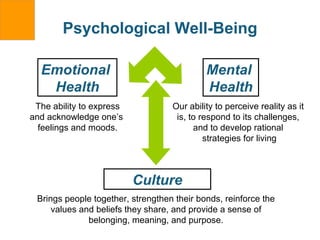
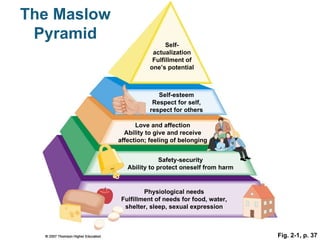
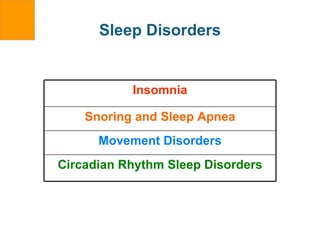
The document discusses various aspects of emotional, spiritual, and psychological well-being. It covers the pillars of authentic happiness, connecting with others, and the health benefits of prayer and sleep. Spiritual health is defined as achieving one's full potential and feeling connected to a greater power. The document provides tips for improving sleep quality and assessing one's spiritual health.