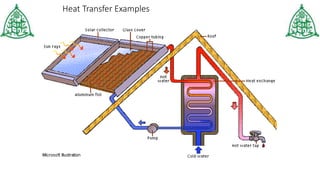
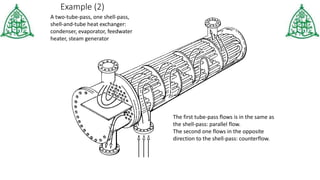
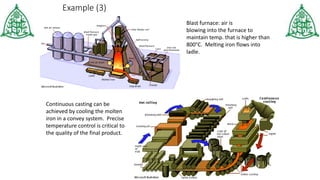
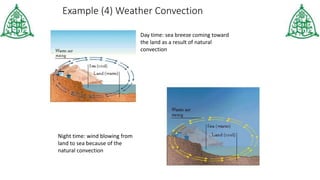
This document provides information about three main modes of heat transfer: radiation, conduction, and convection. Radiation involves the transfer of thermal energy through electromagnetic waves without touching objects, such as heat from the sun. Conduction requires direct contact as heat transfers from faster moving molecules to slower ones. Convection involves the movement of gases or liquids as warmer parts rise and cooler parts sink, transferring heat through examples like boiling water. The document also includes examples and a quiz to test understanding of the different heat transfer methods.