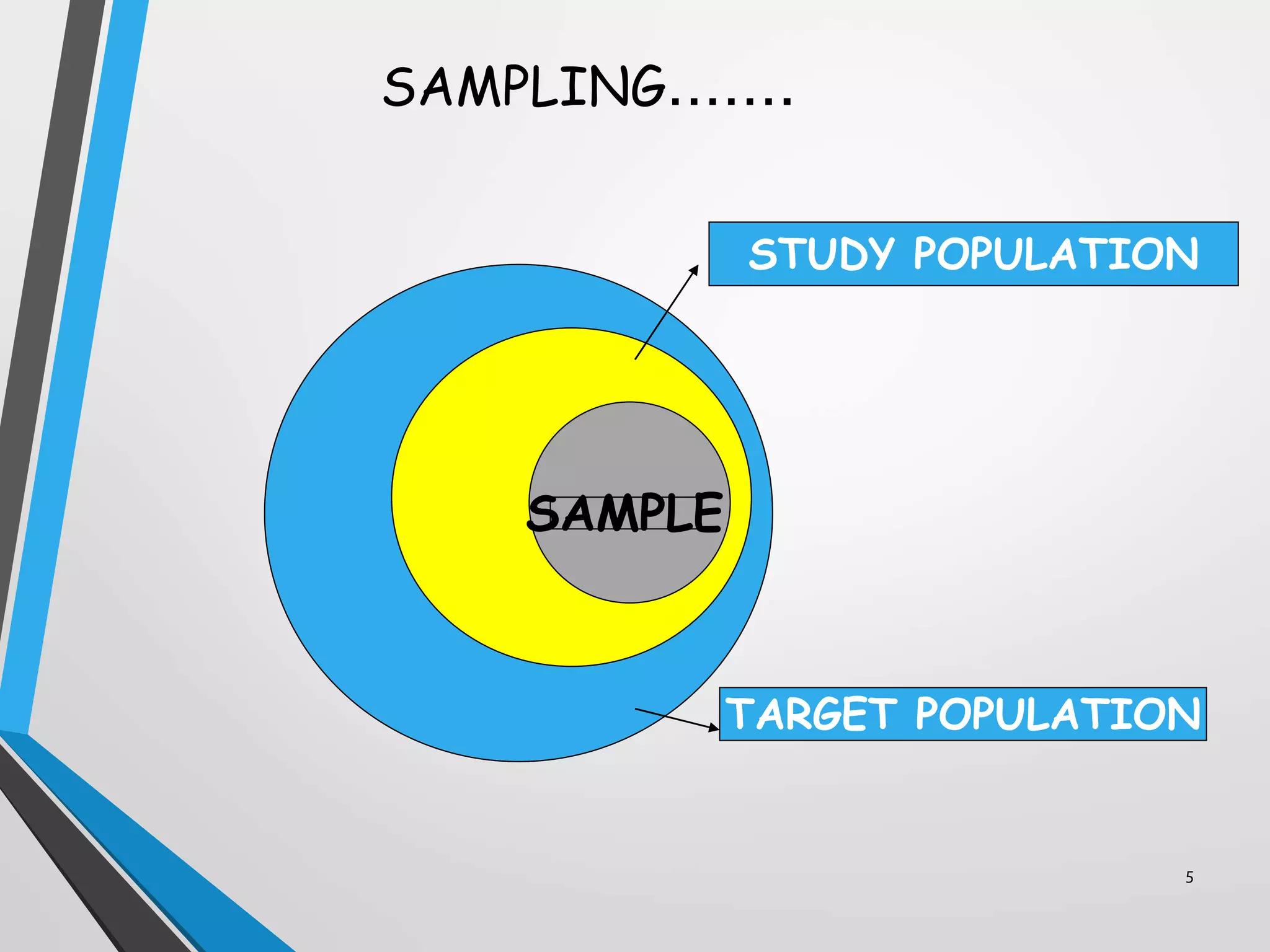
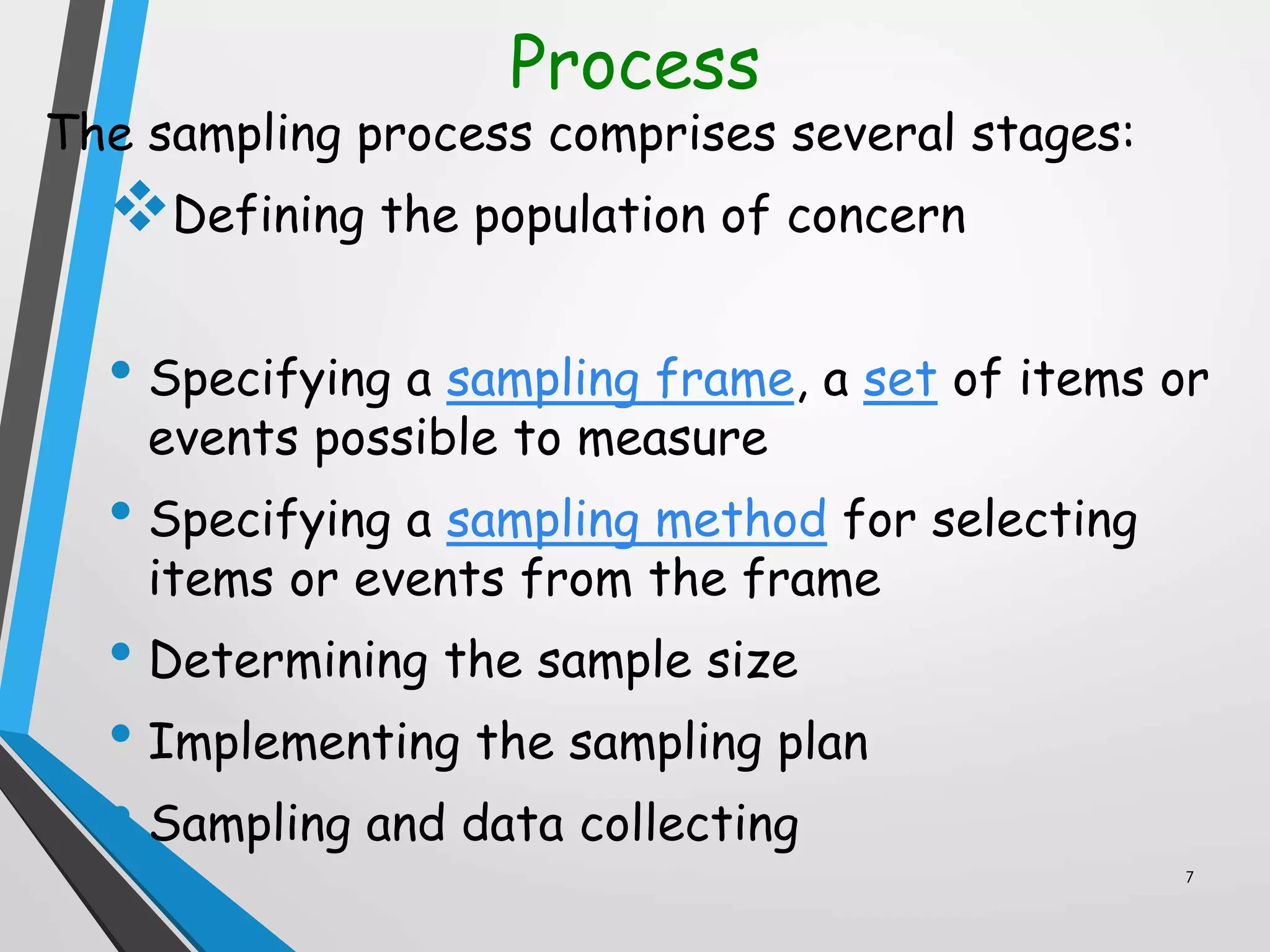
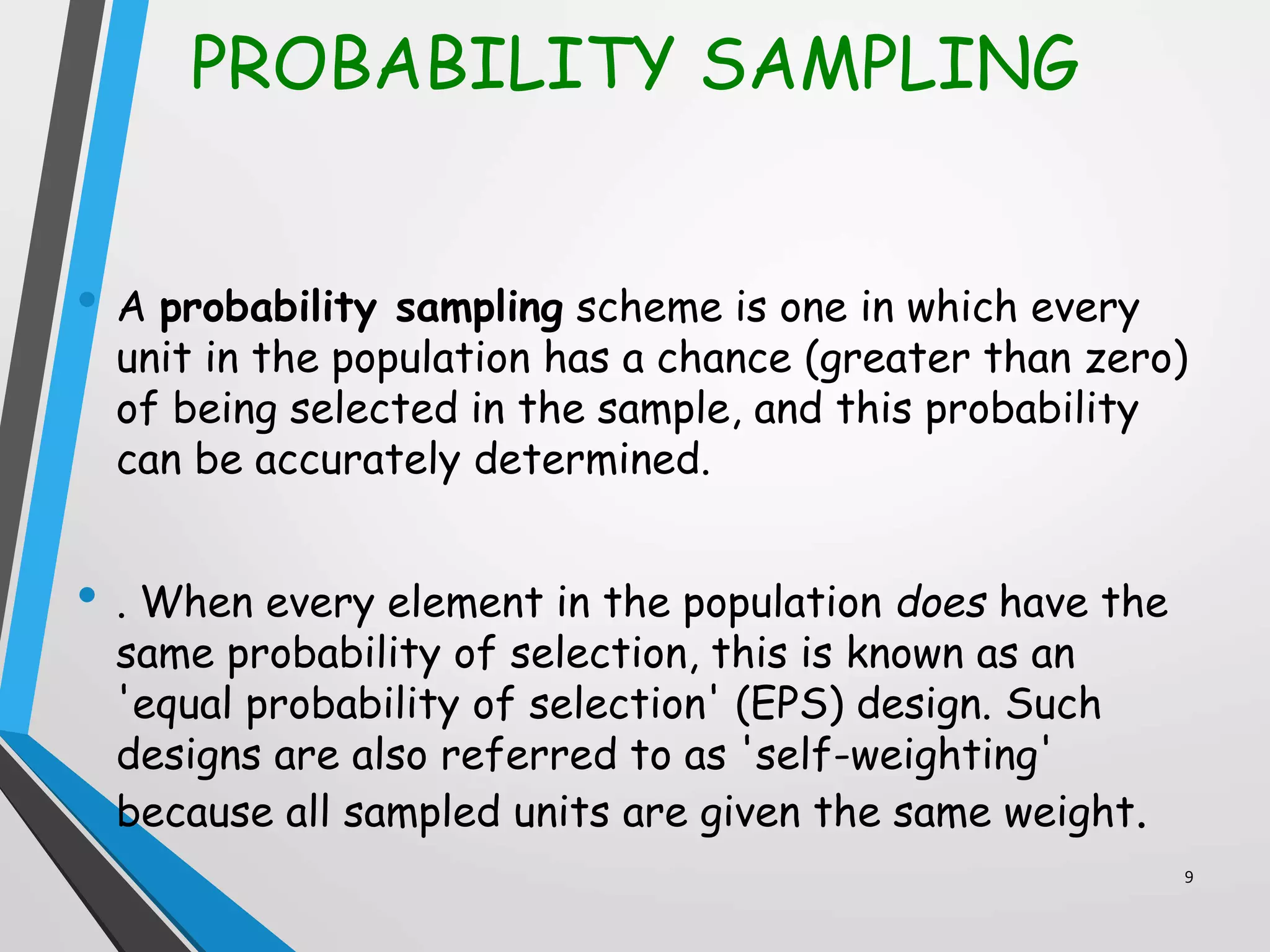
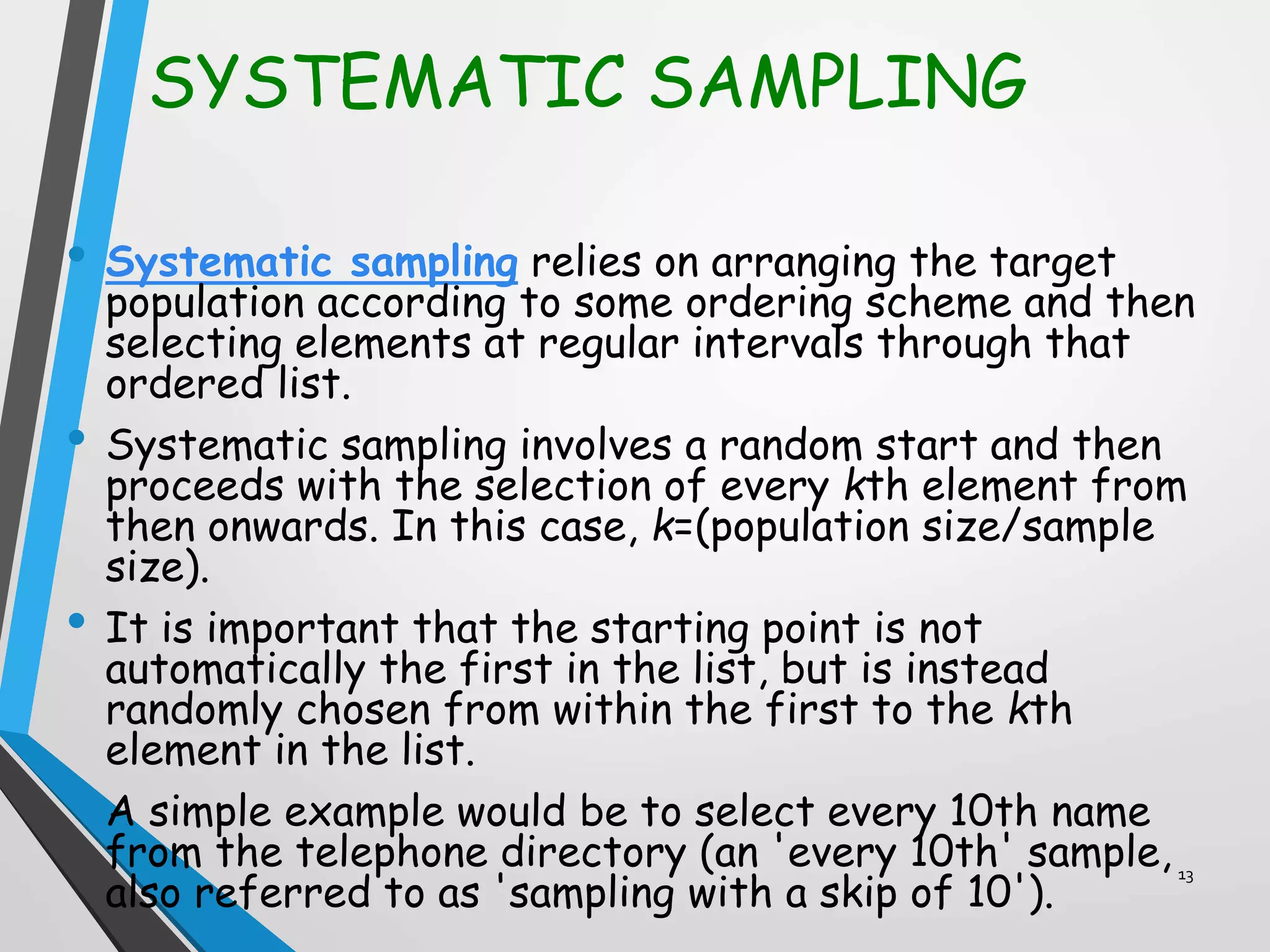
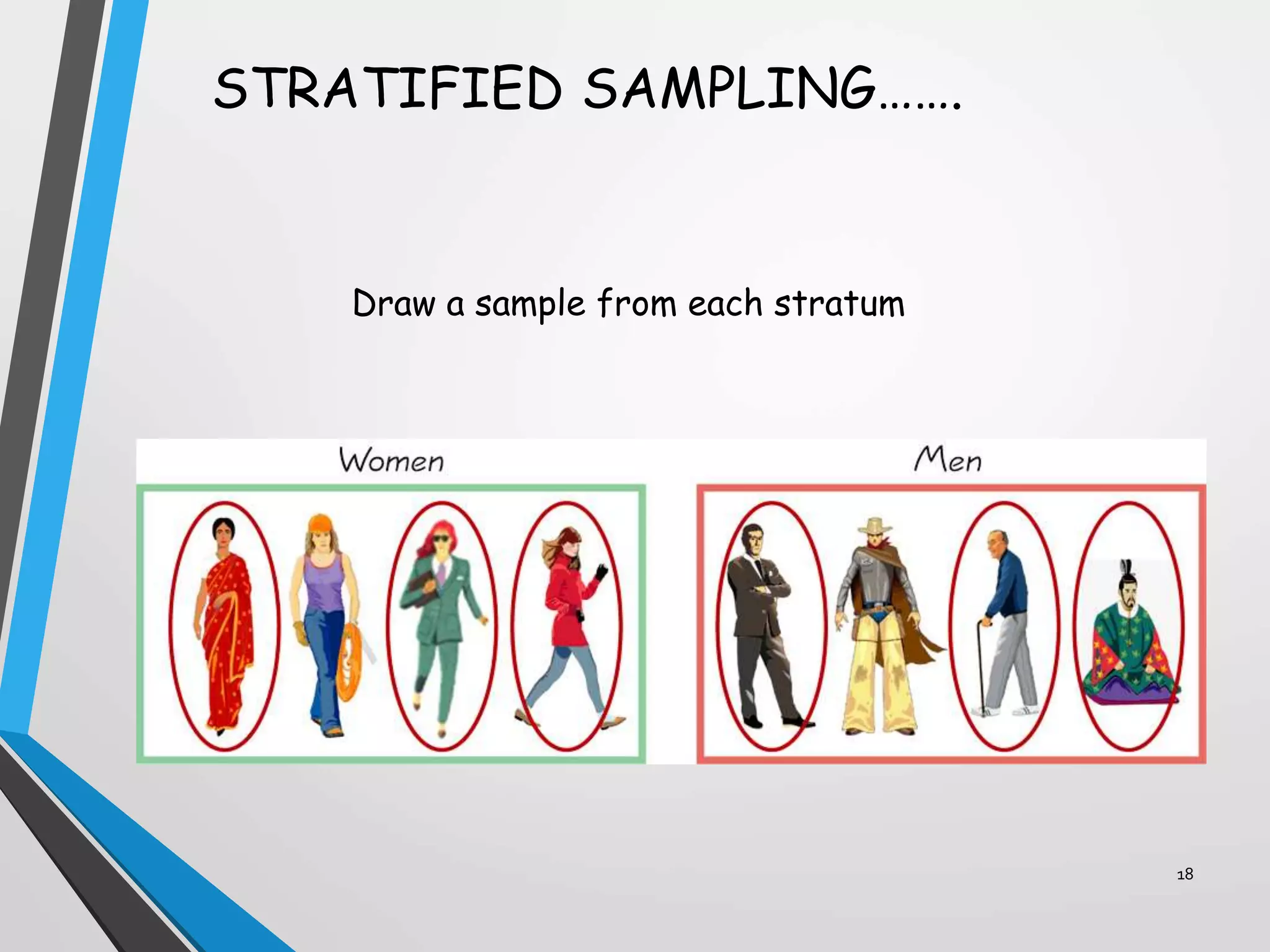
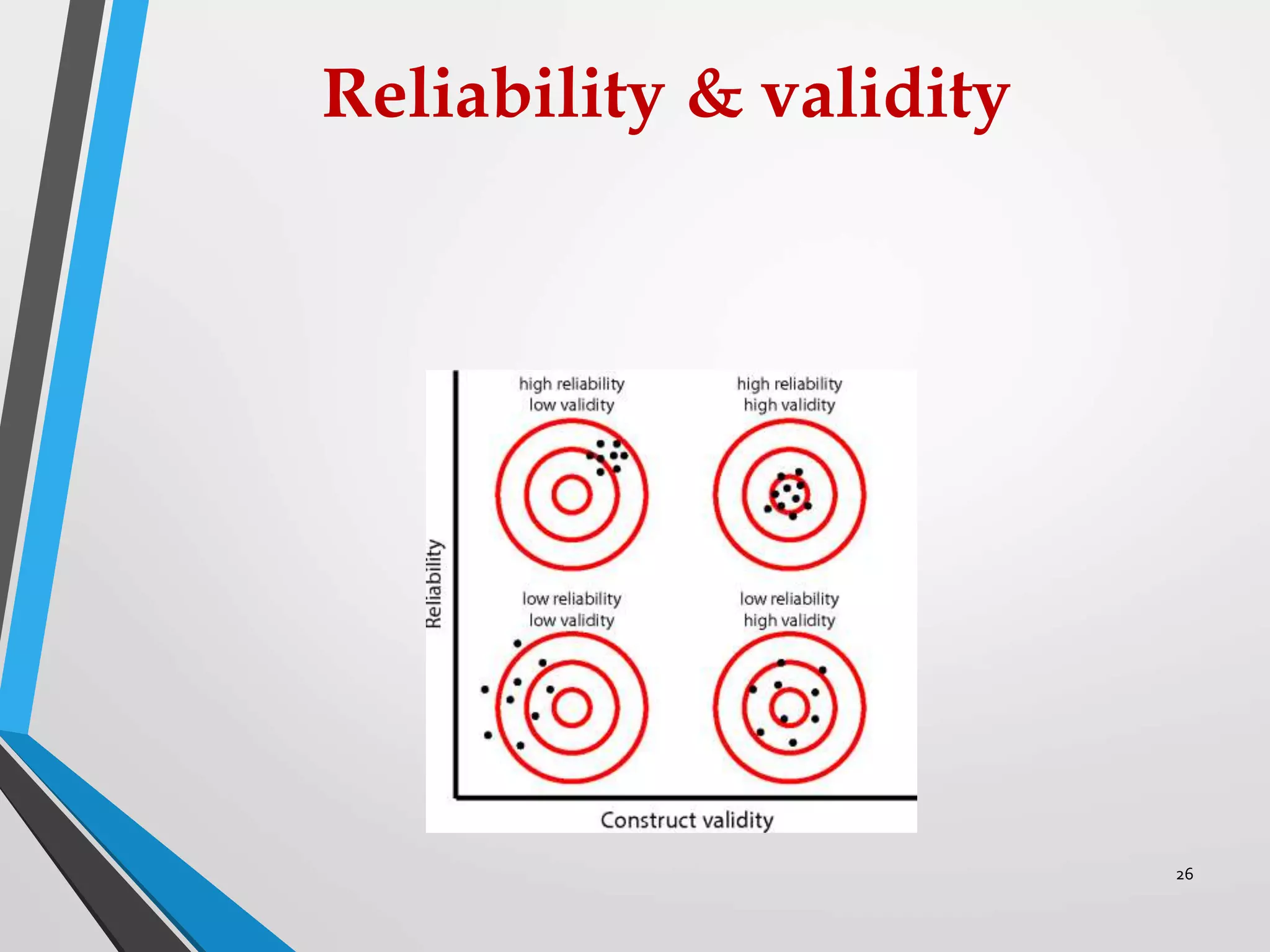
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It defines a population as all people or items with the same characteristics that researchers want to generalize results to. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every unit has a known chance of selection; and non-probability sampling, where the probability of selection cannot be determined. Some common probability sampling methods described include simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. The document also discusses non-probability sampling techniques like convenience sampling and snowball sampling.