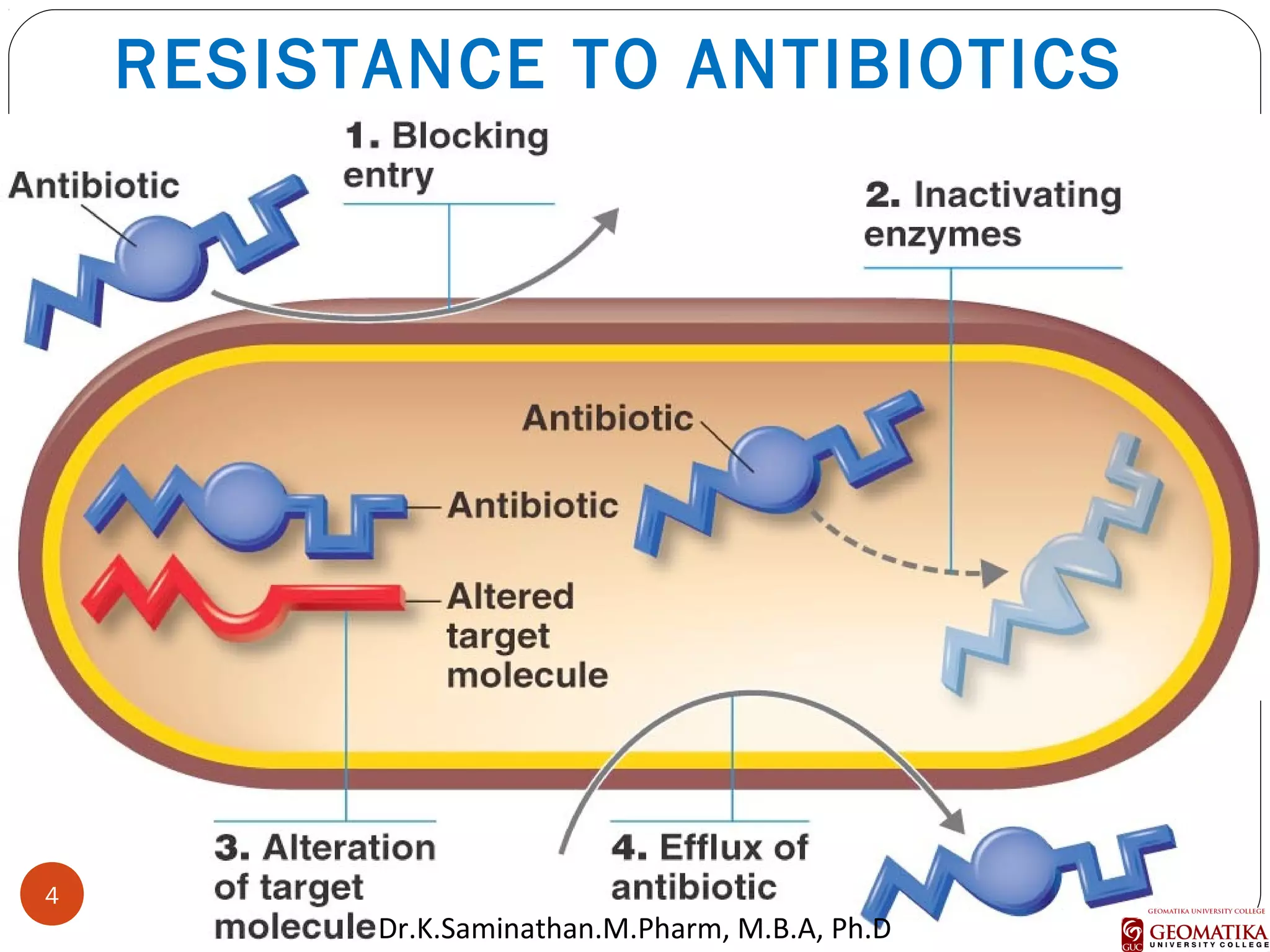
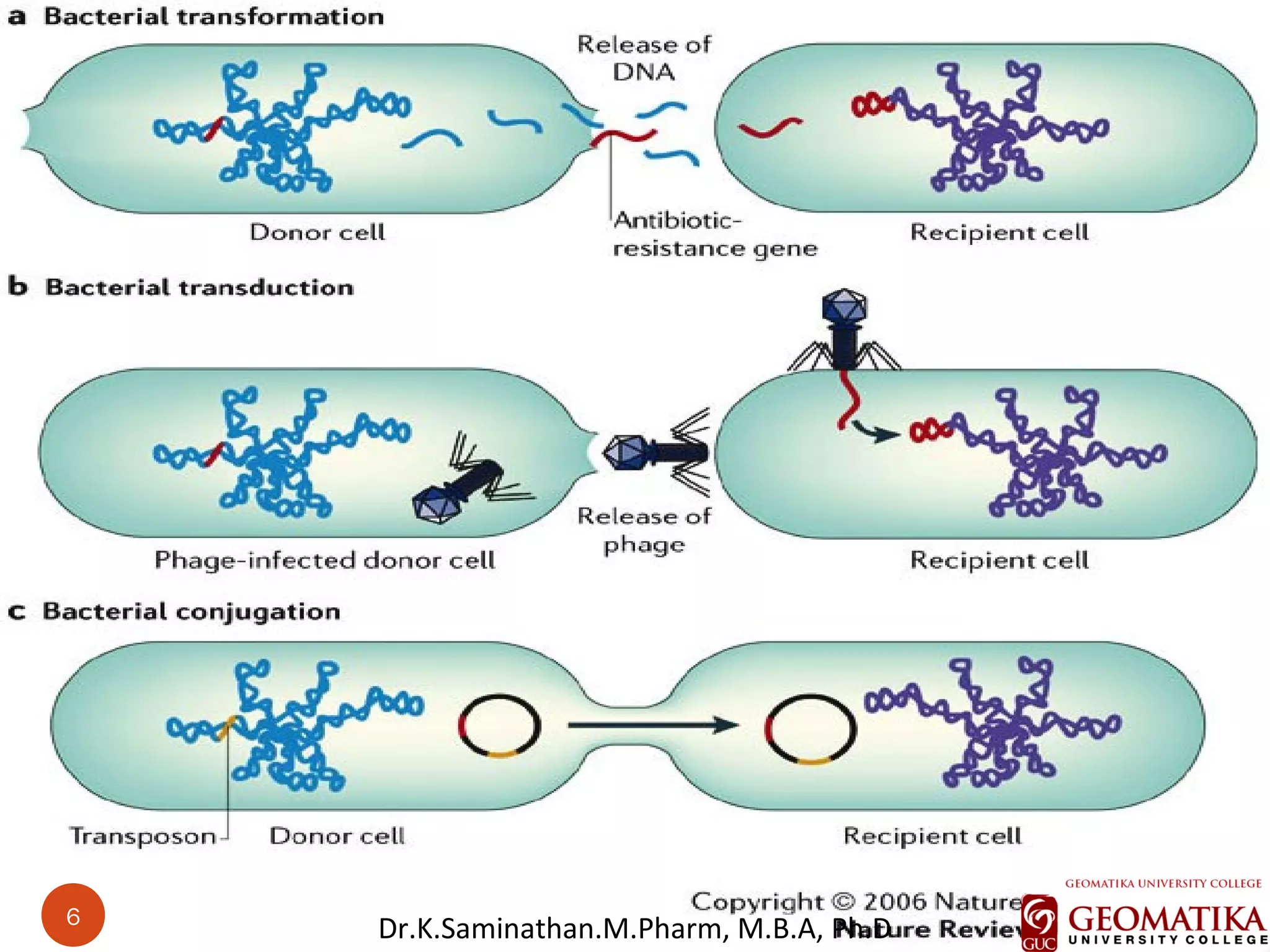
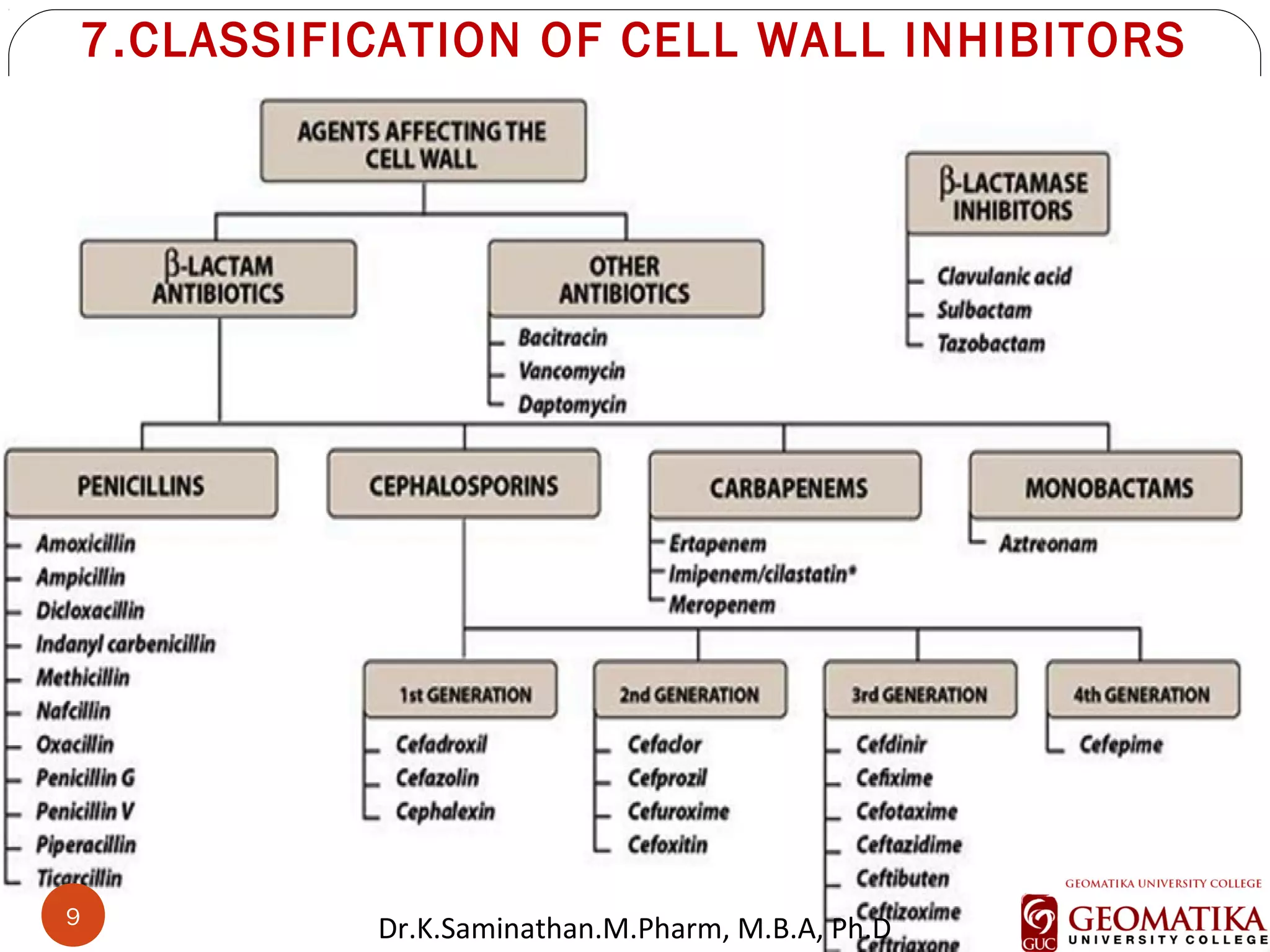
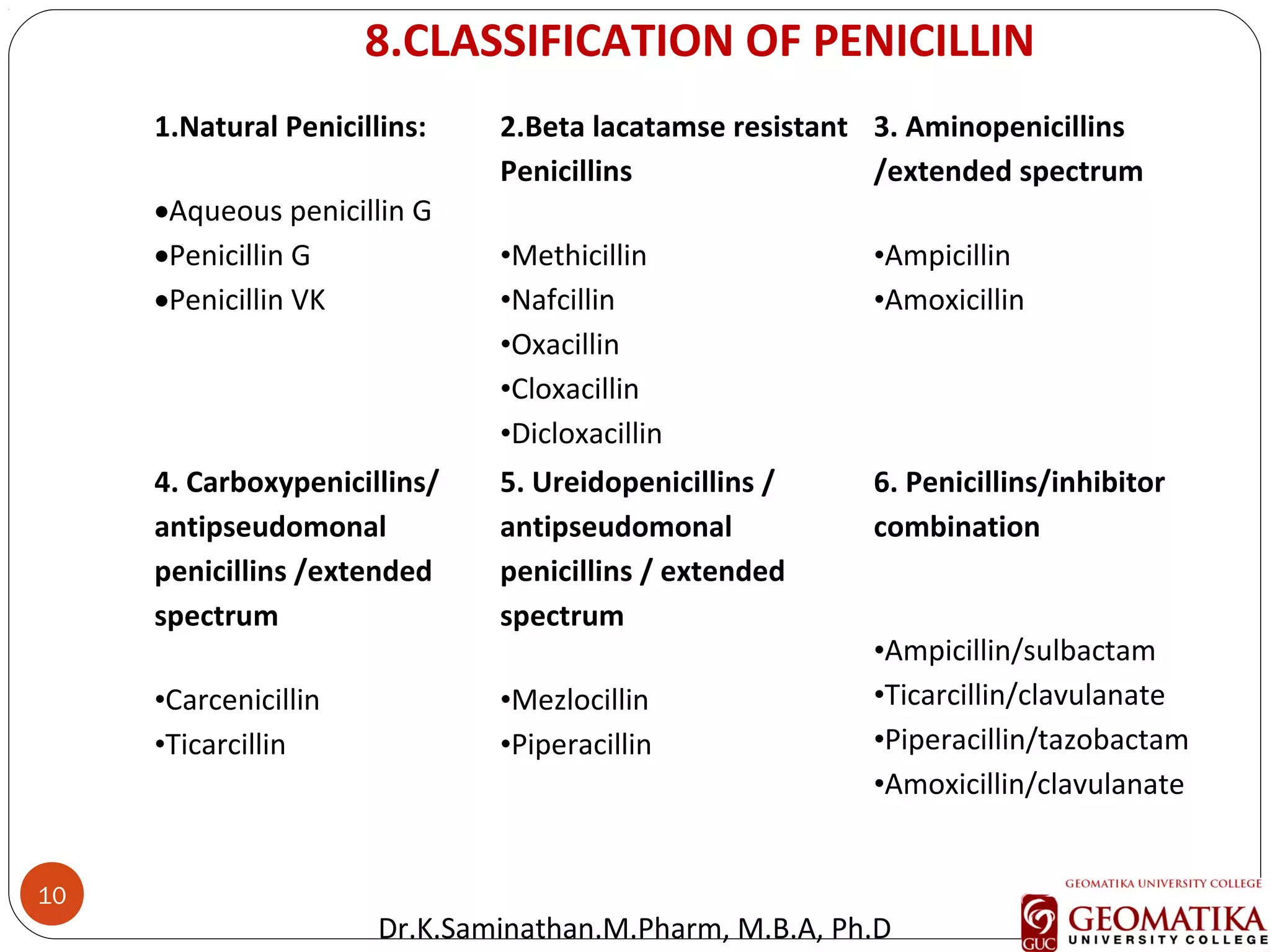
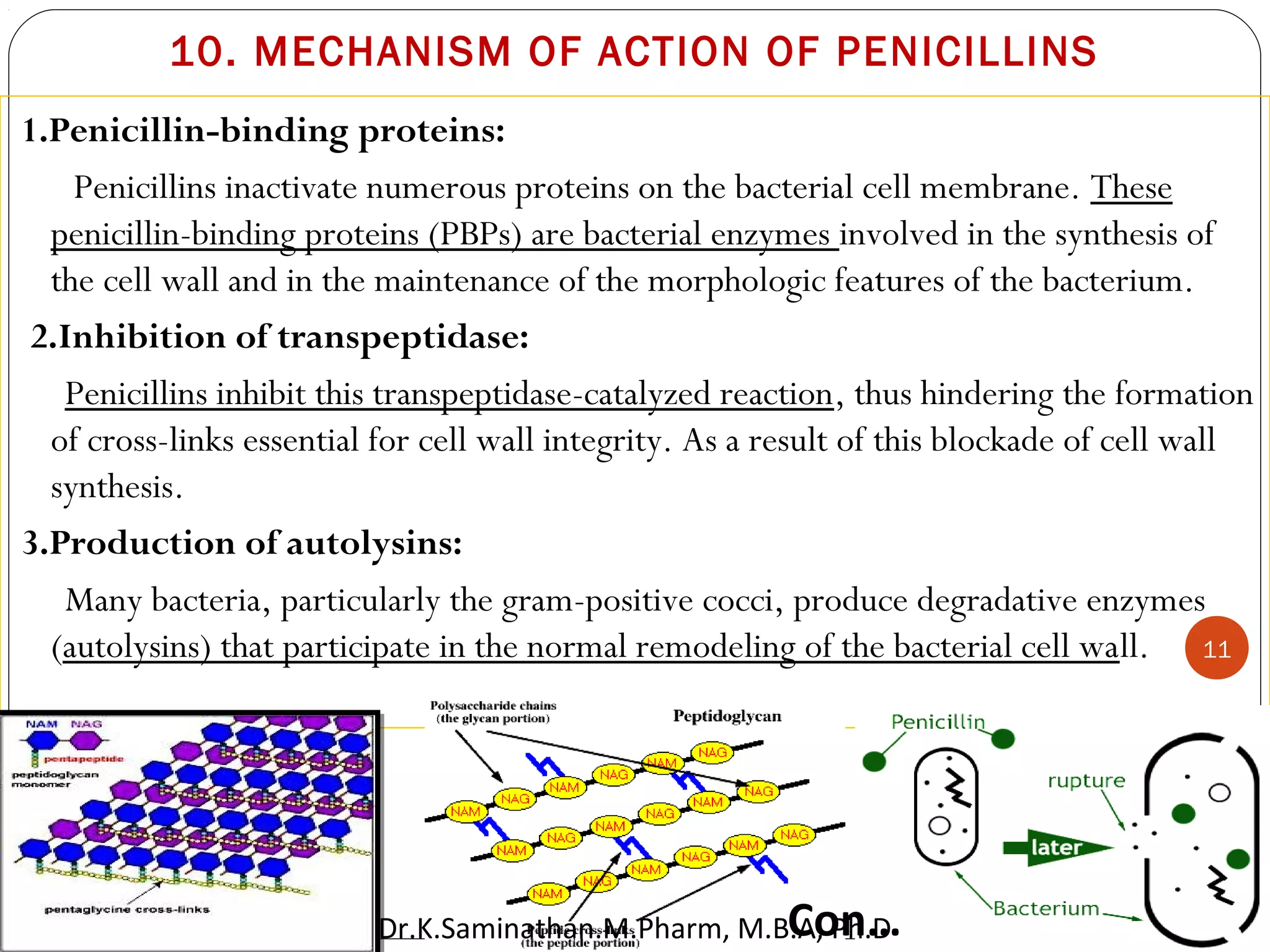
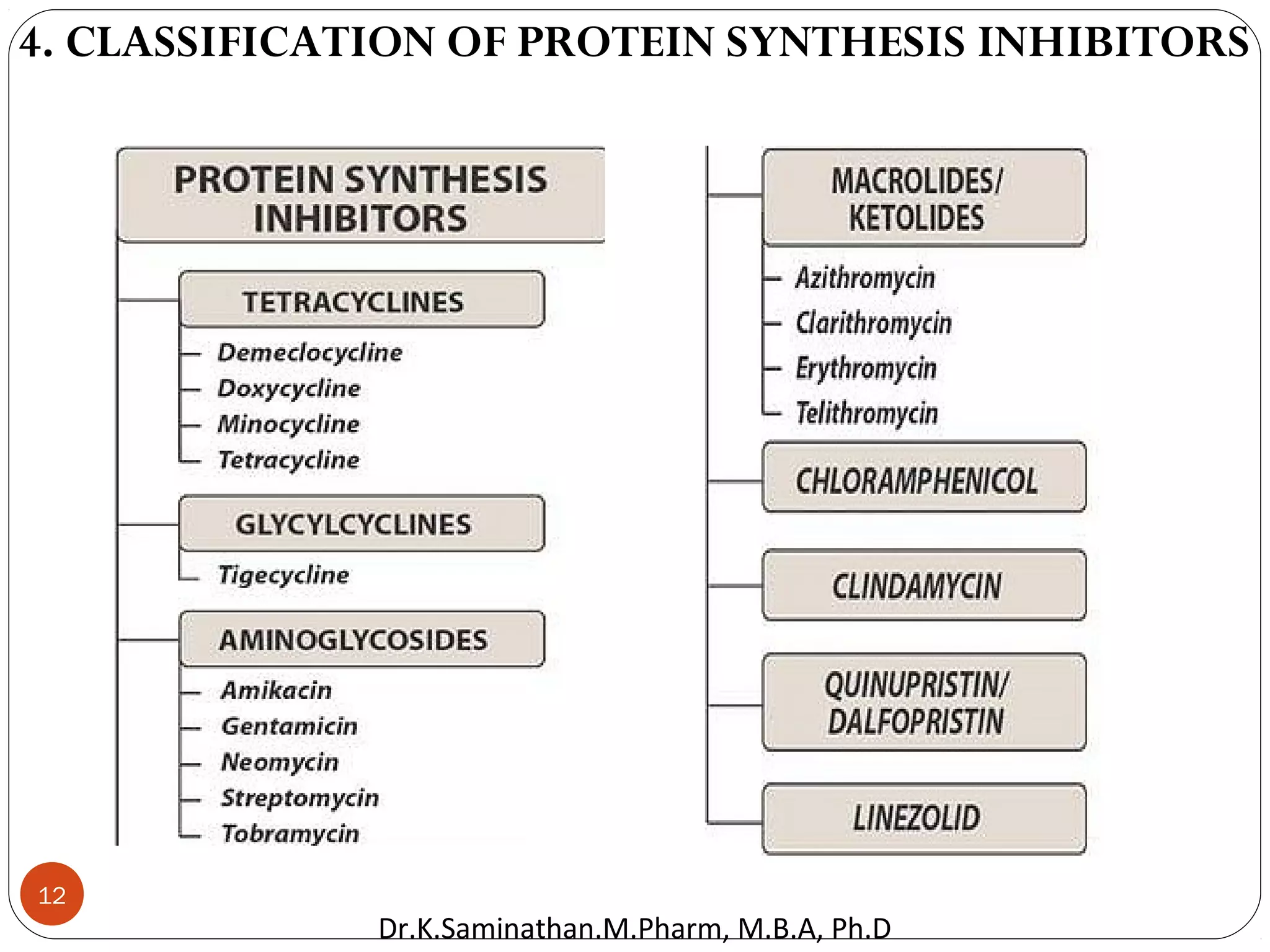
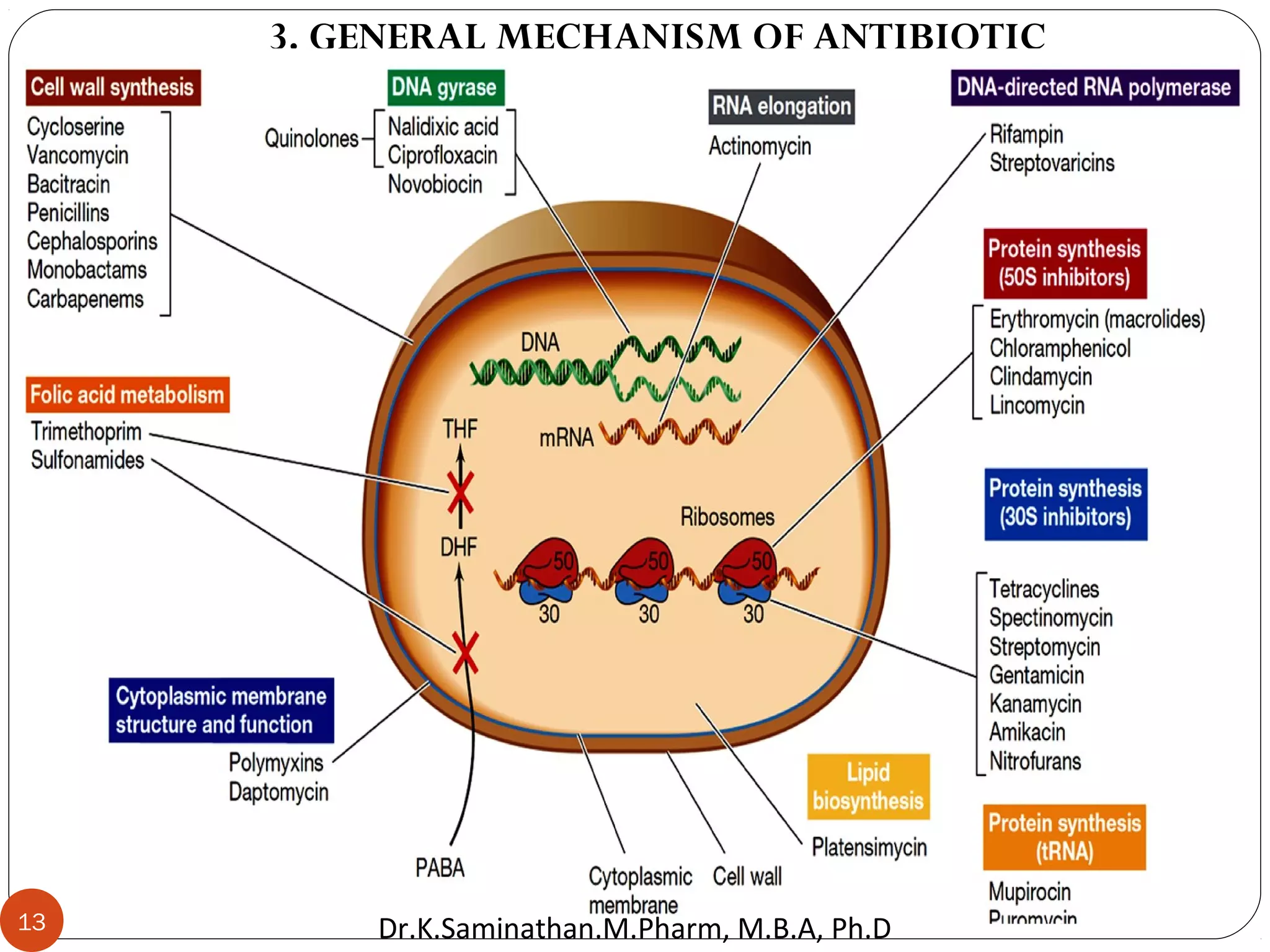
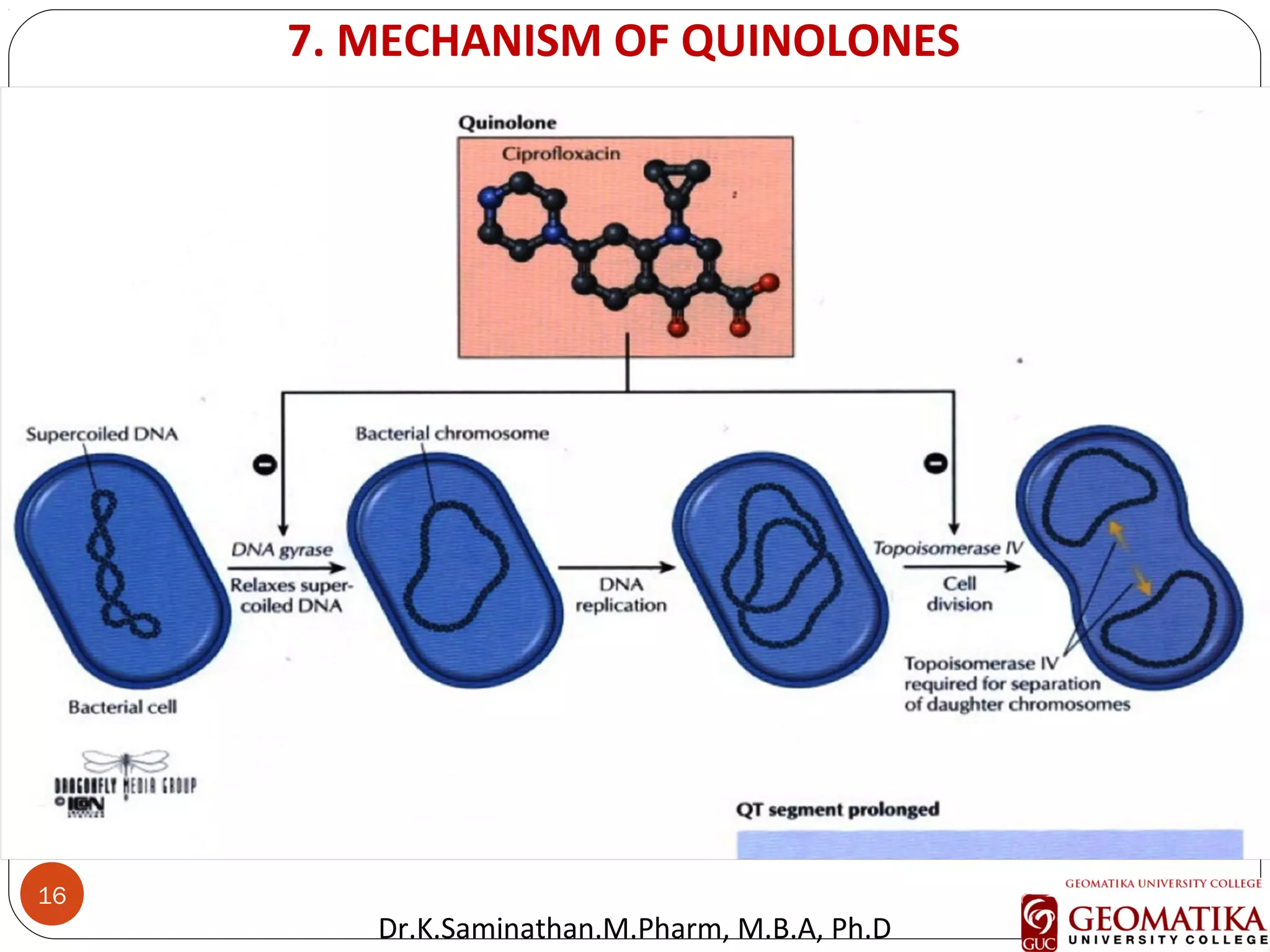
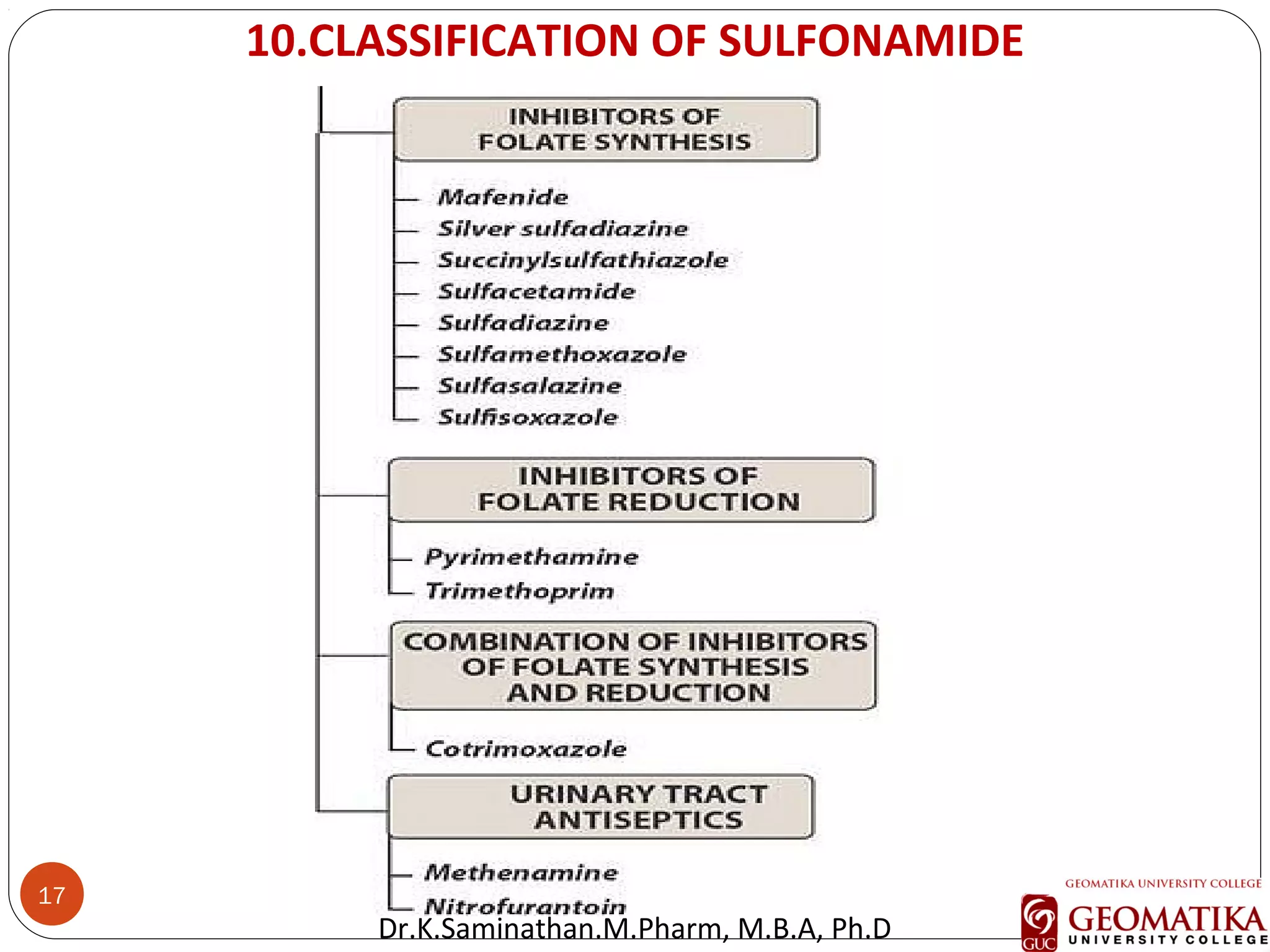
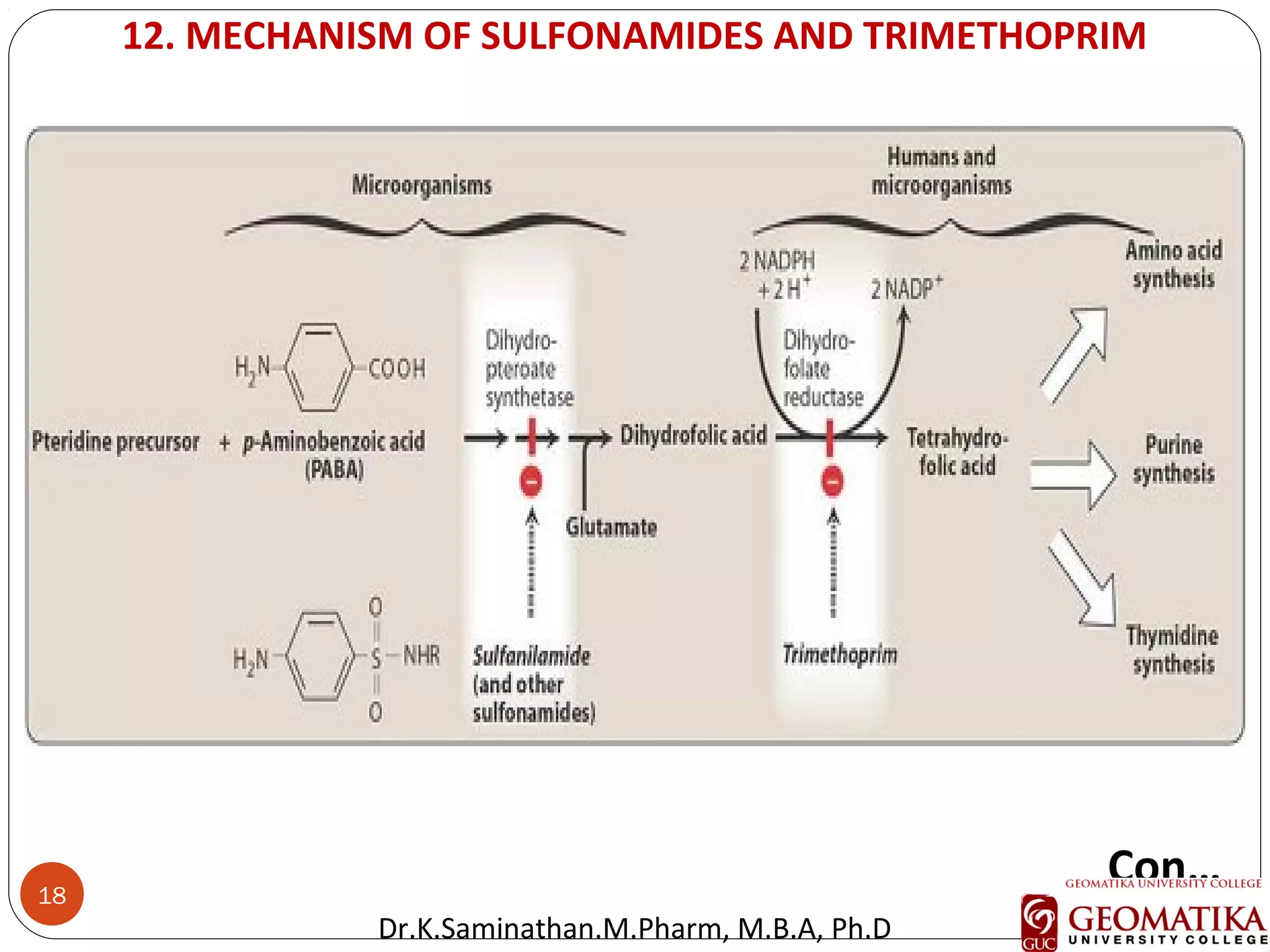
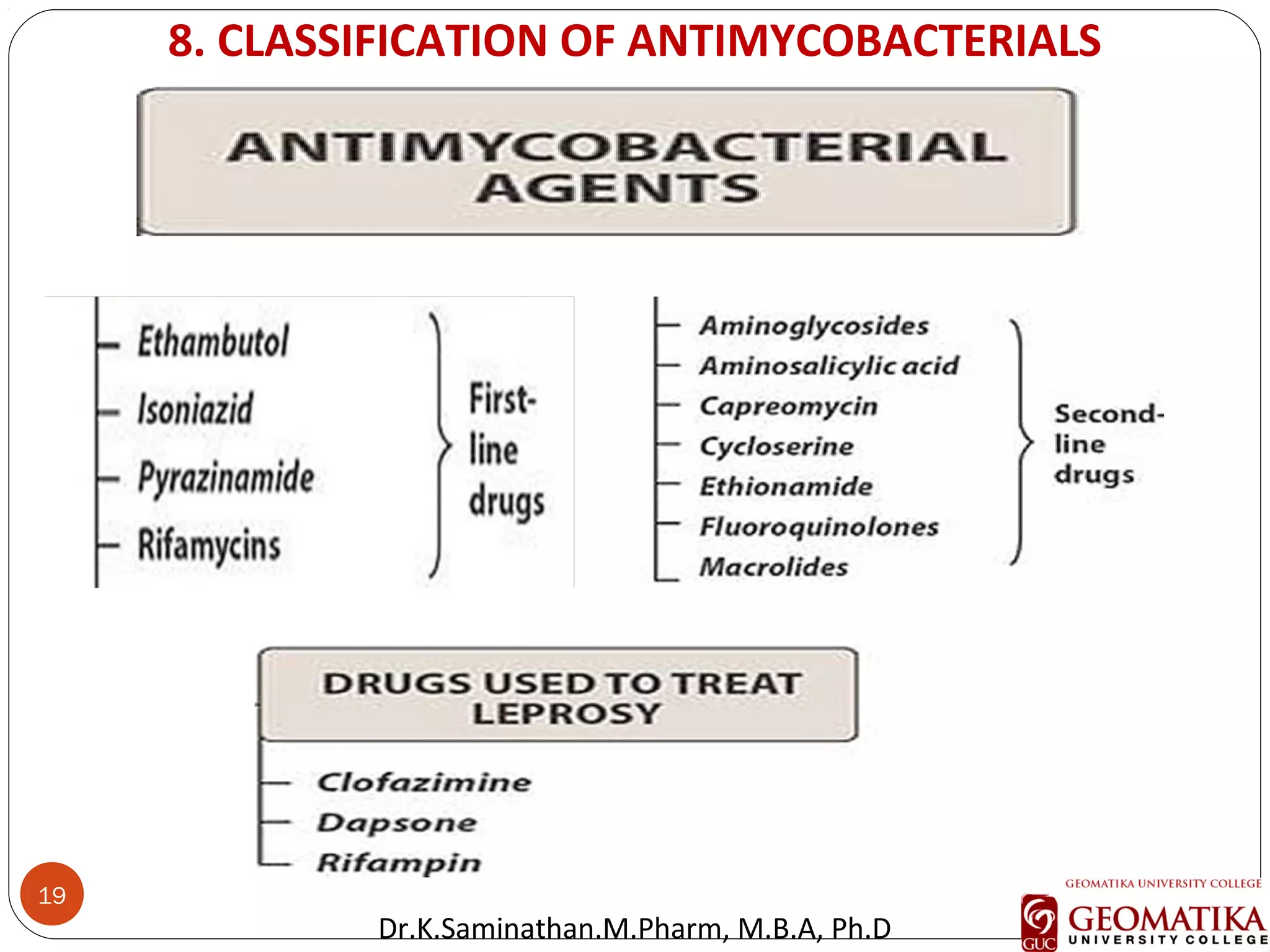
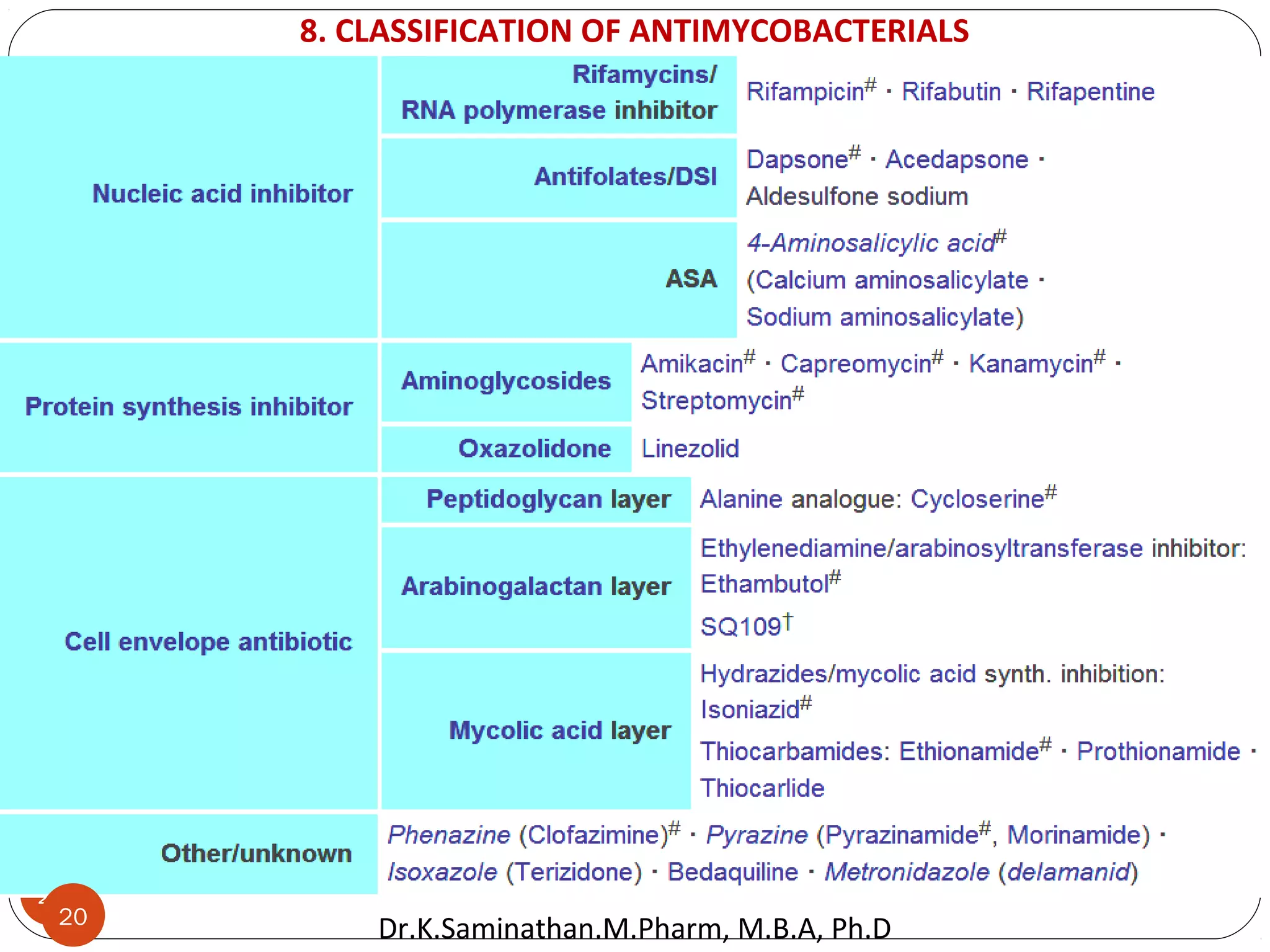
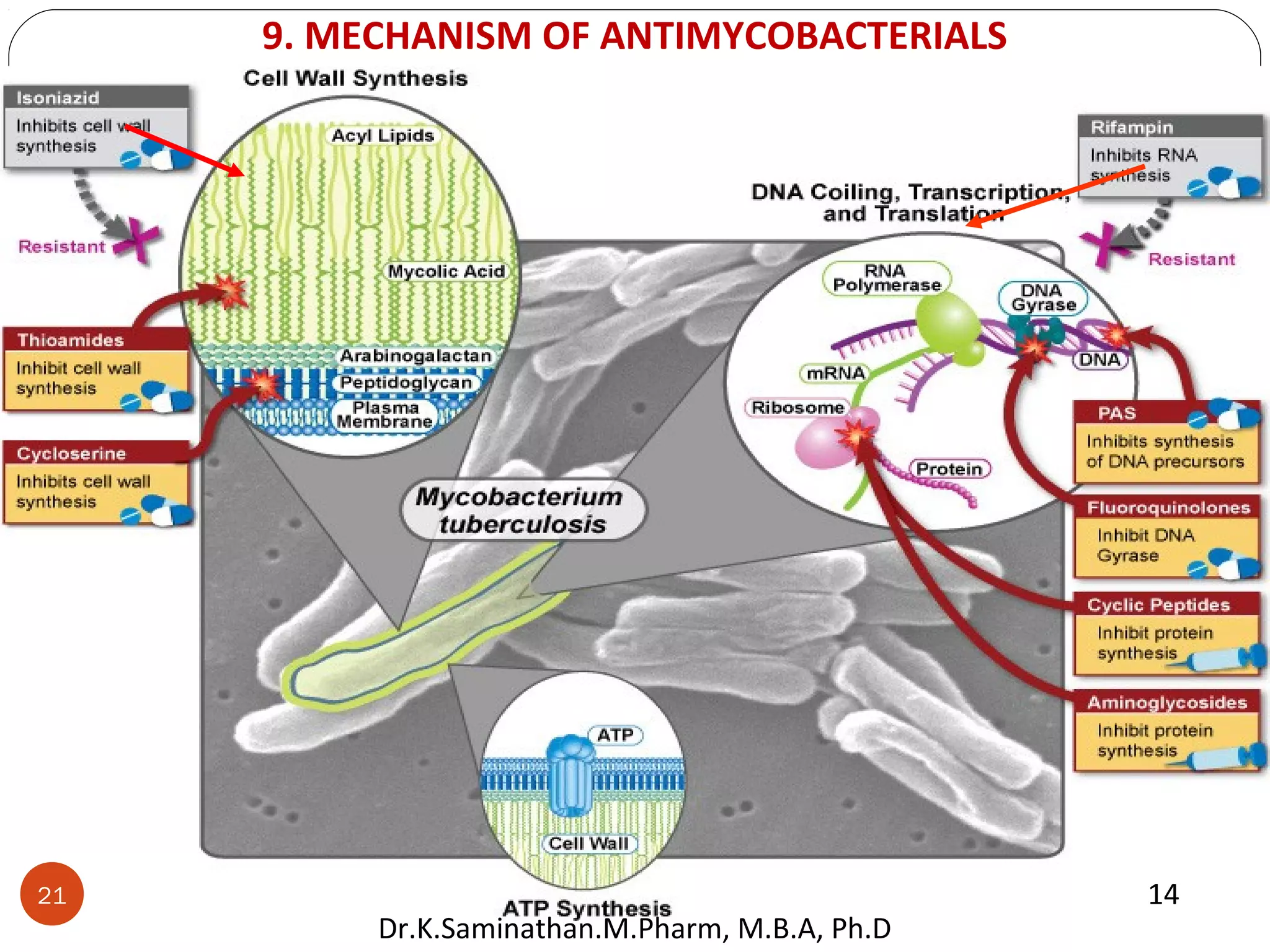
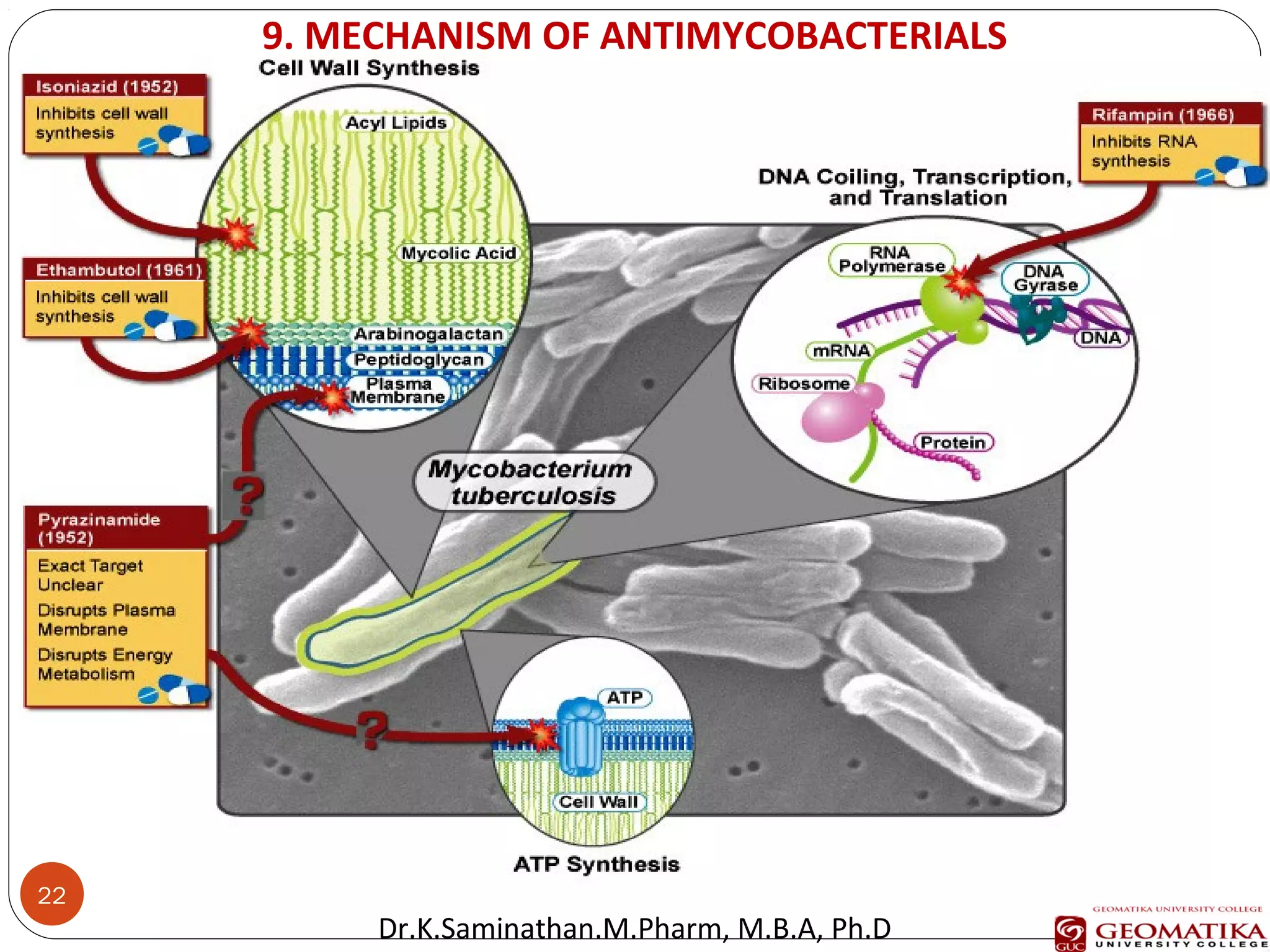
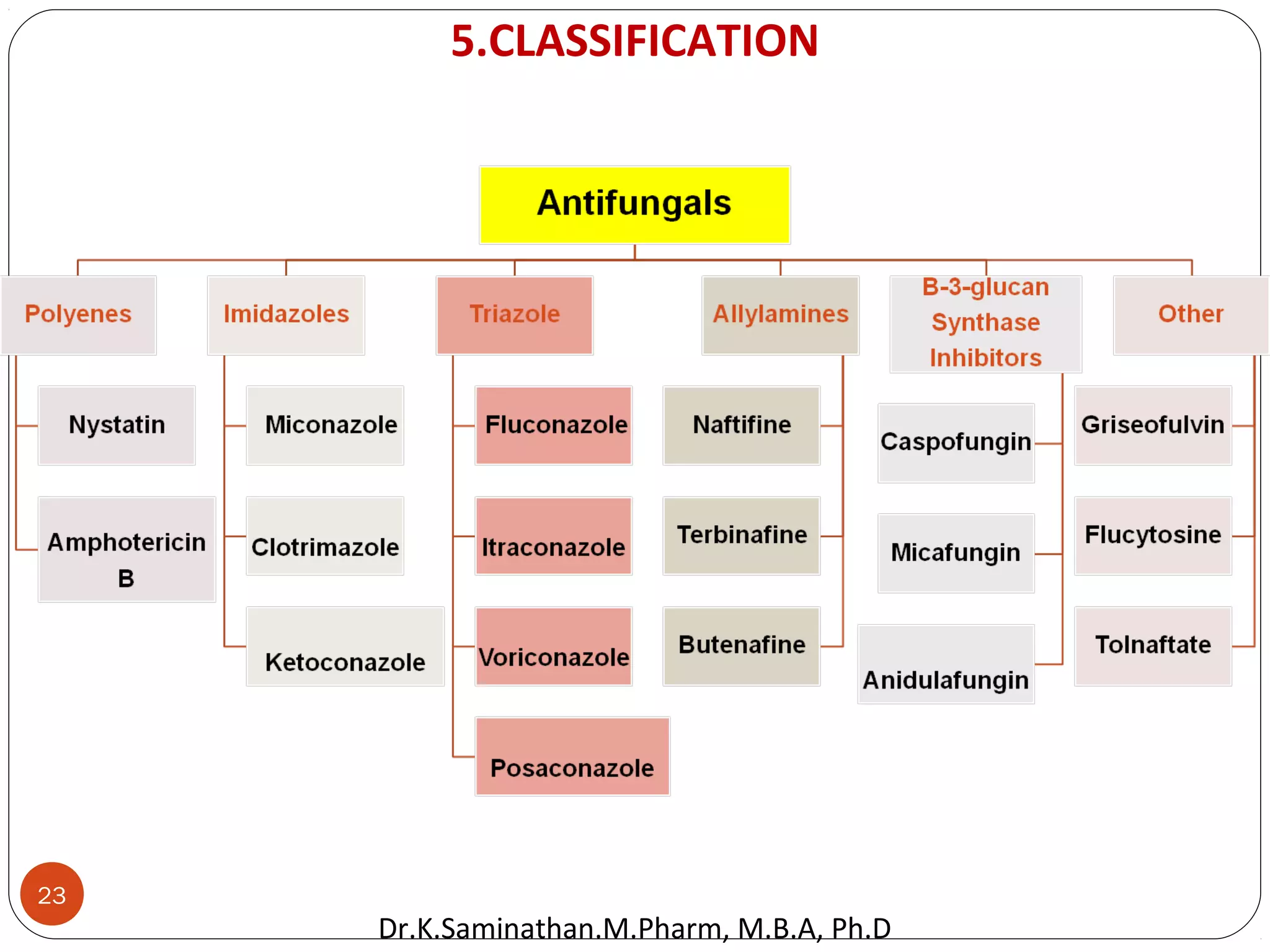
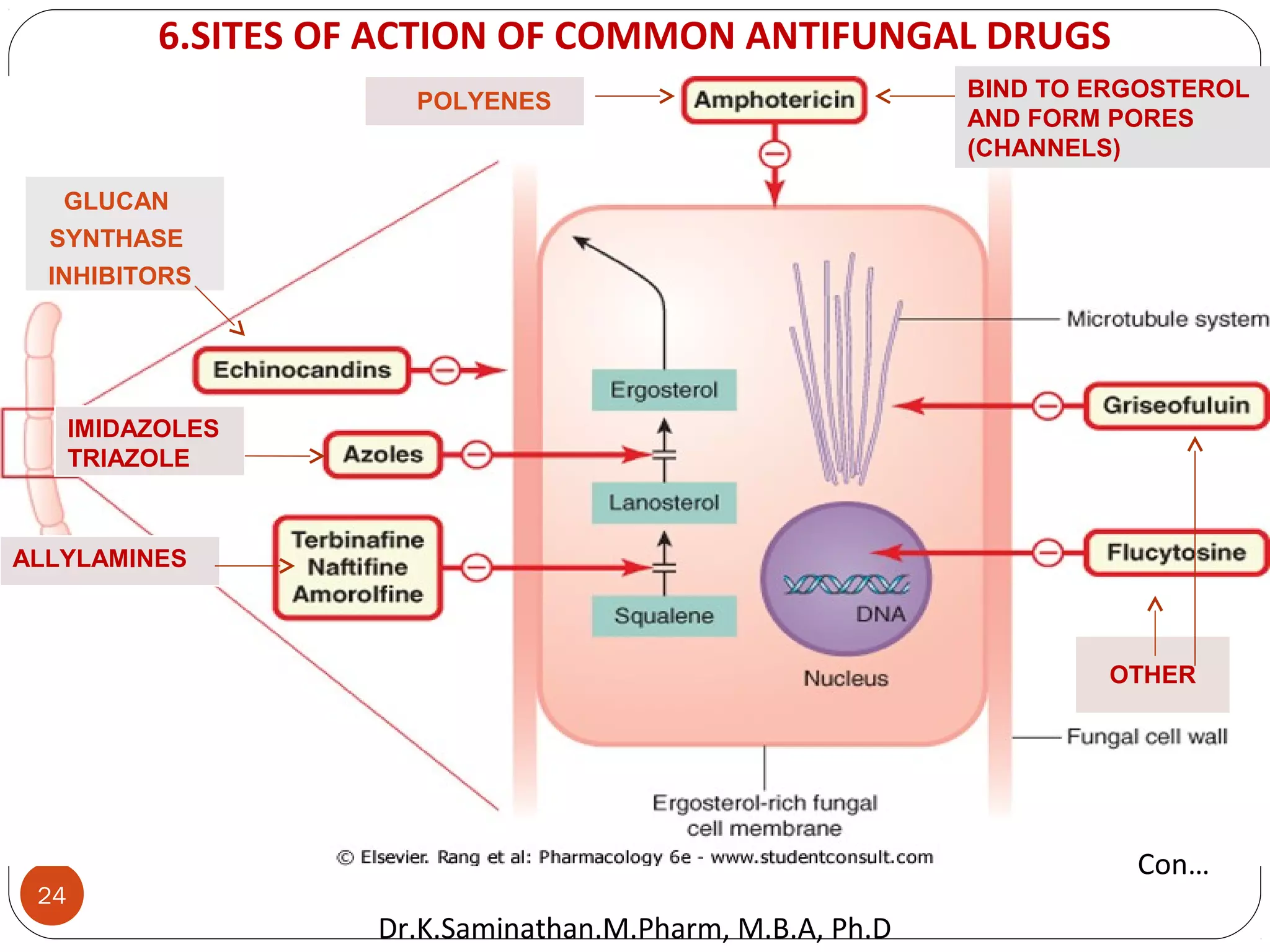
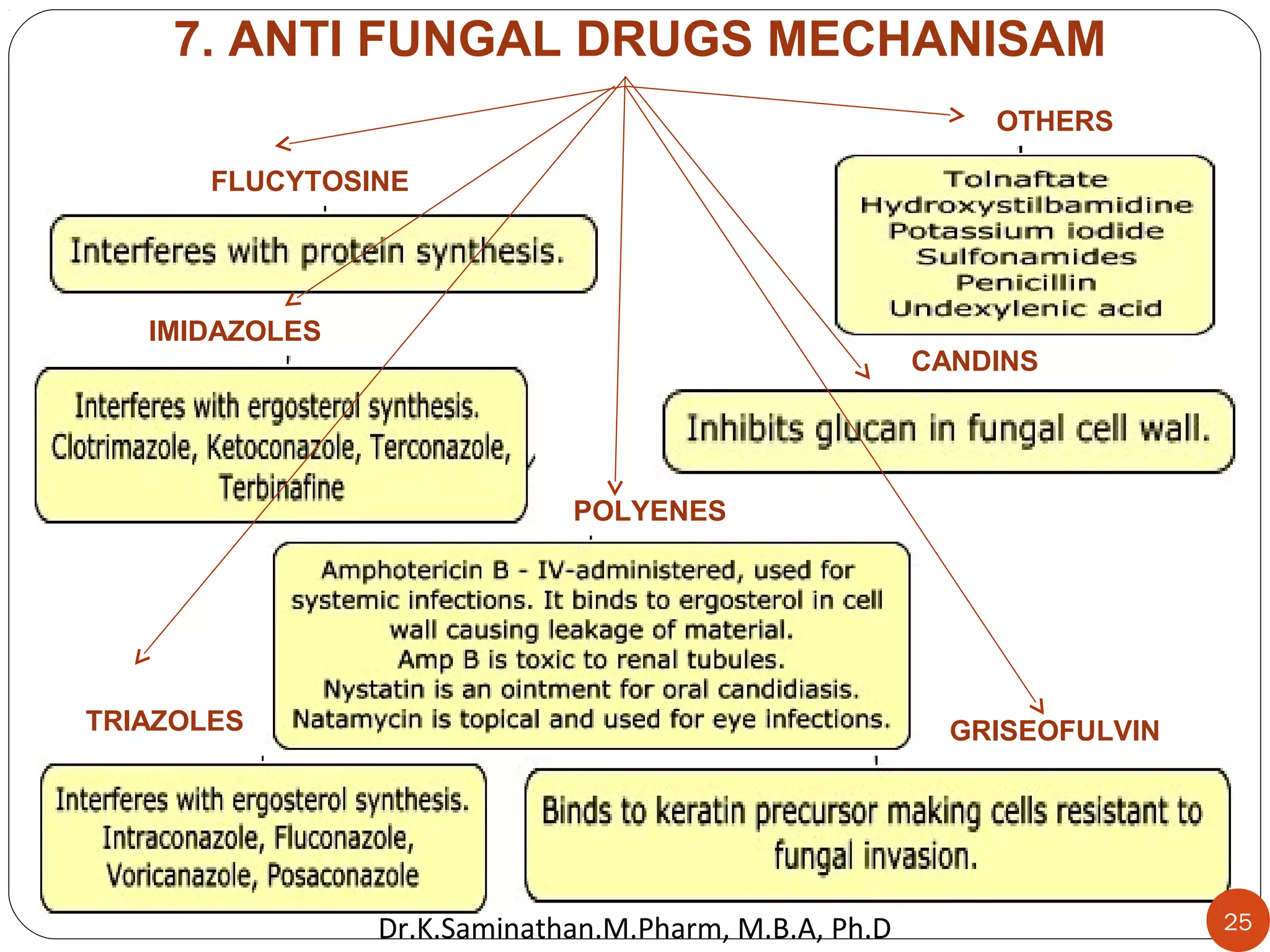
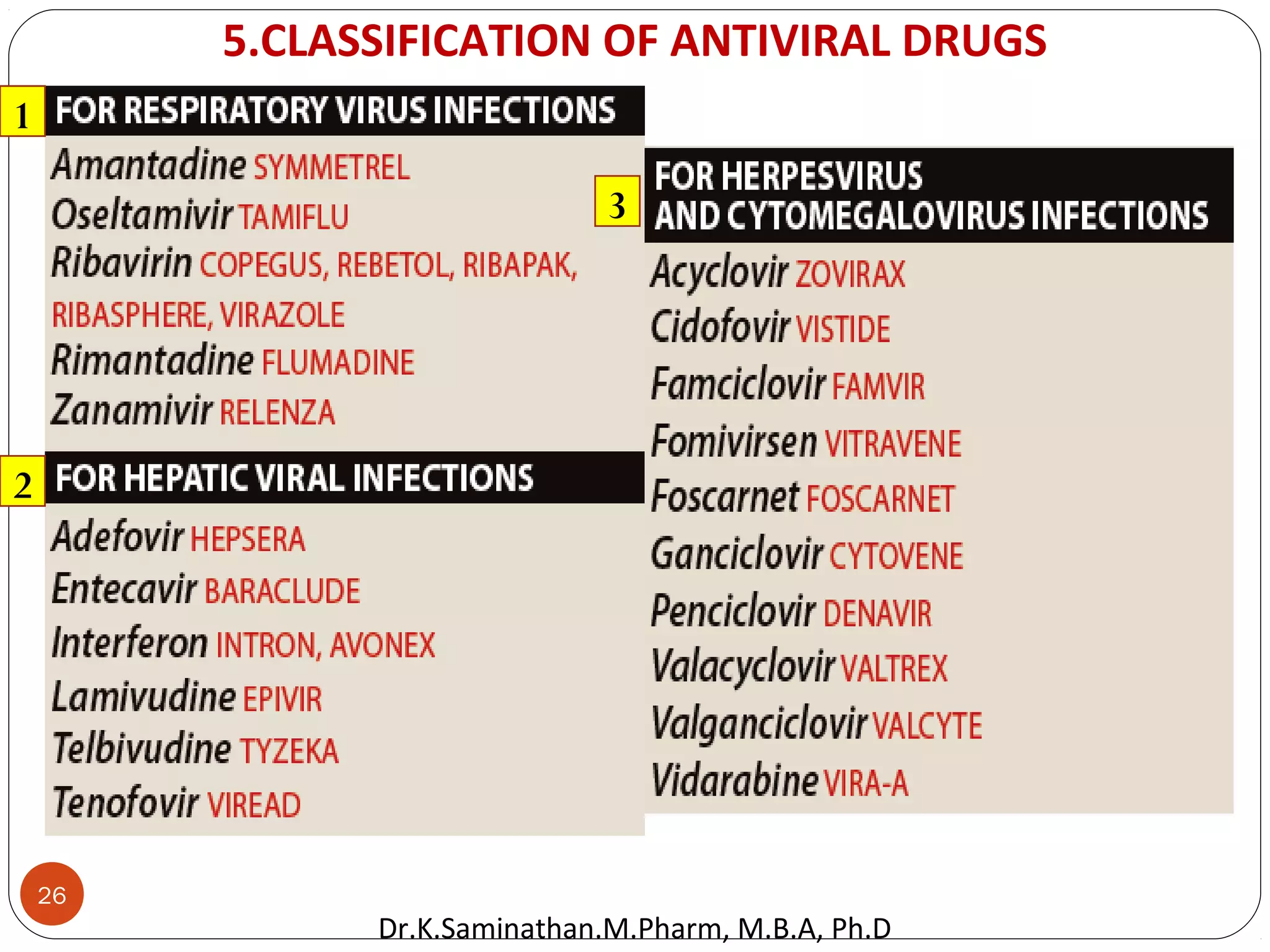
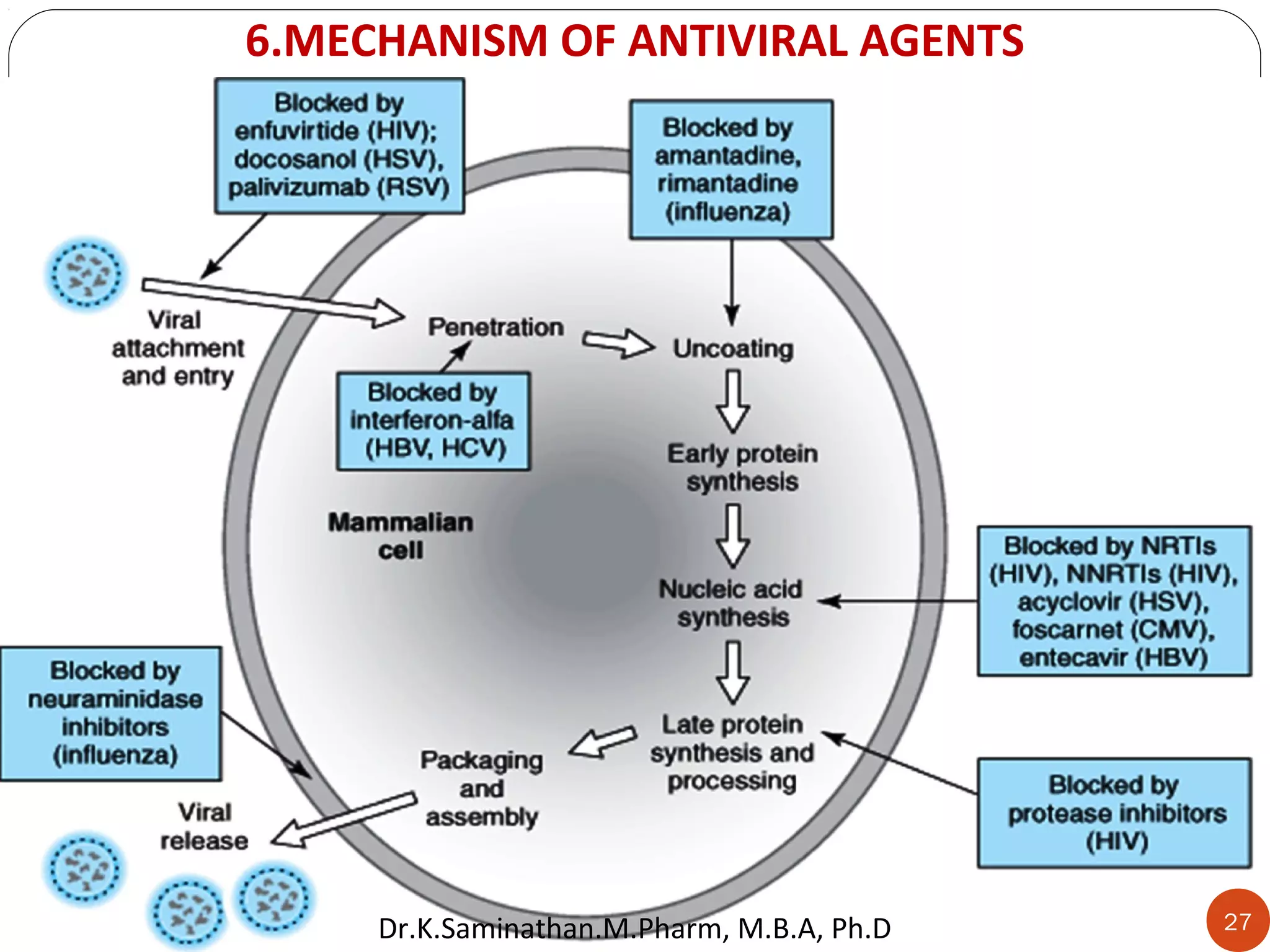
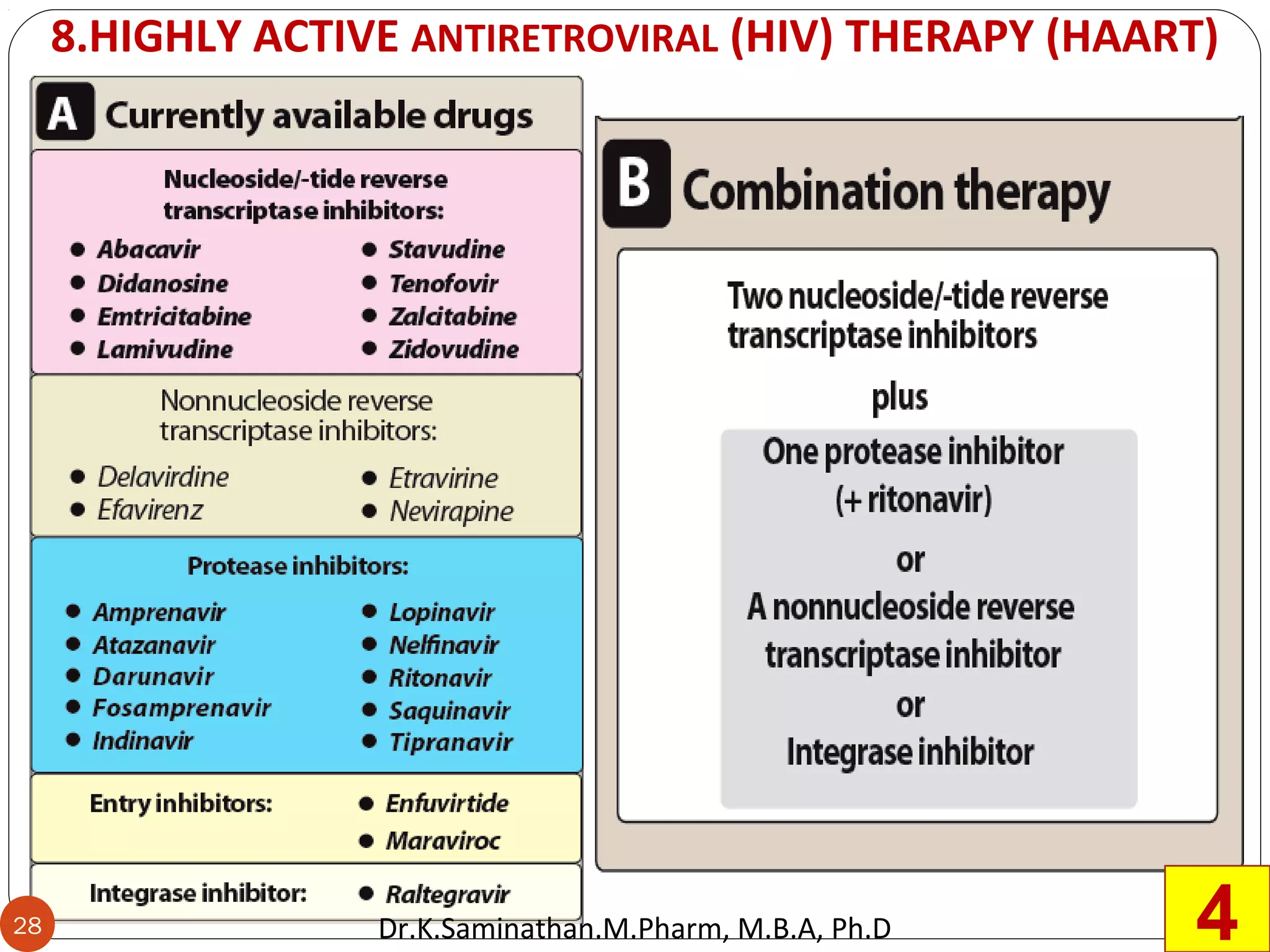
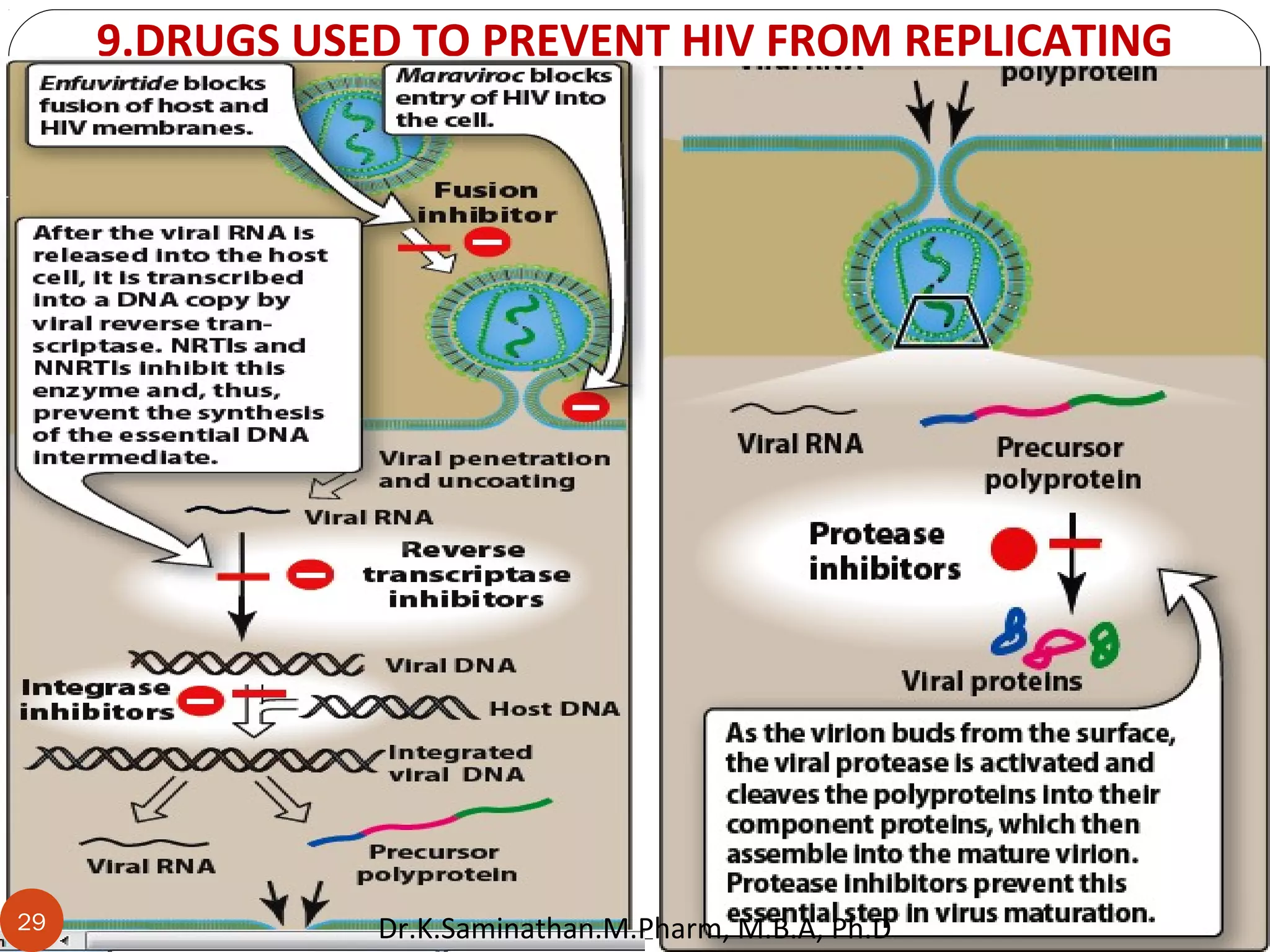
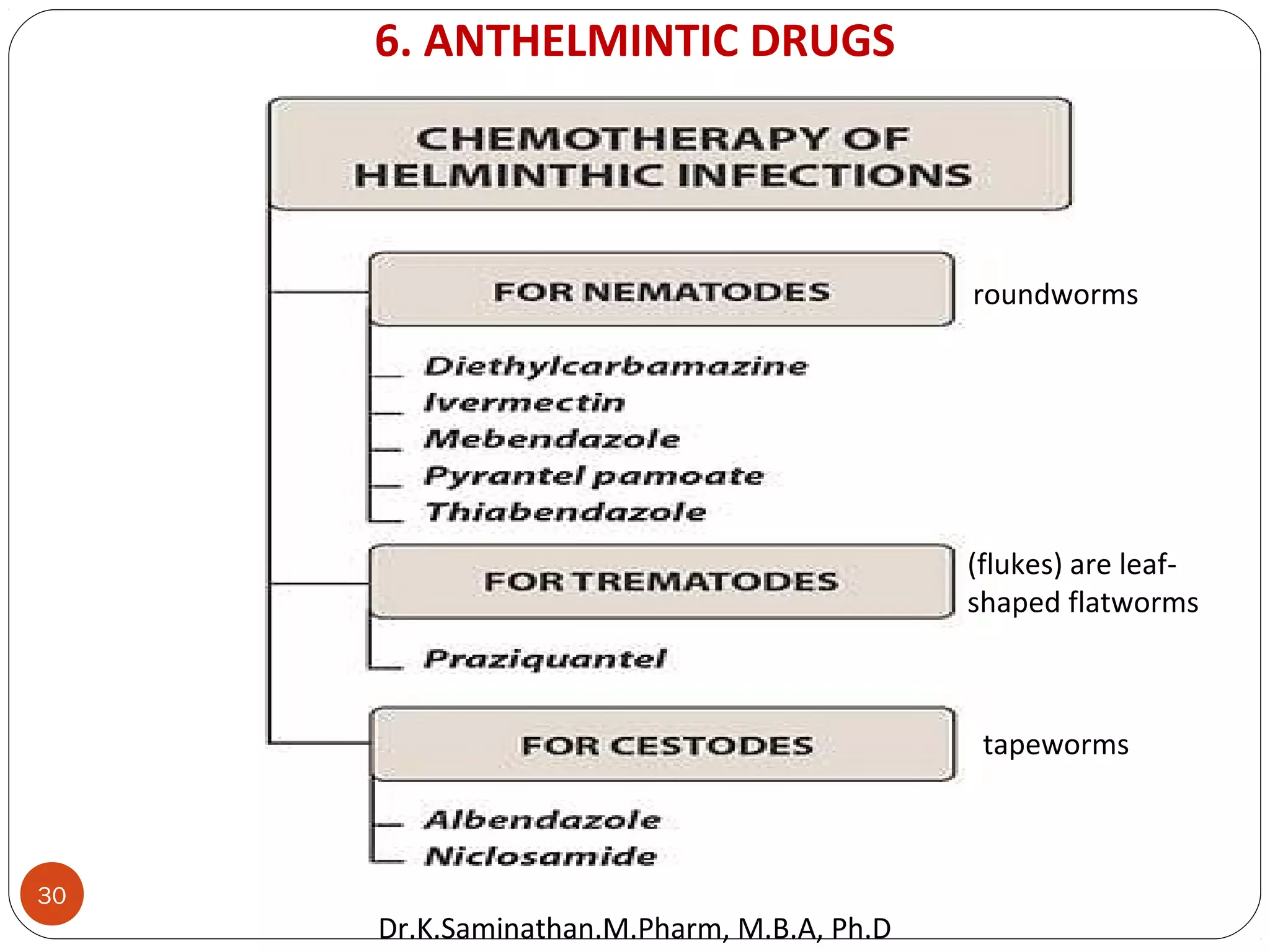
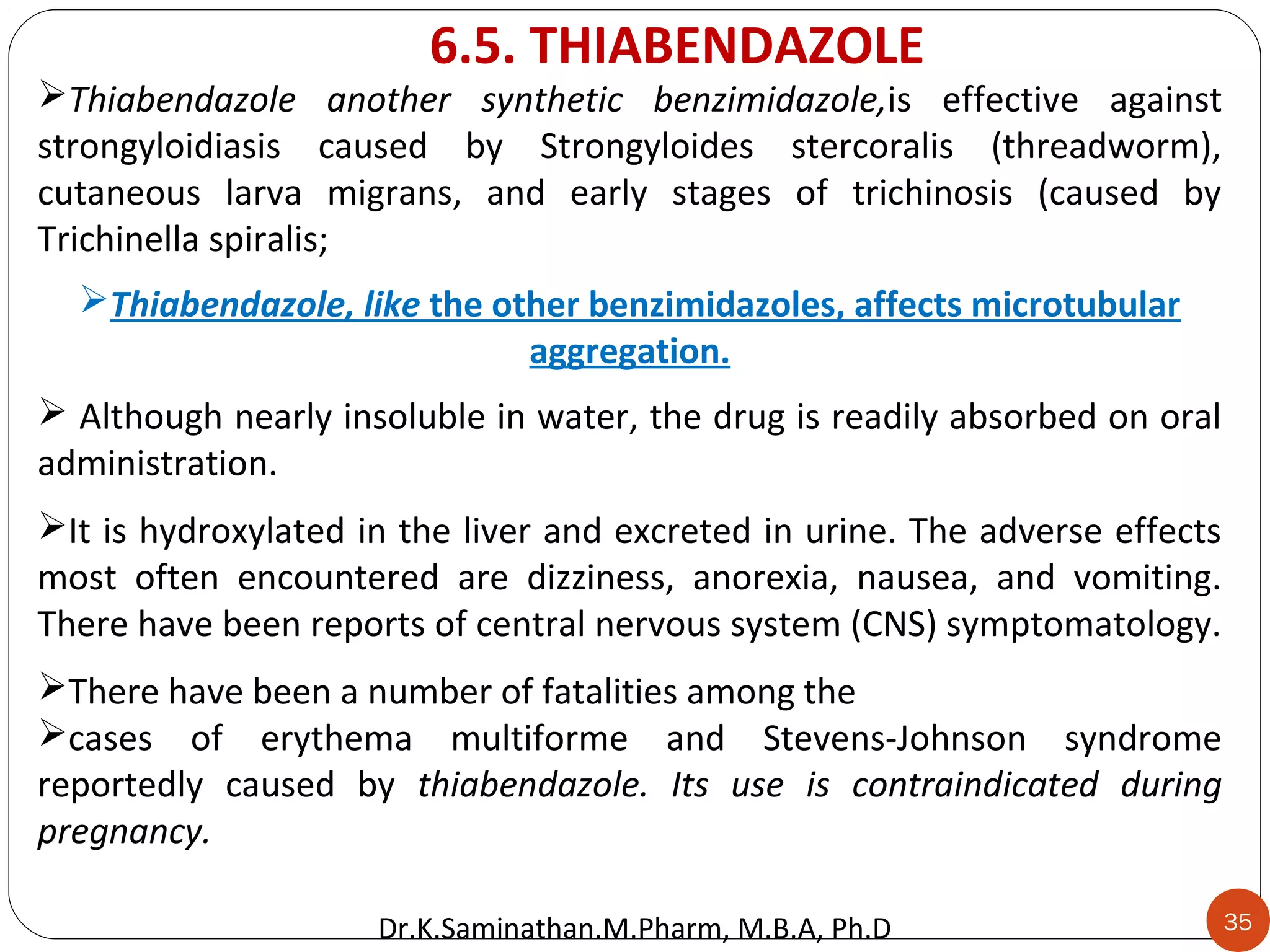
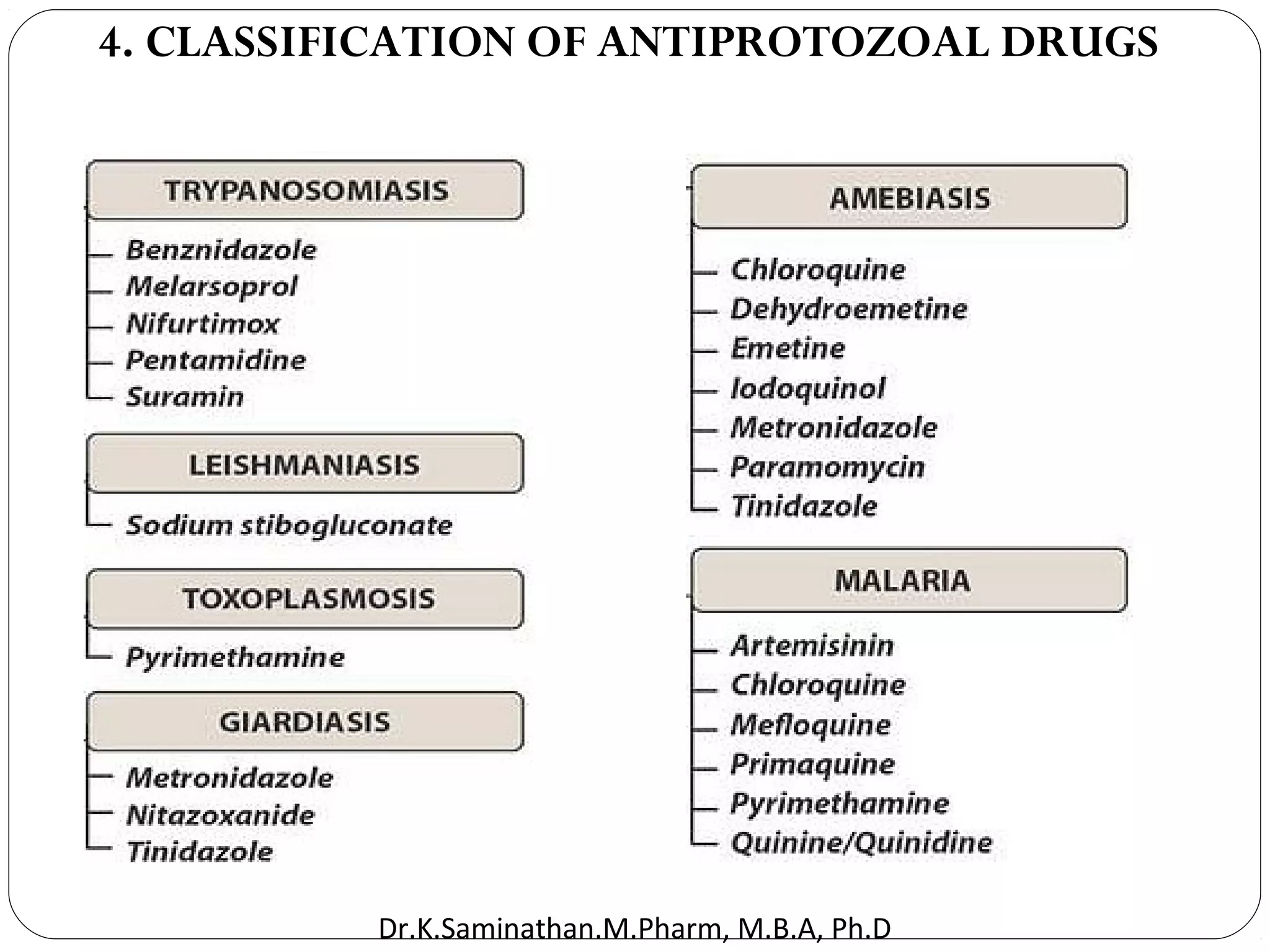
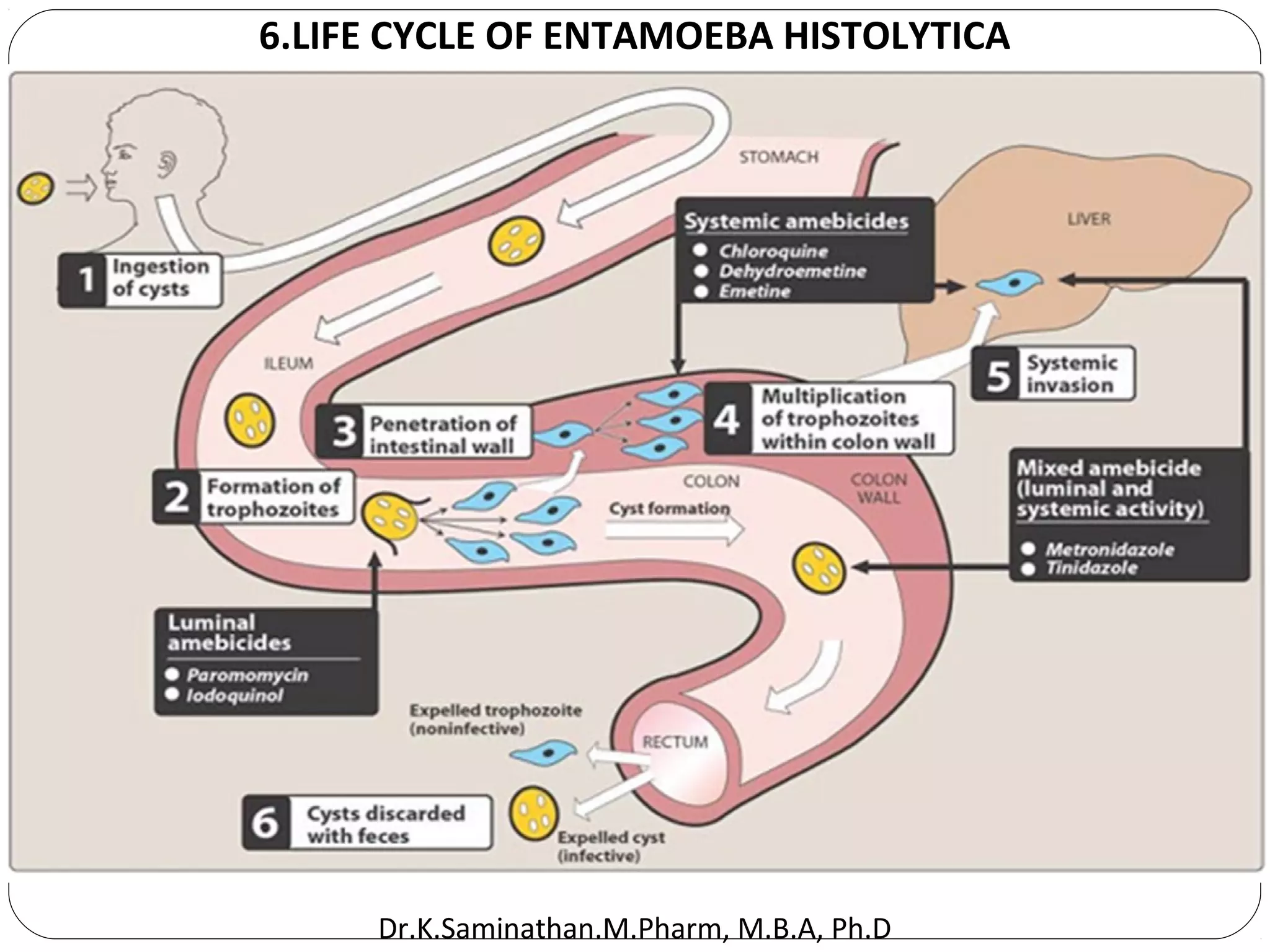
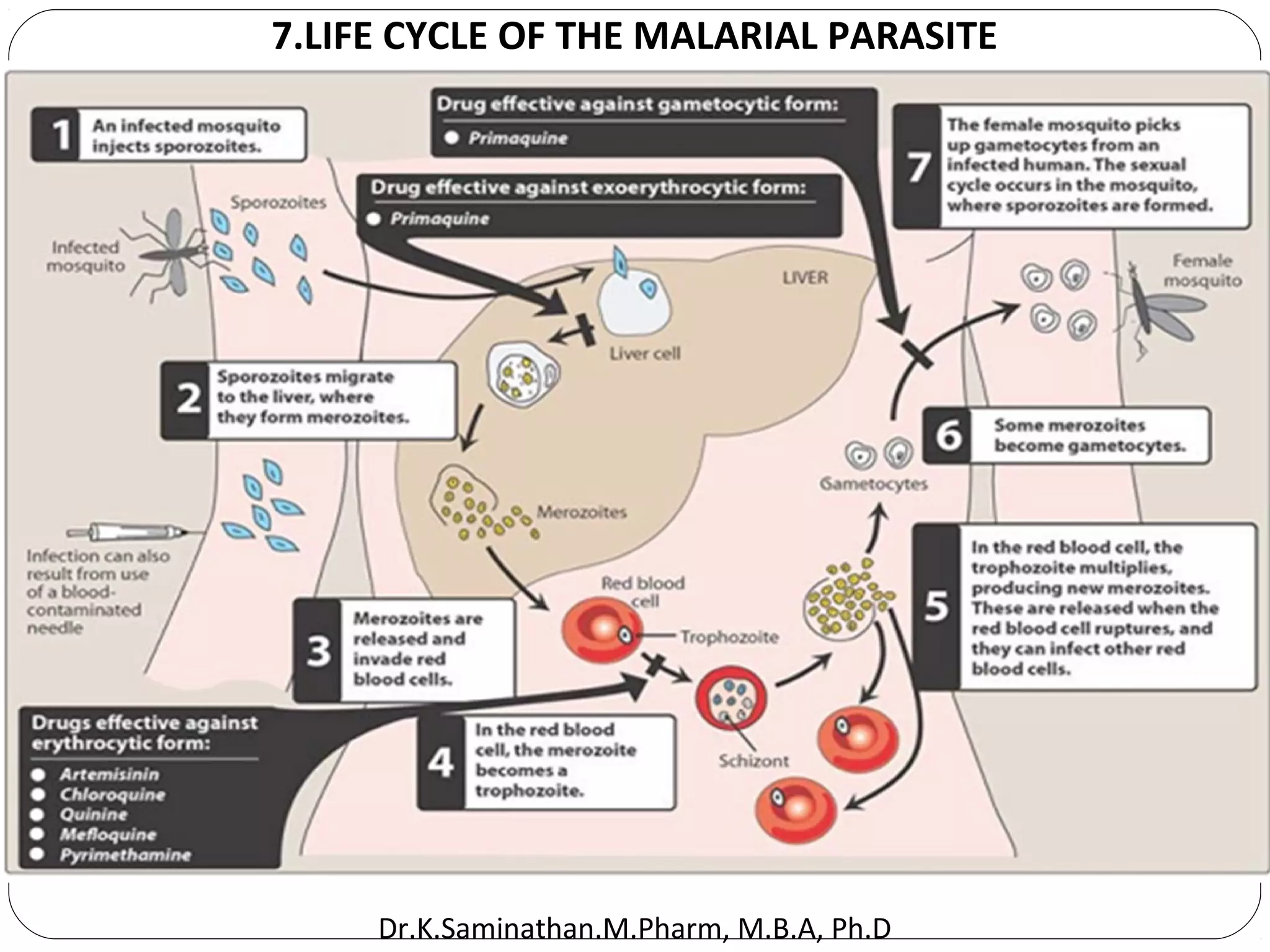
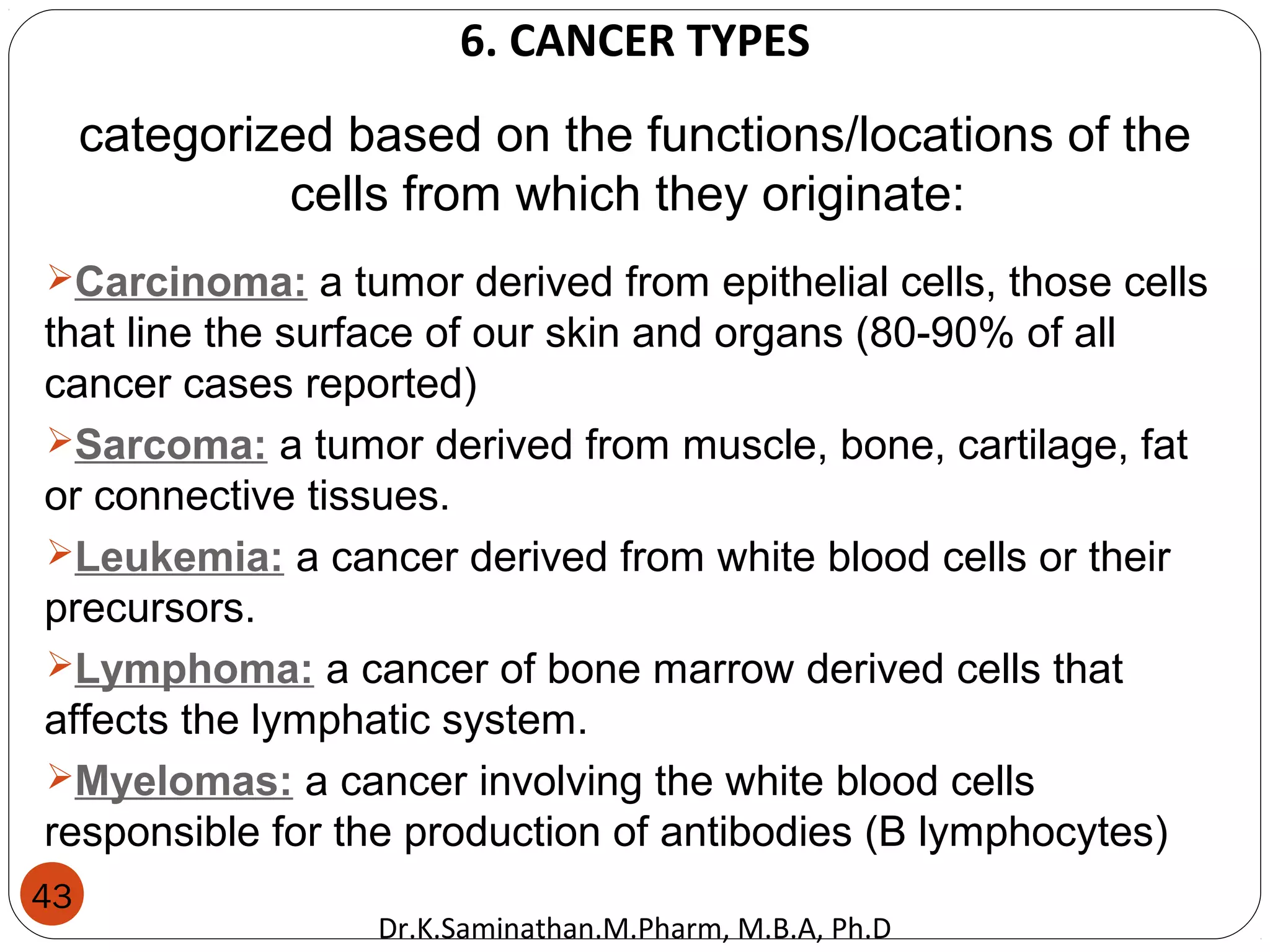
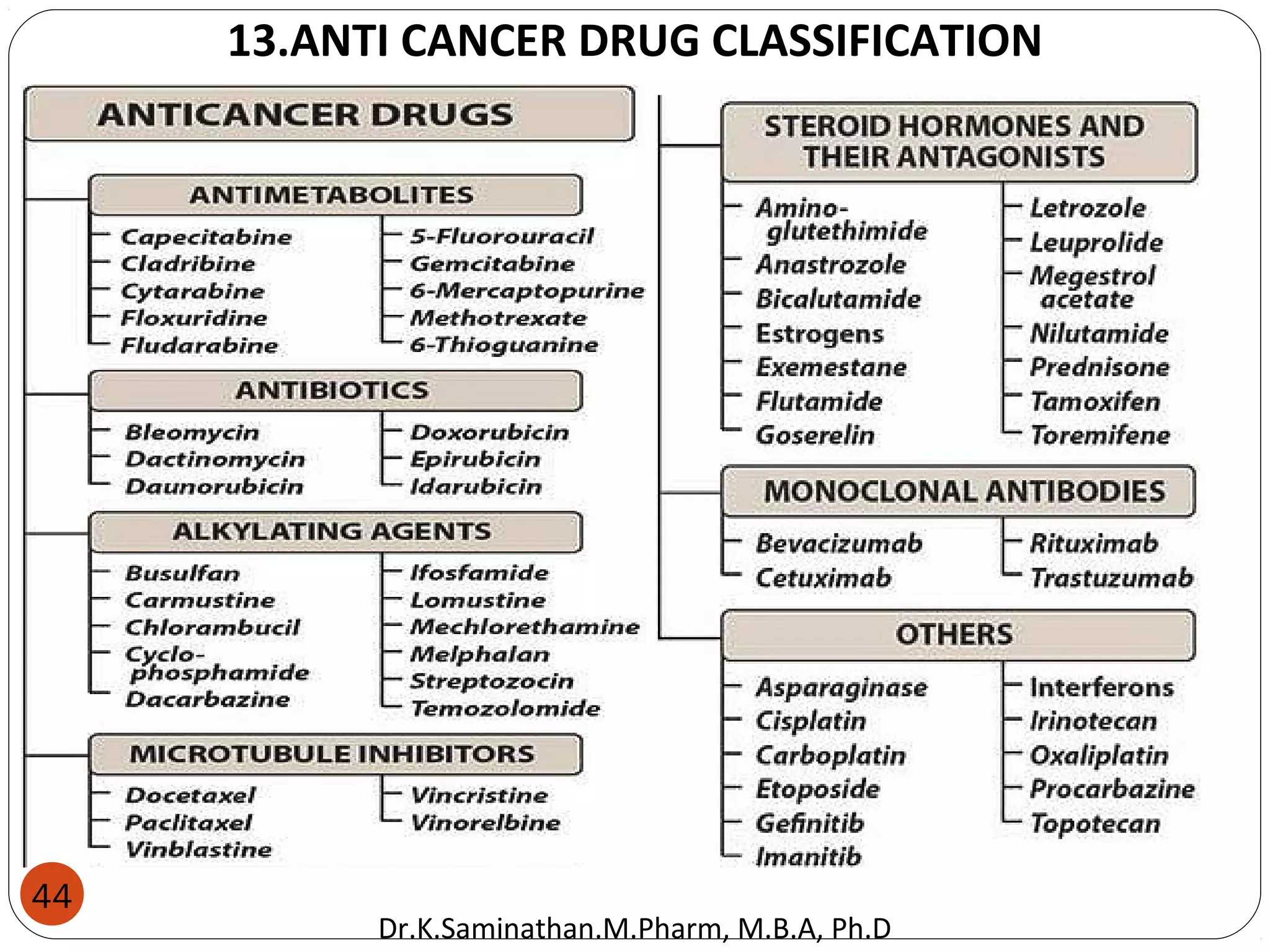
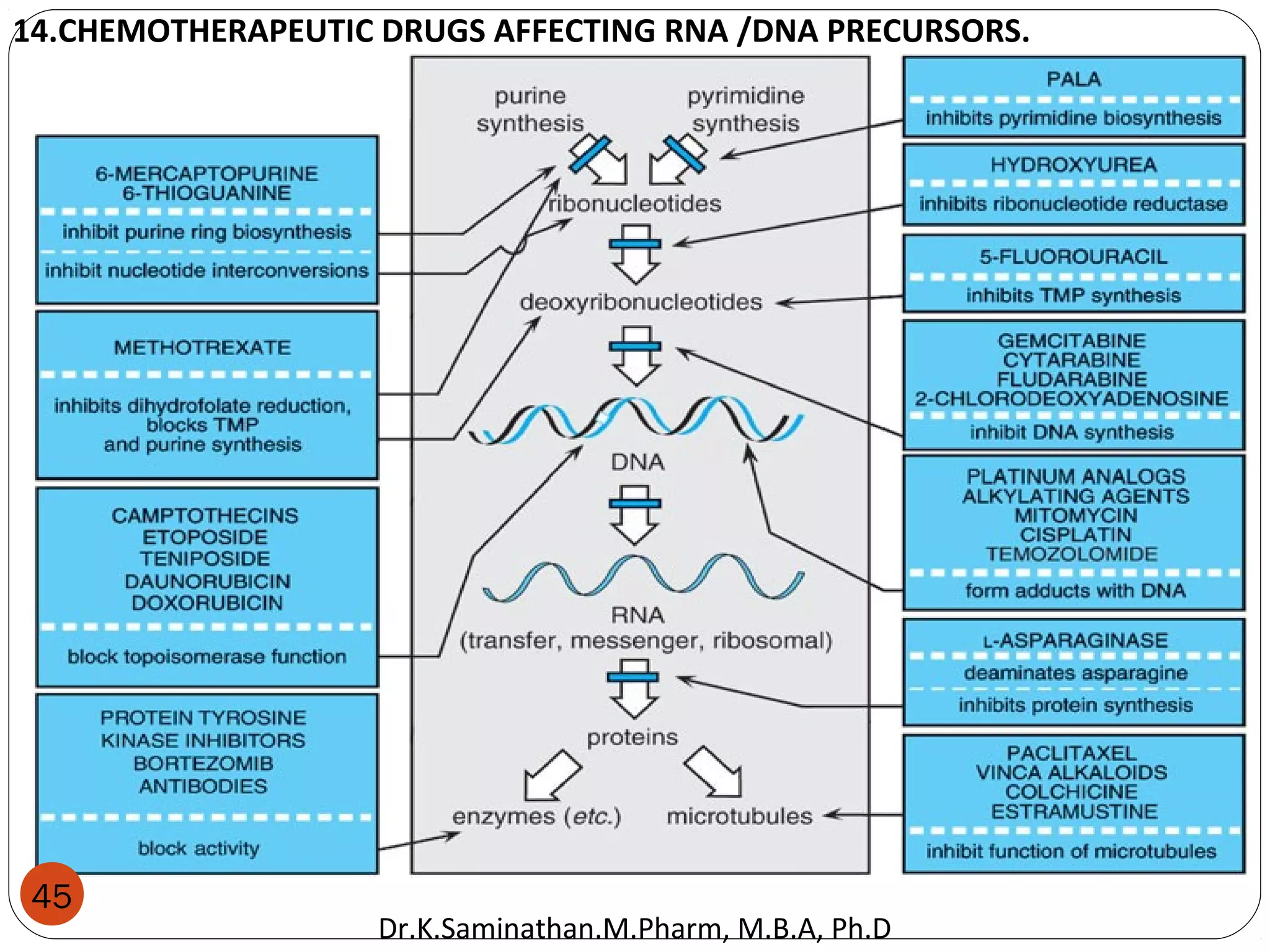
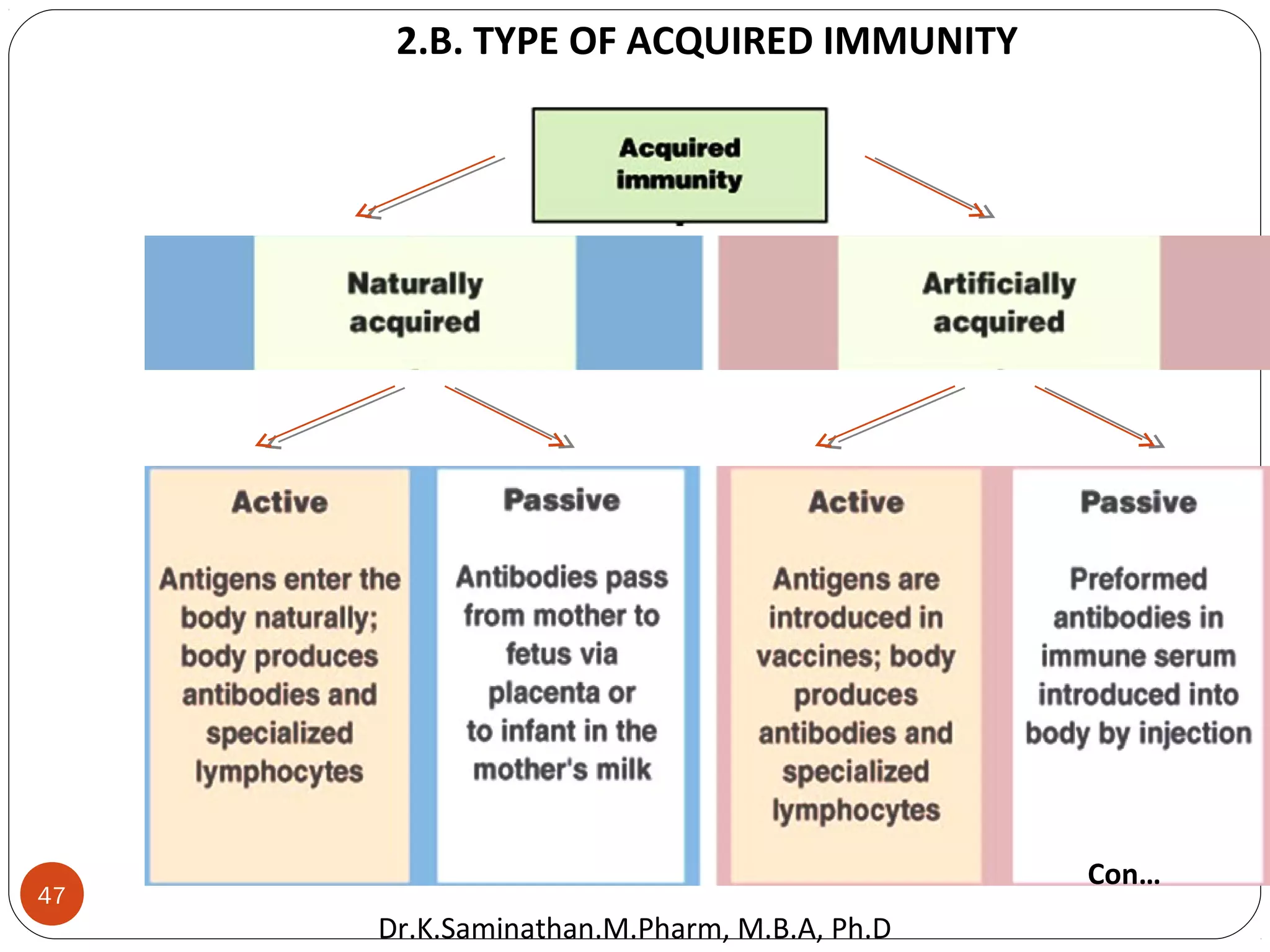
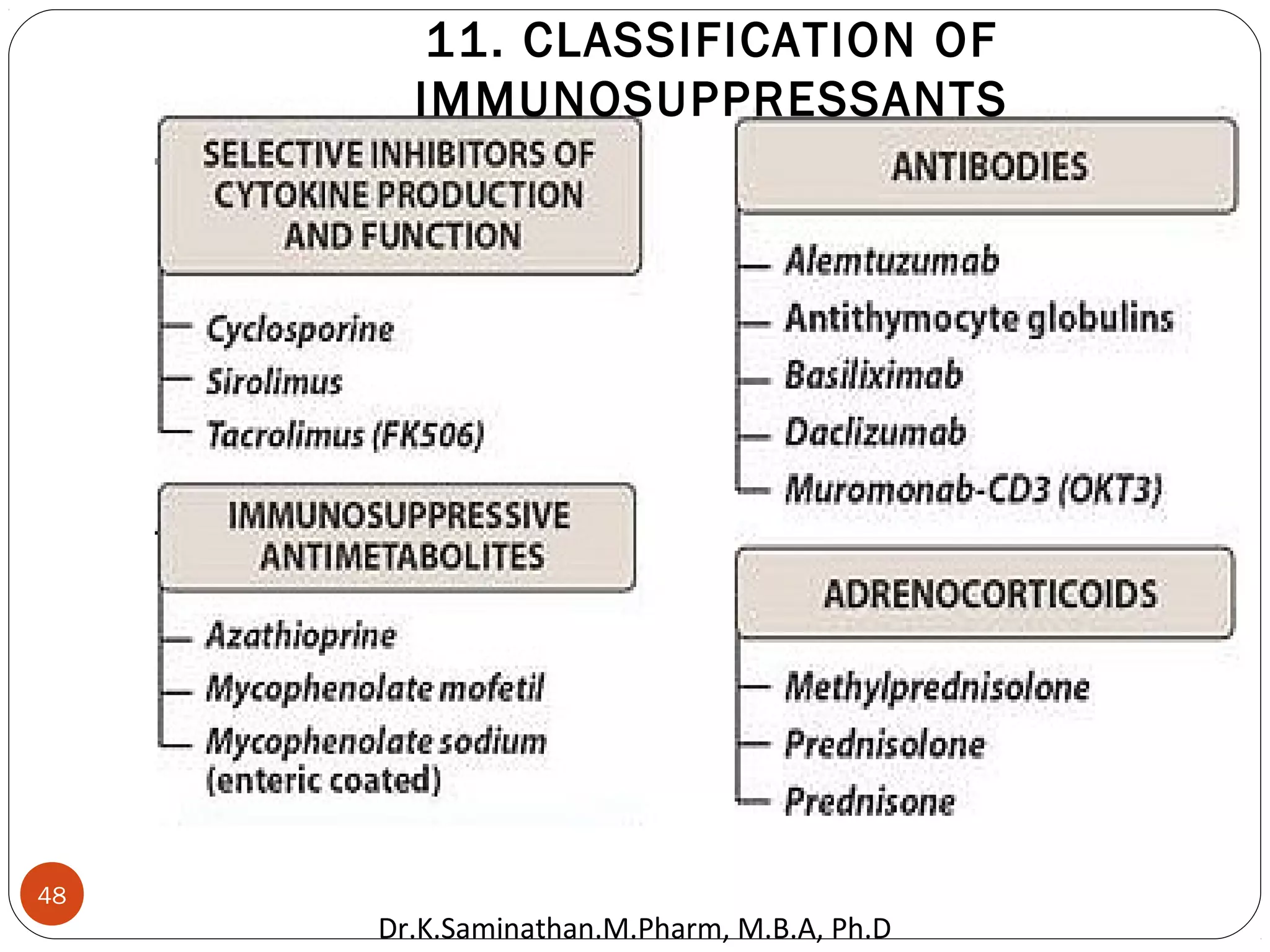
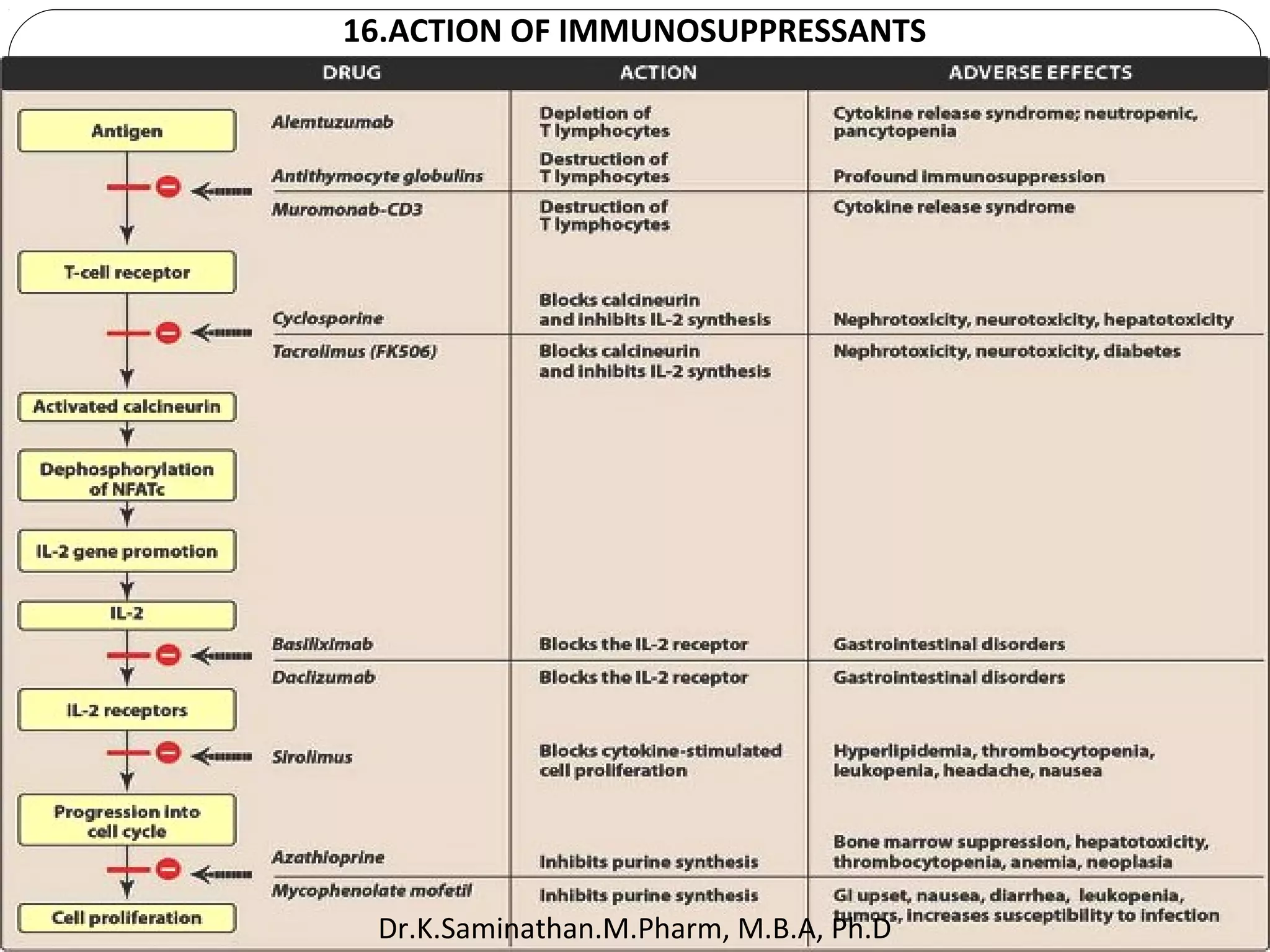
The document discusses the mechanisms and classifications of various antimicrobial agents, including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and anthelmintics. It outlines the ways in which bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics and provides guidelines for both patients and healthcare professionals to prevent antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, it details the characteristics of ideal antimicrobial drugs and various treatment protocols for infections.