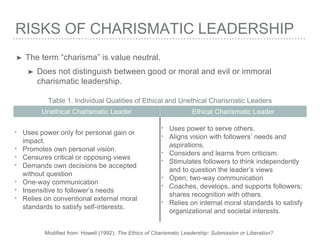
Charismatic leadership emerged as a theory in 1976 proposed by Robert House. It emphasizes symbolic behaviors of leaders who inspire followers through personal charm and magnetism. Charismatic leaders display confidence and are highly persuasive, motivating creativity and satisfaction, though there are also risks if the leader's goals are self-serving rather than for the group. In occupational therapy, charismatic traits could be used to advocate for clients, provide vision, and influence organizations, if balanced with consideration of followers' needs.