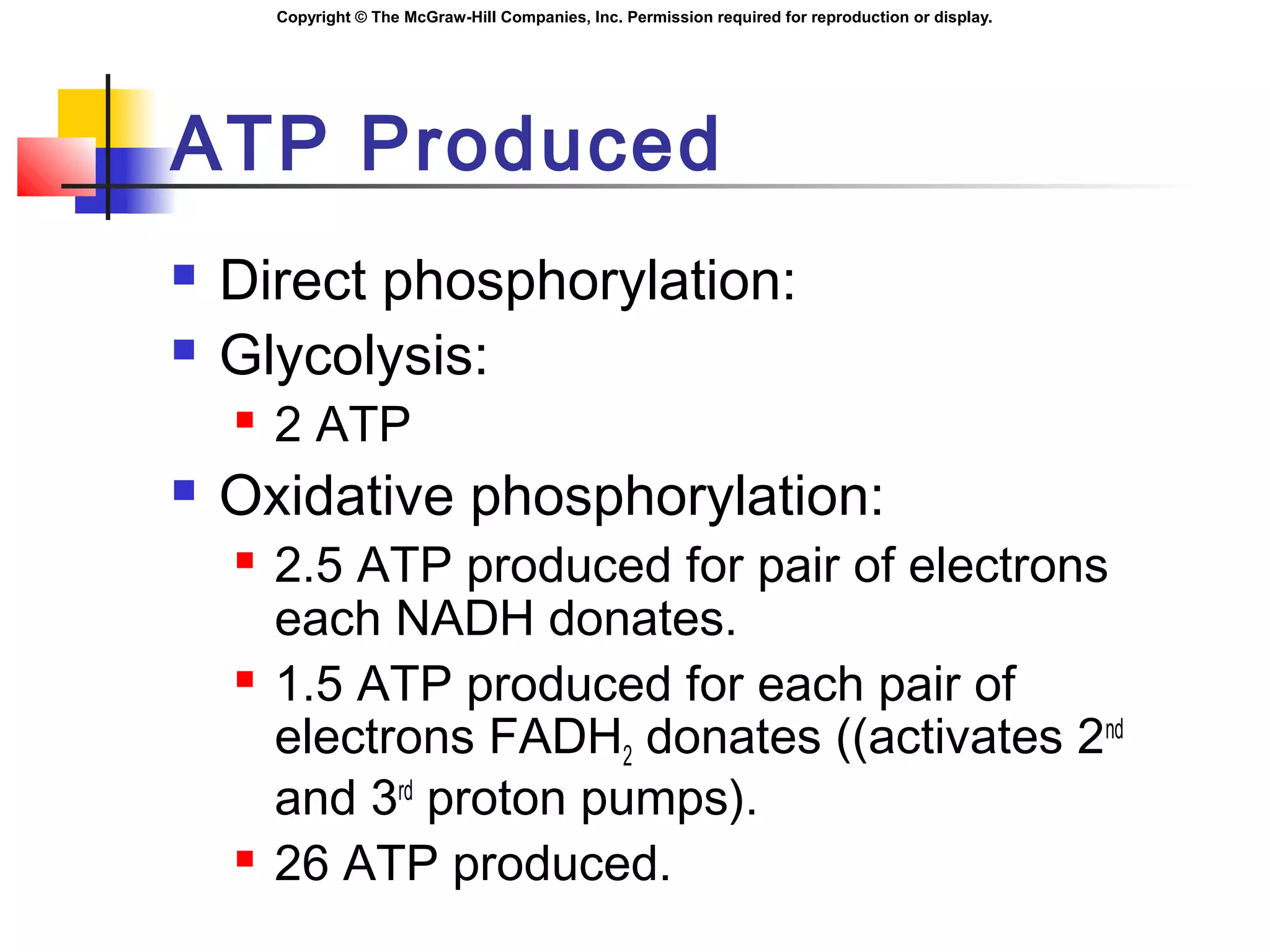
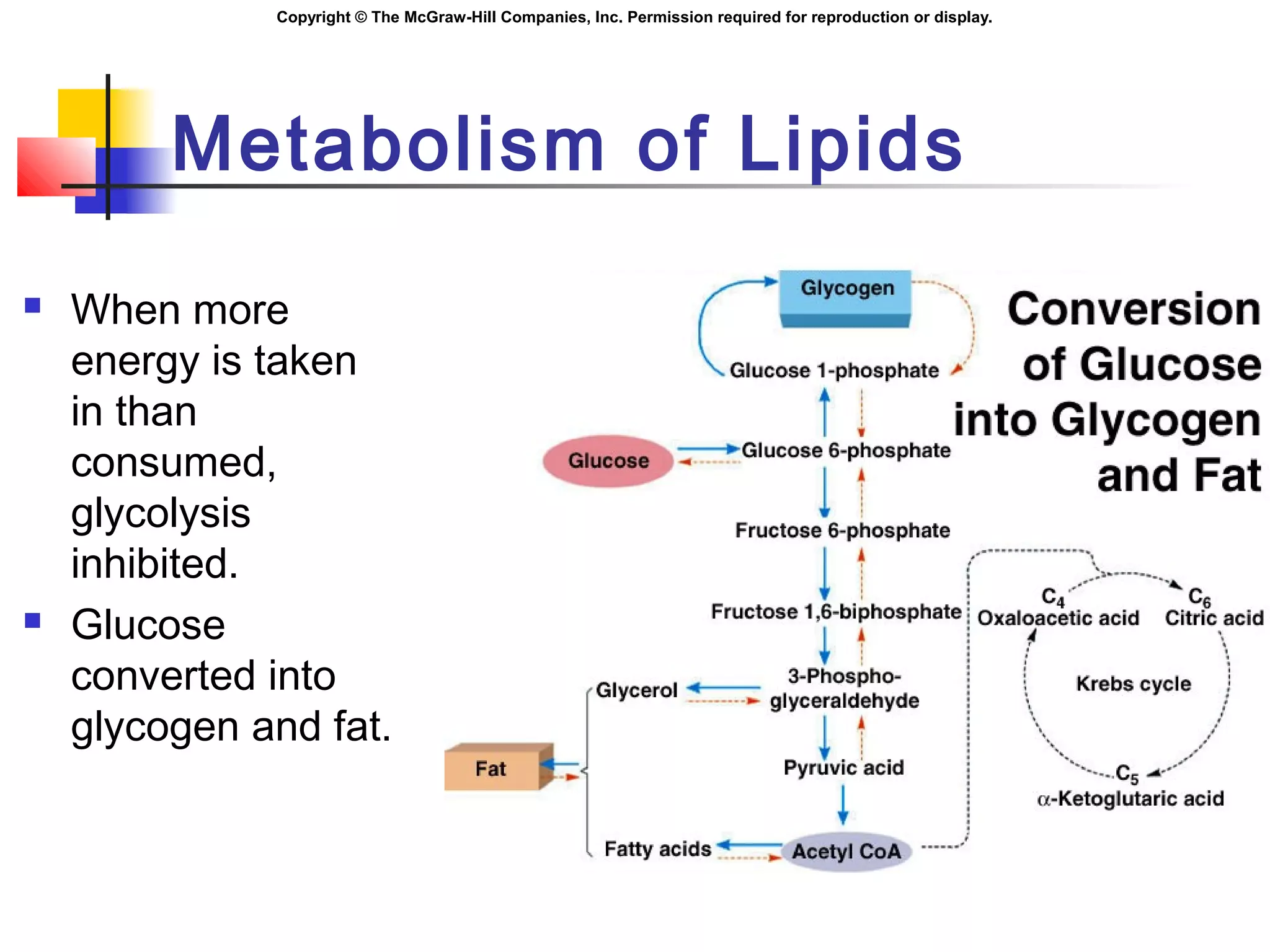
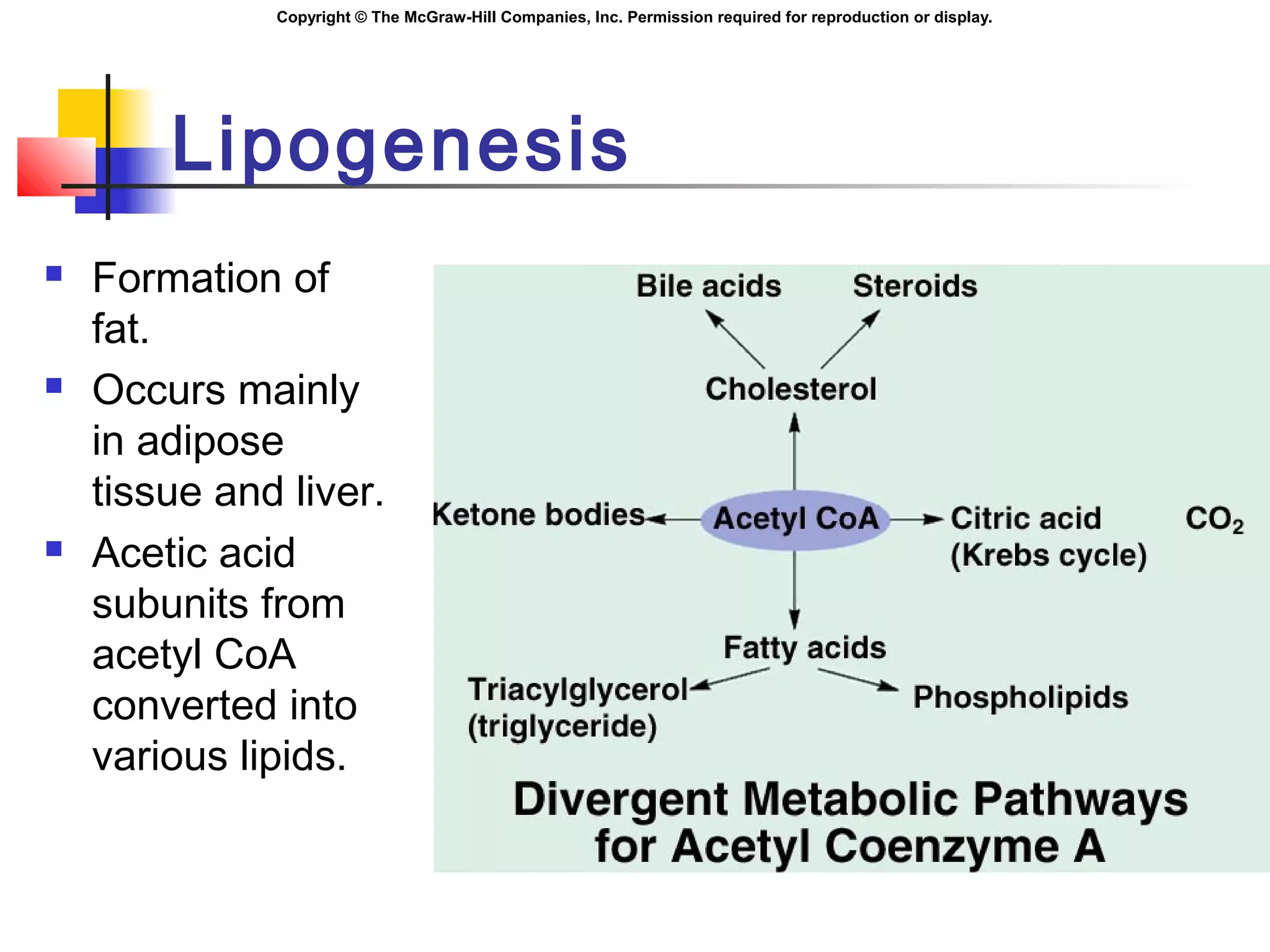
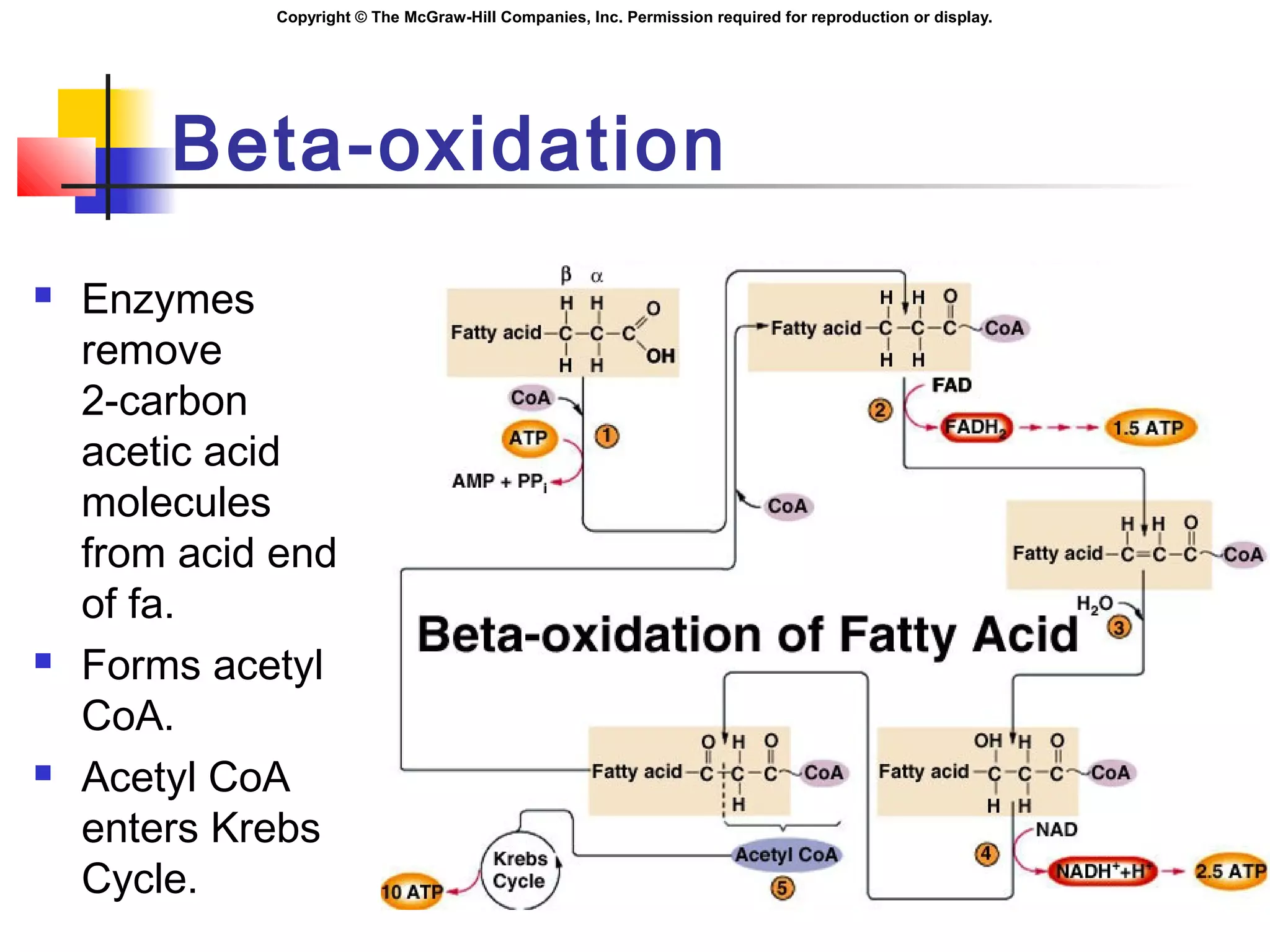
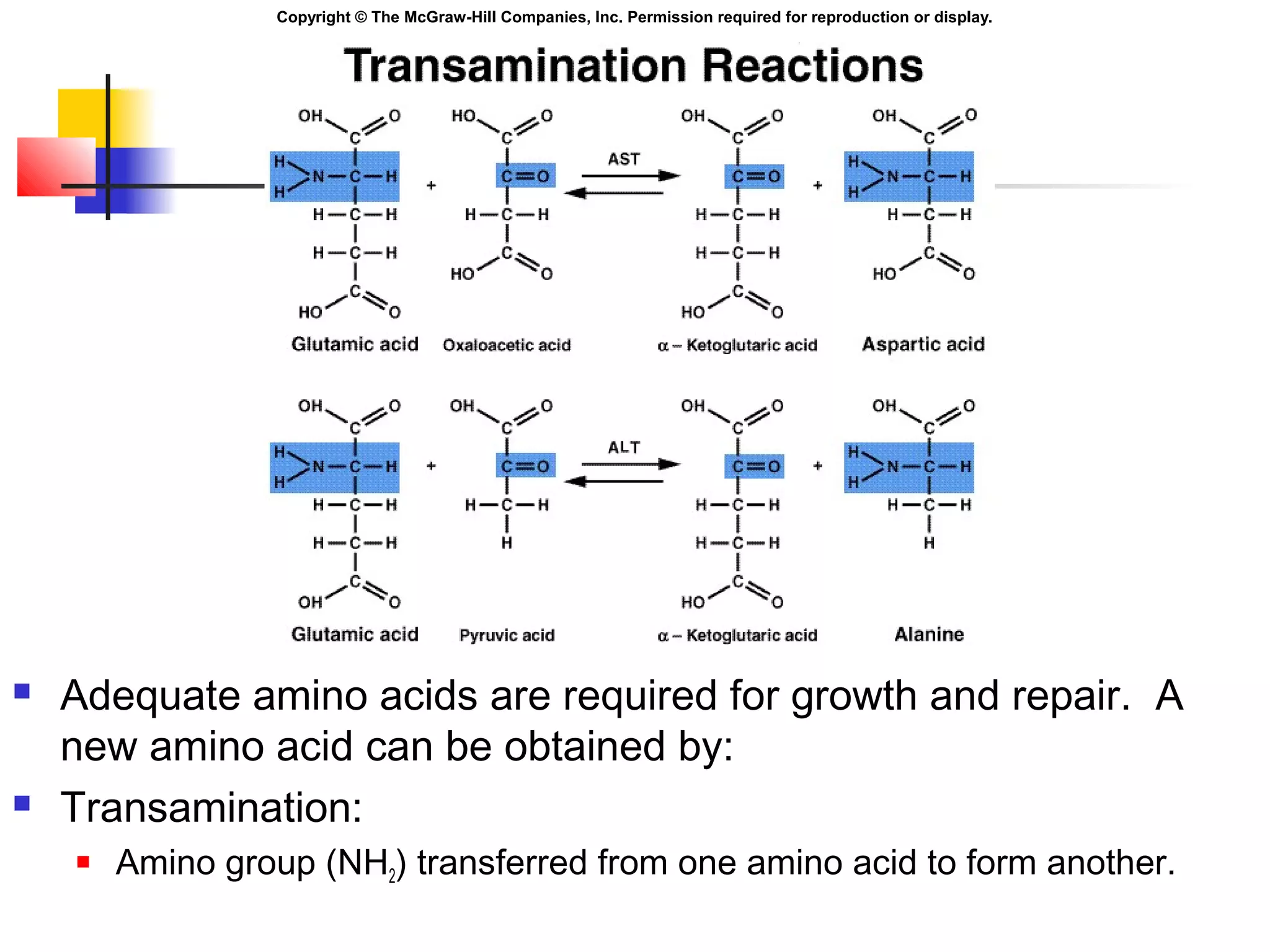
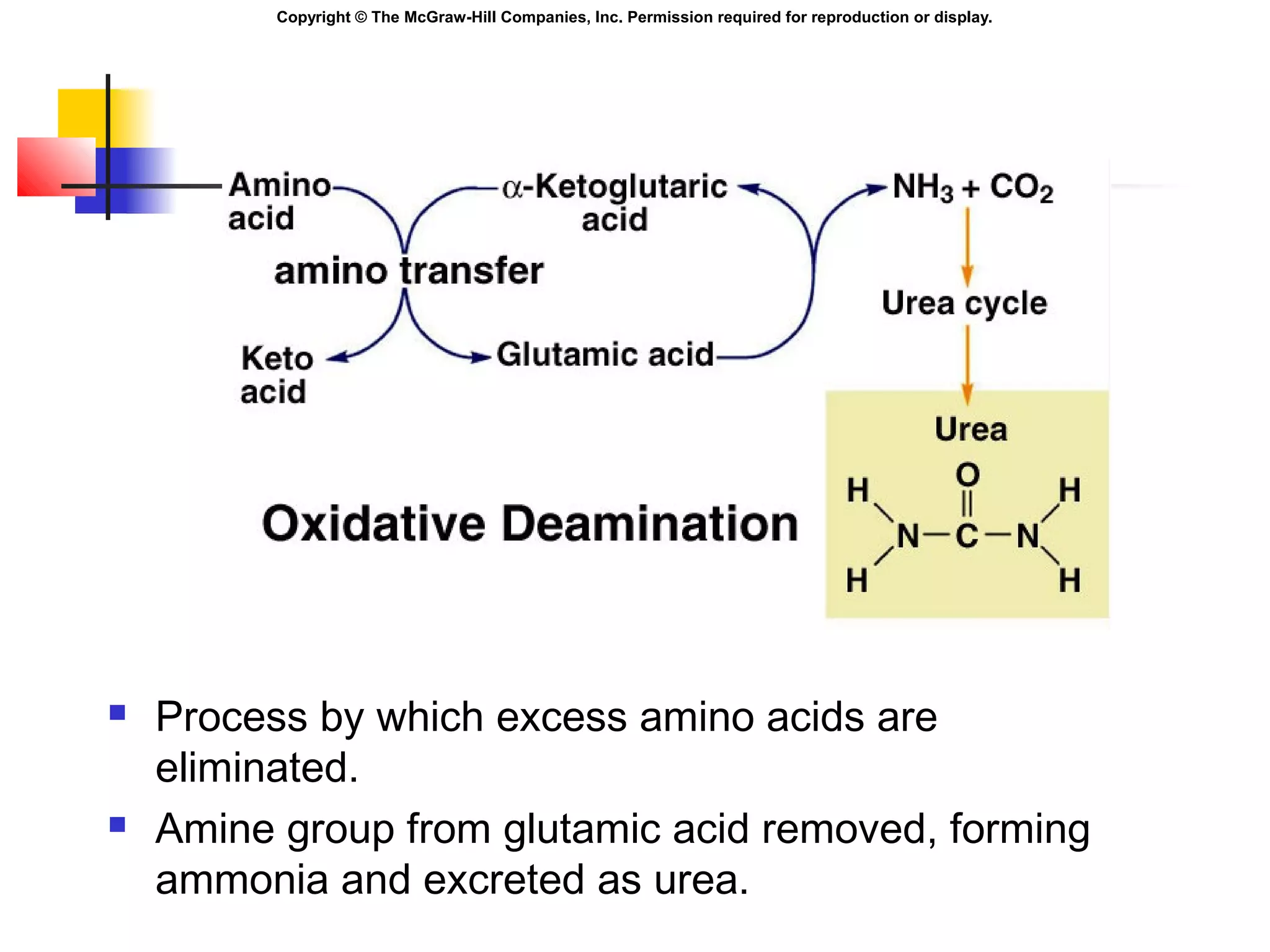
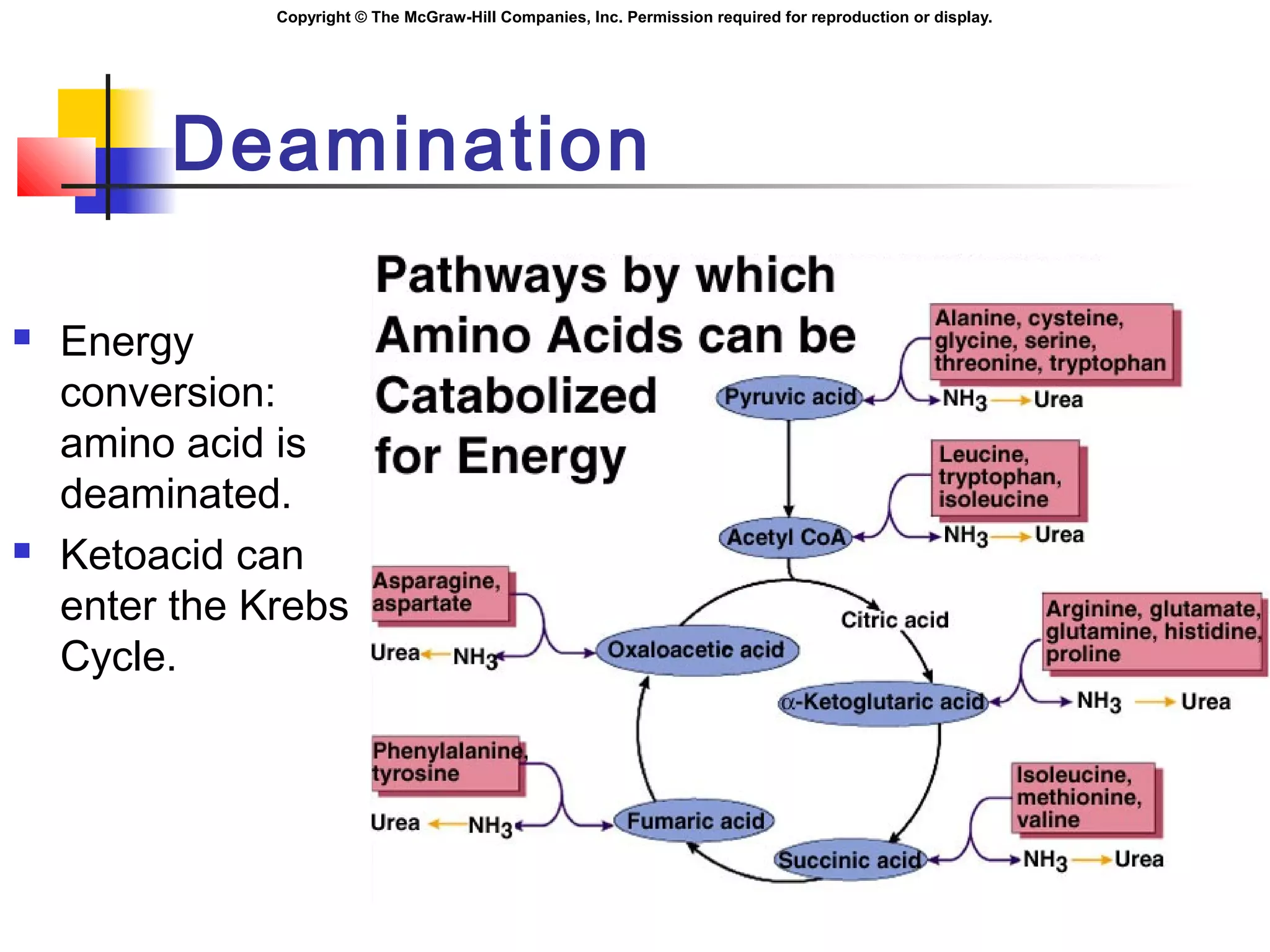
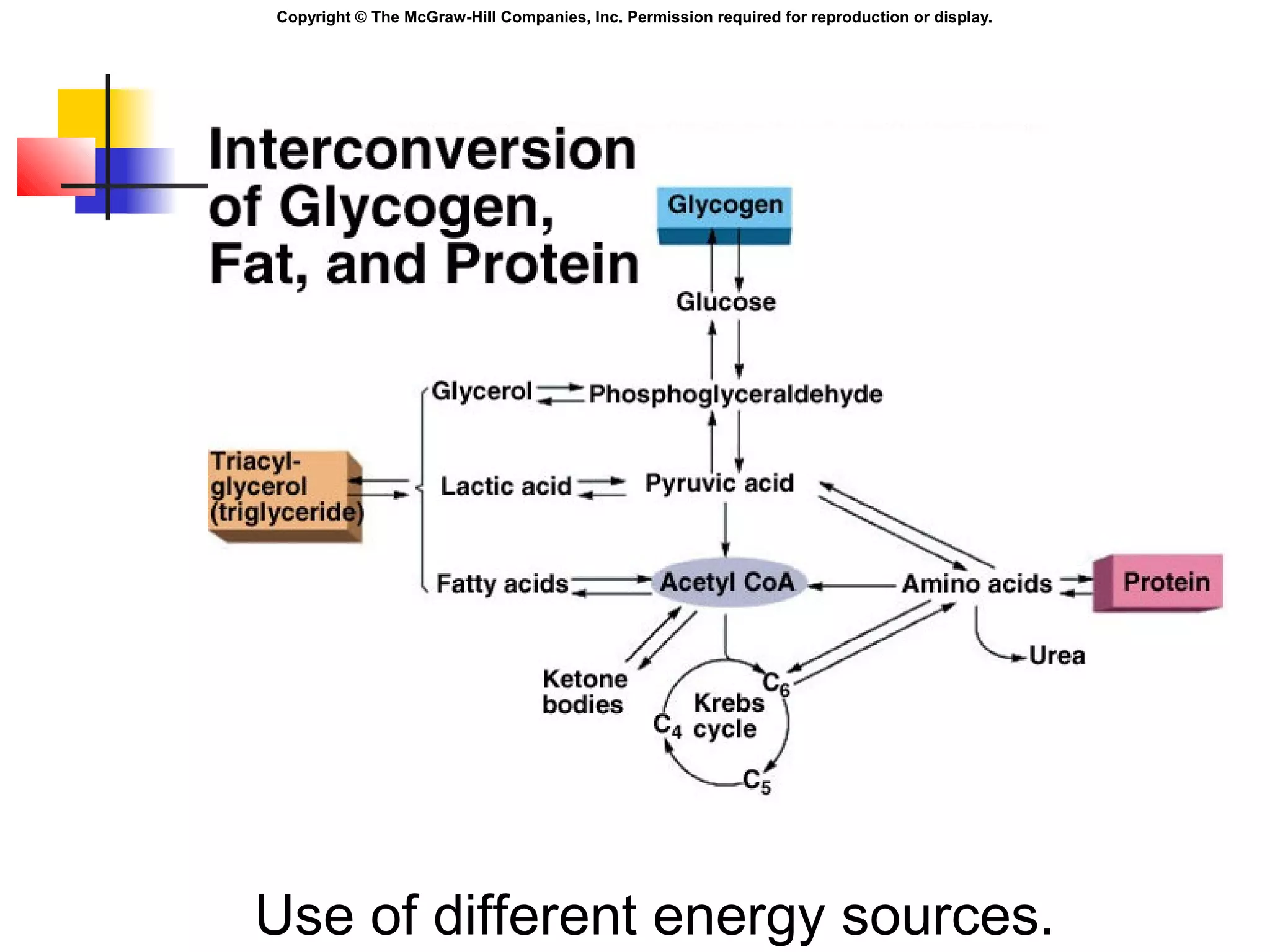
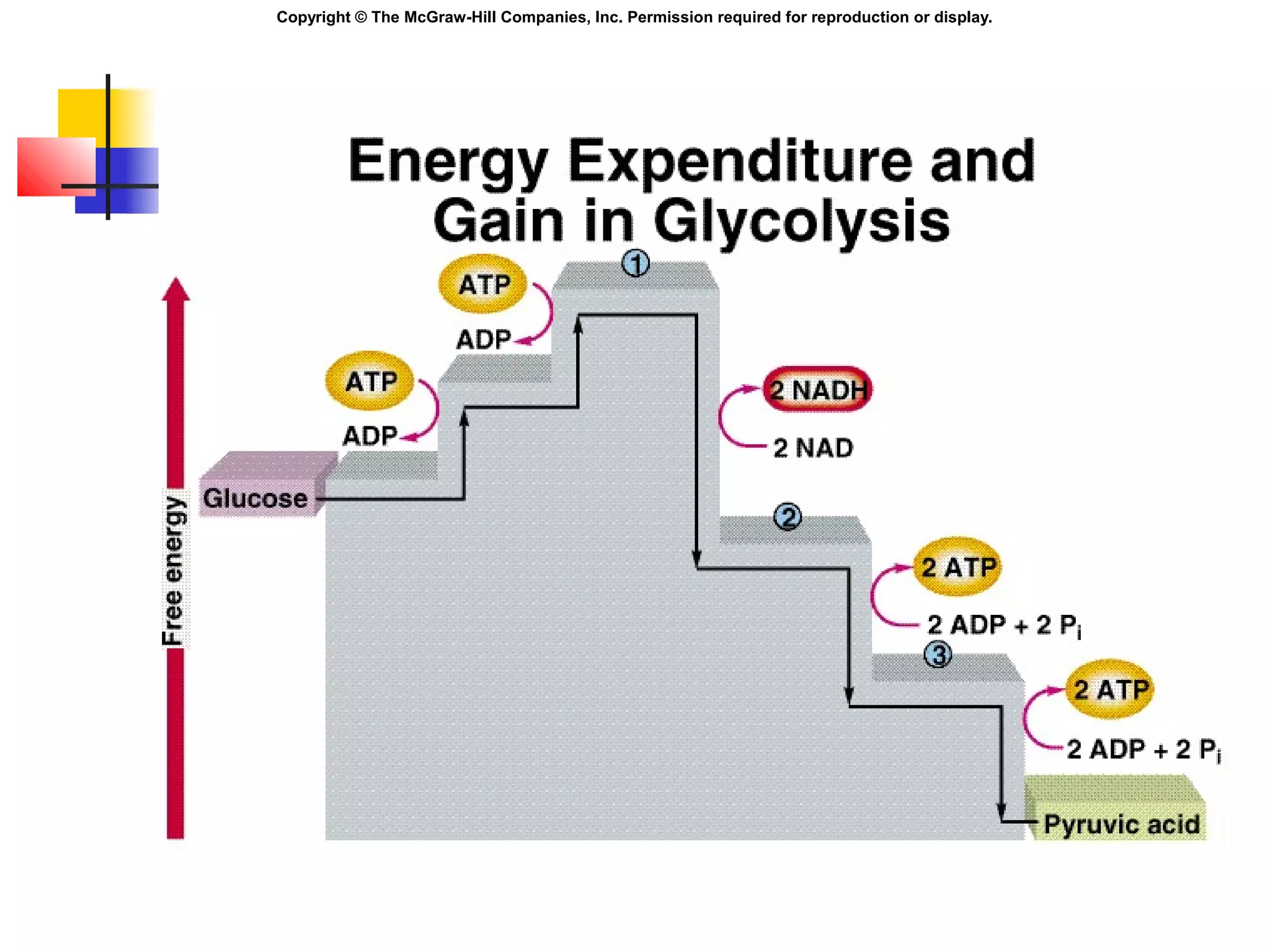
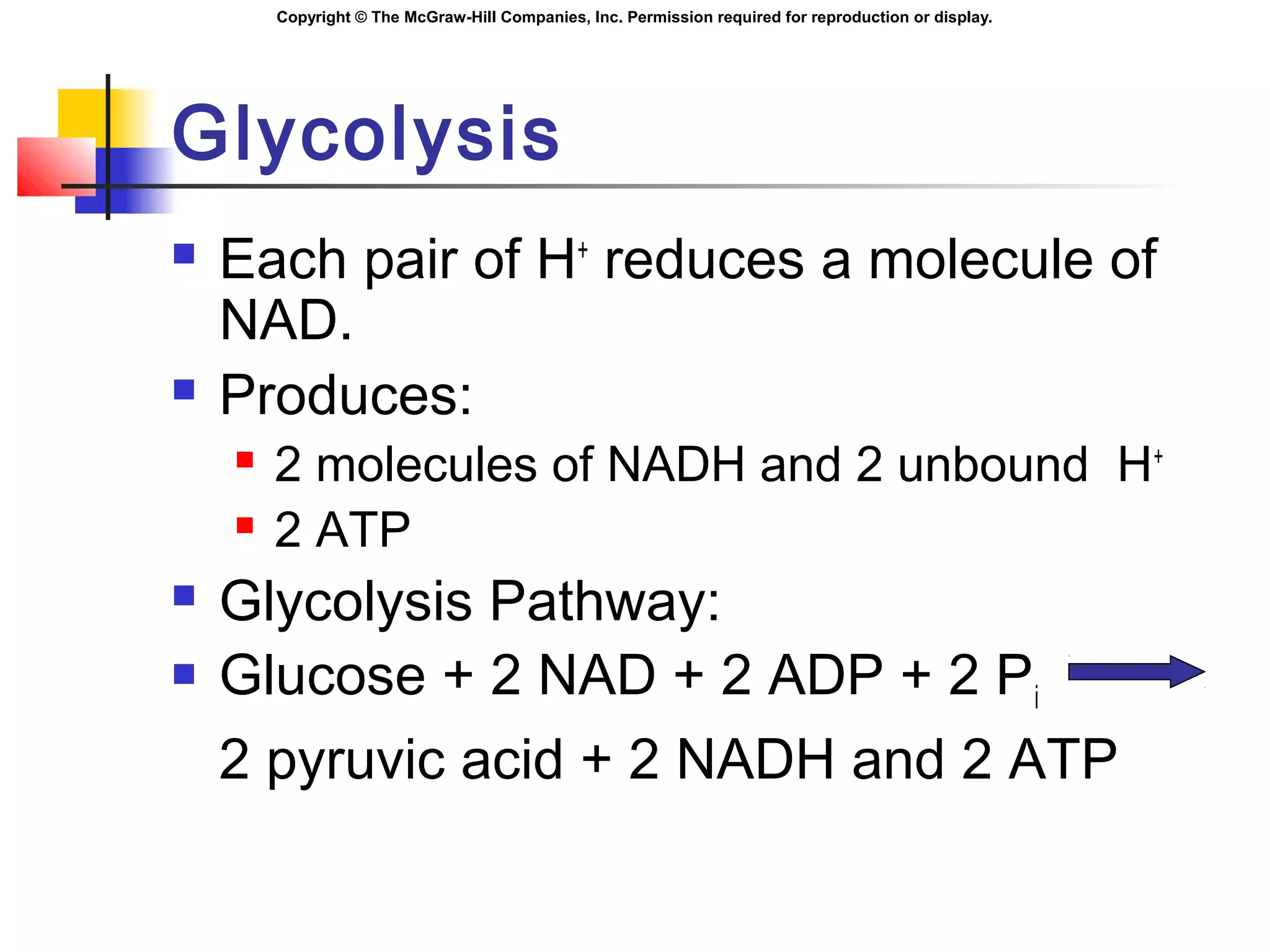
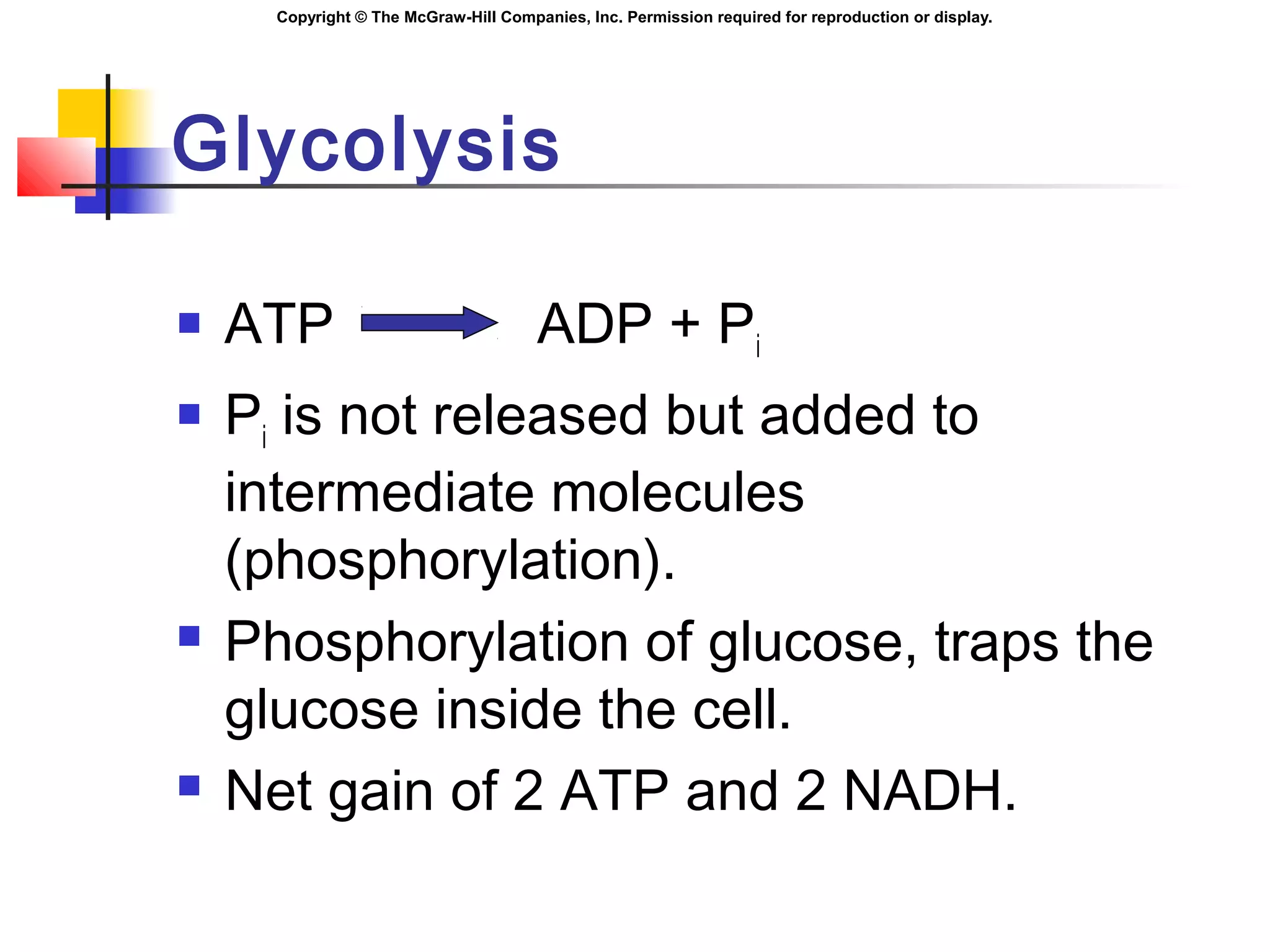
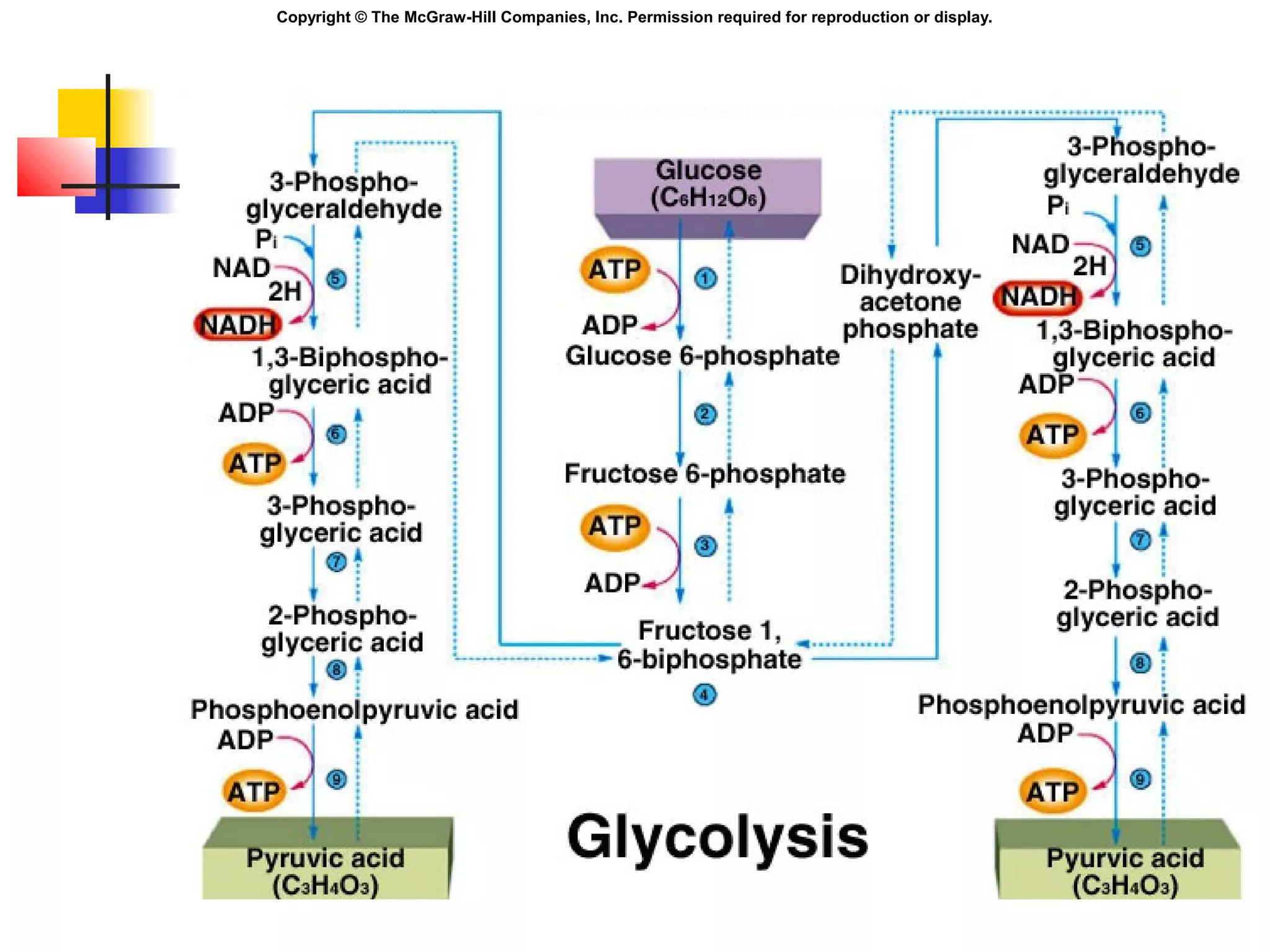
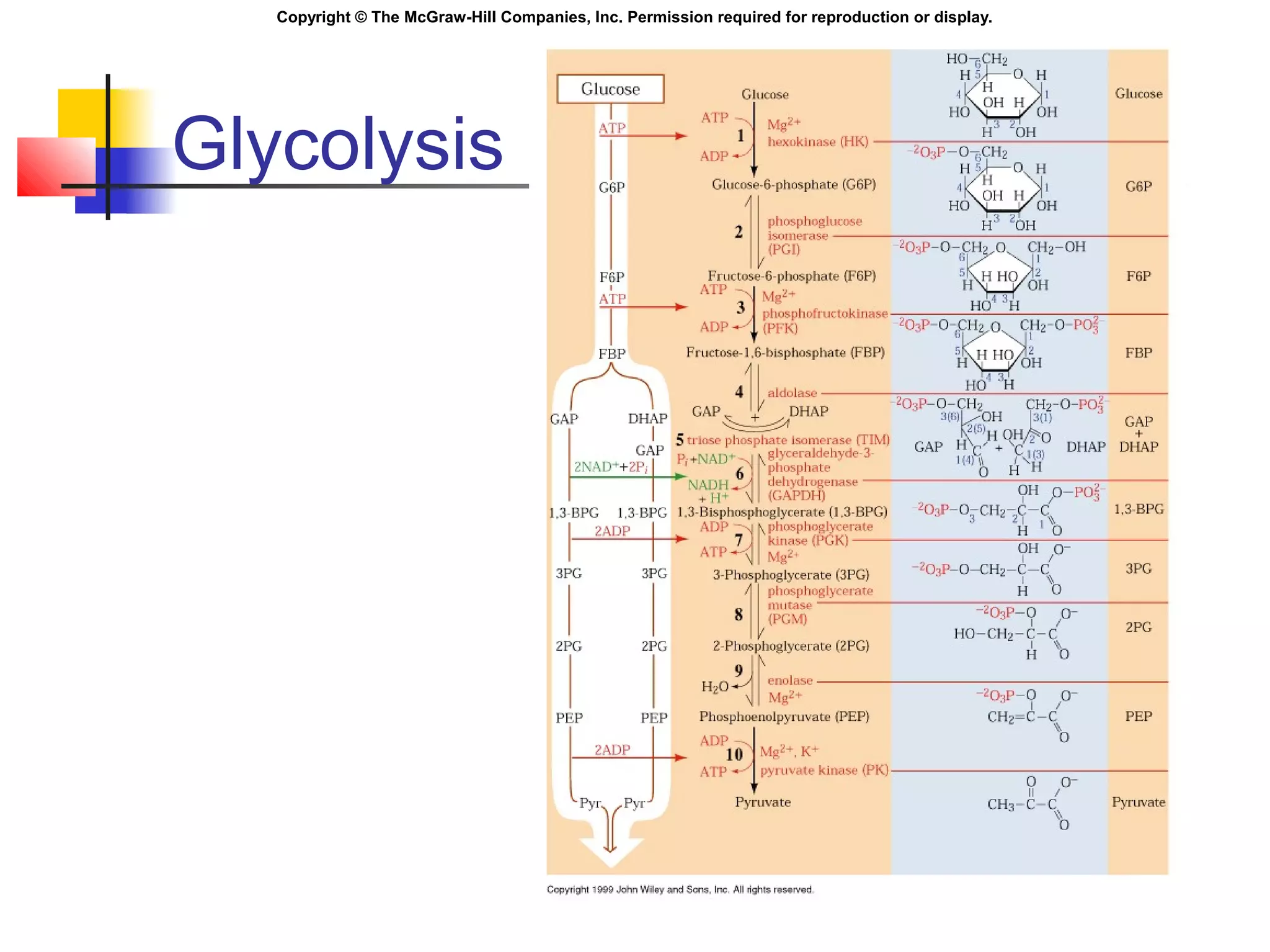
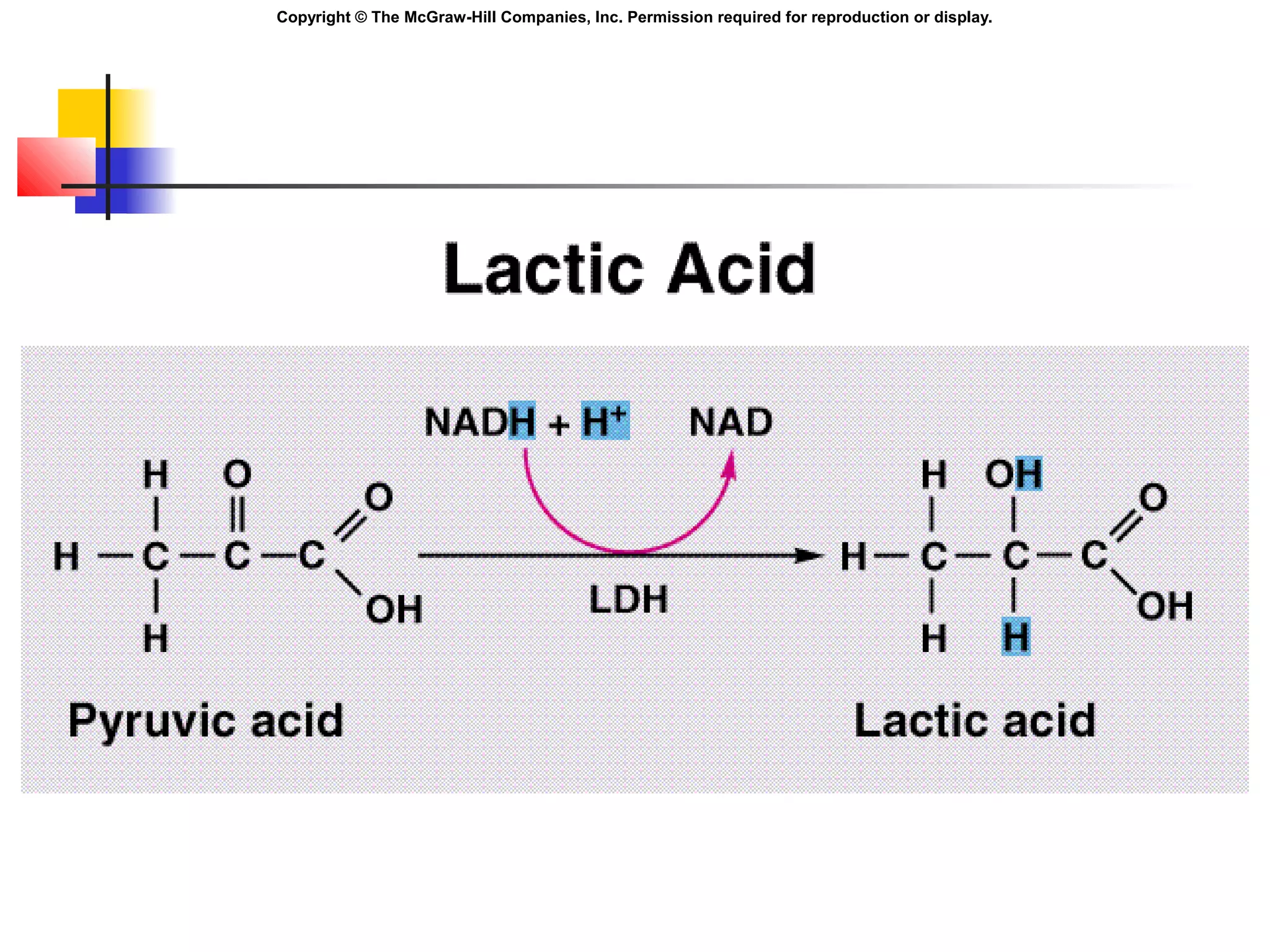
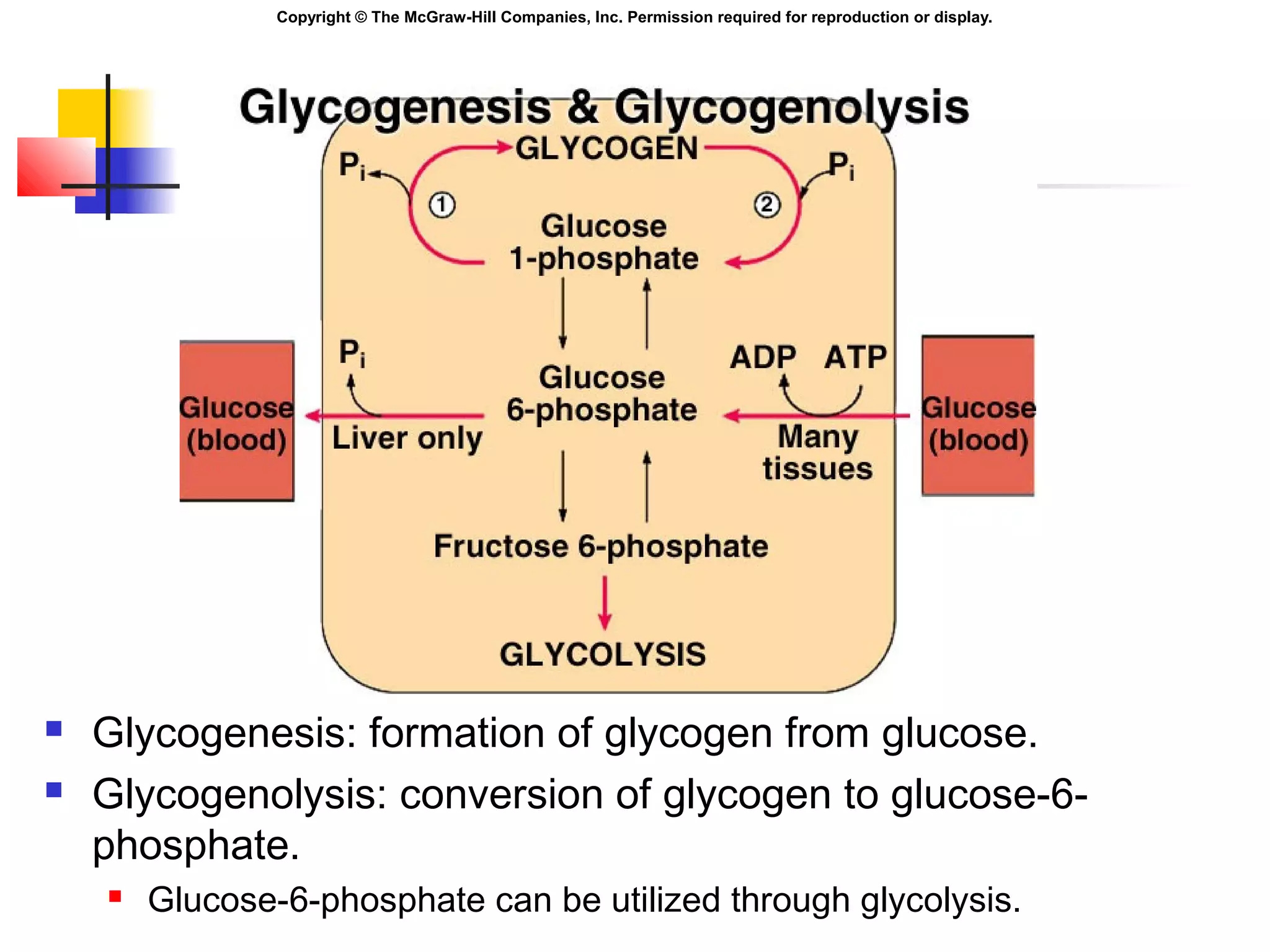
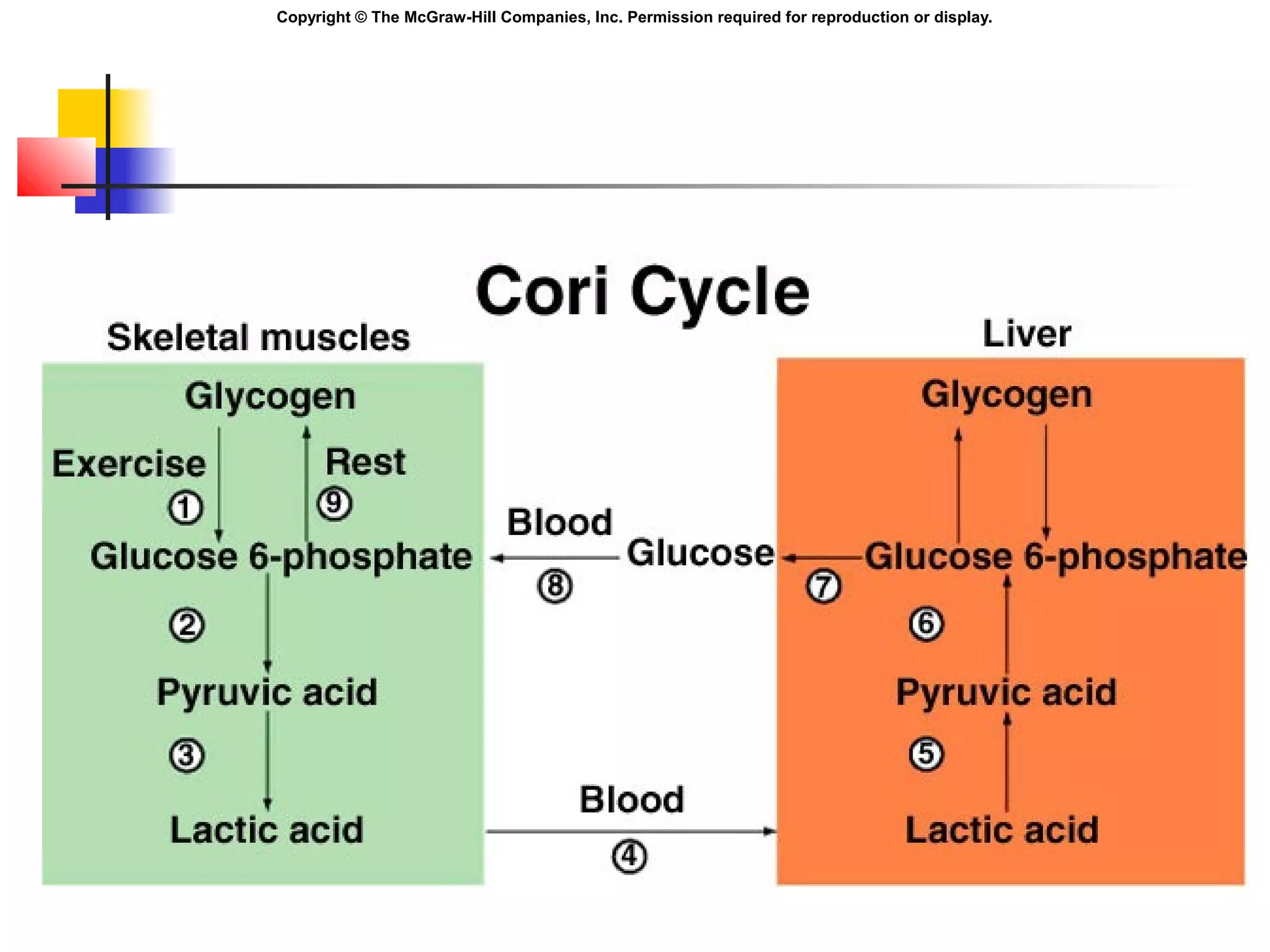
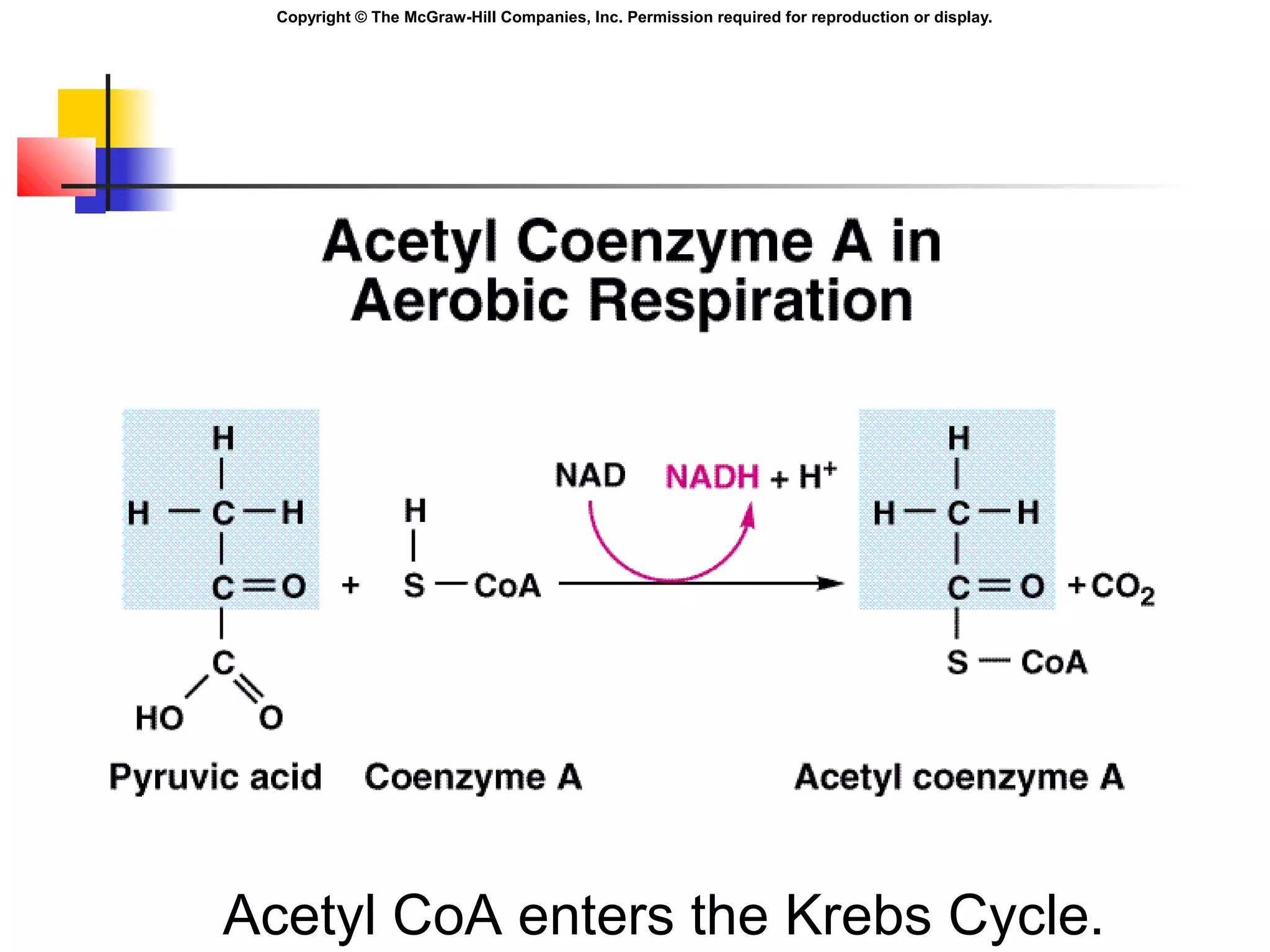
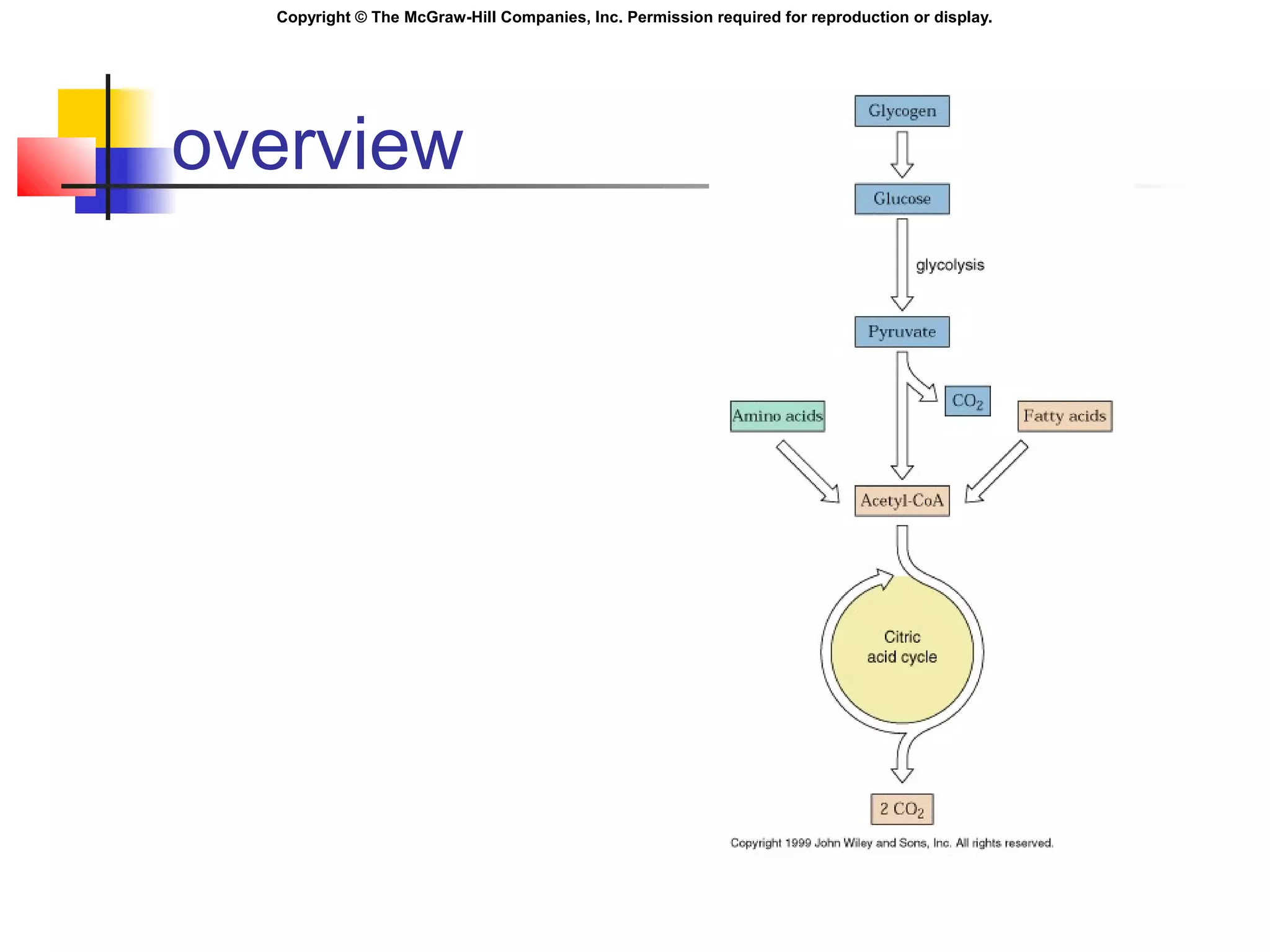
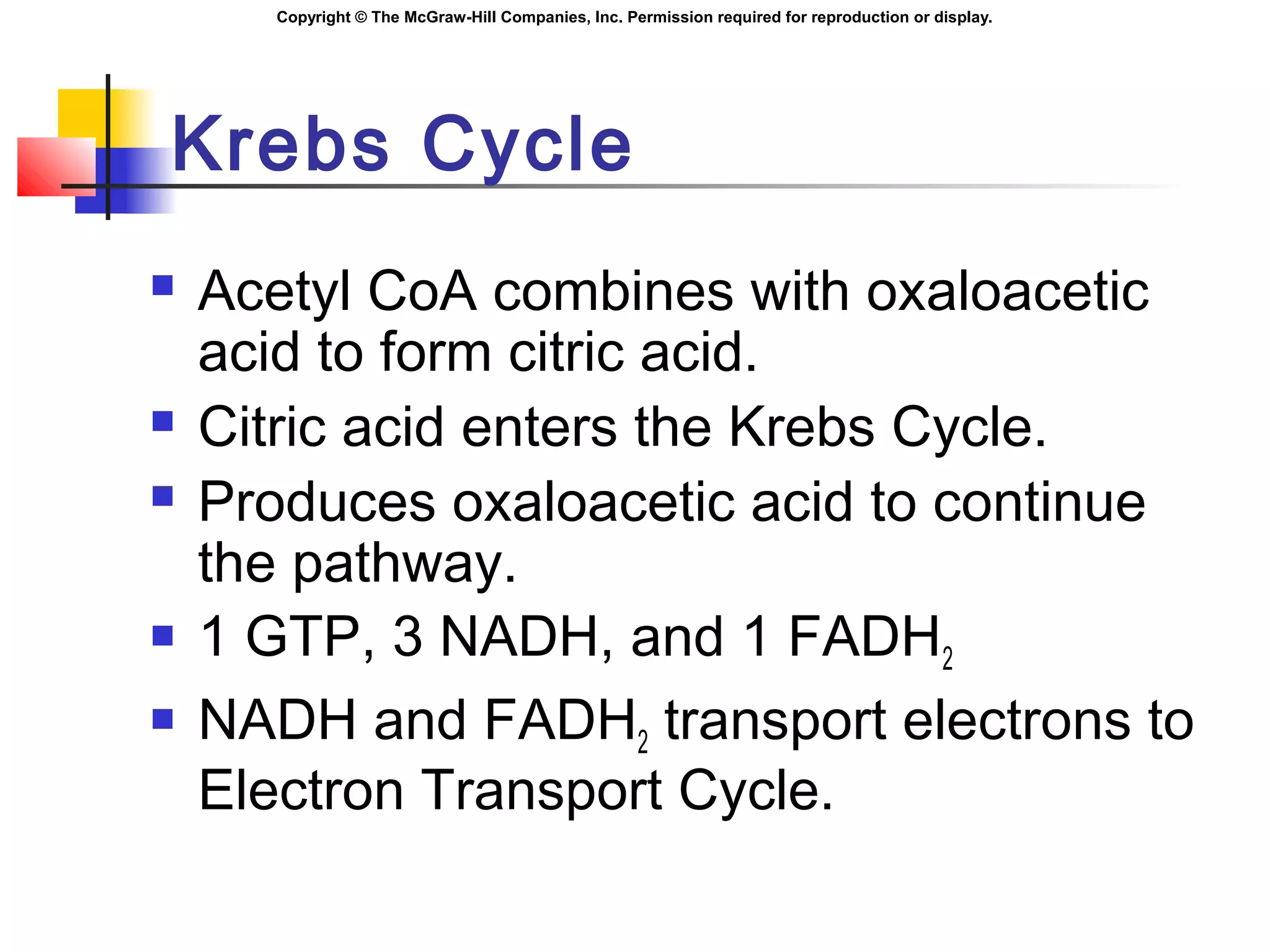
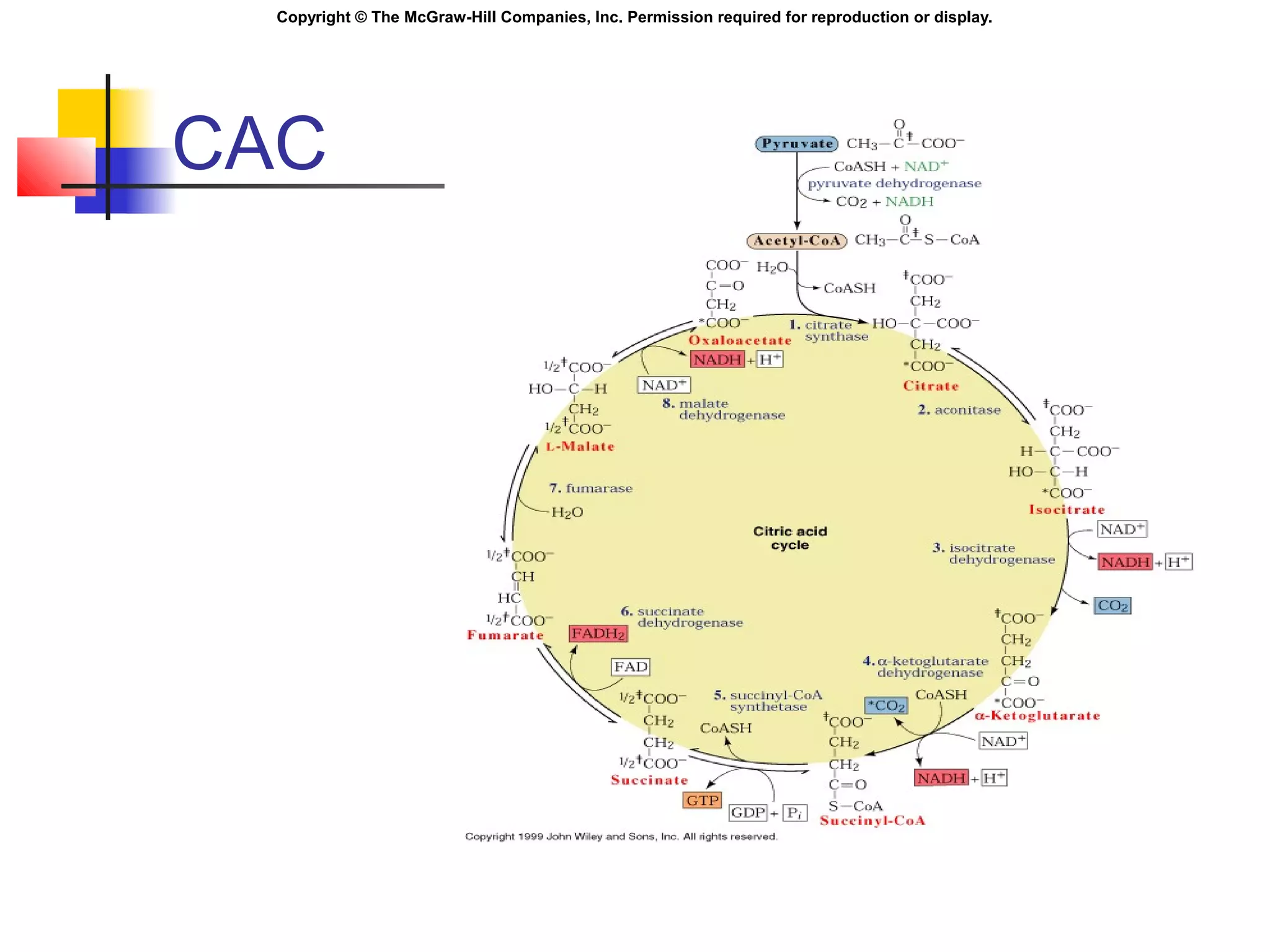
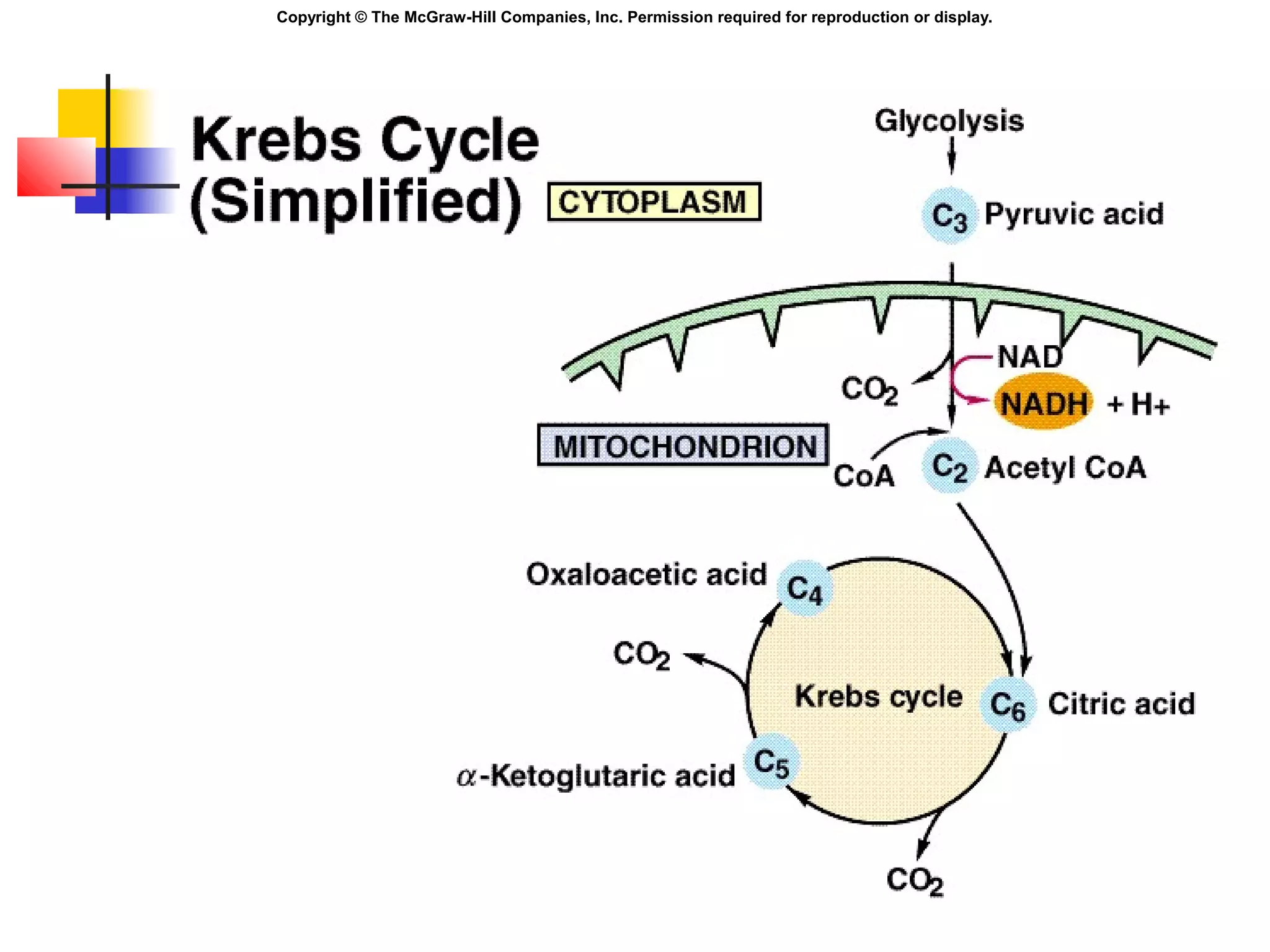
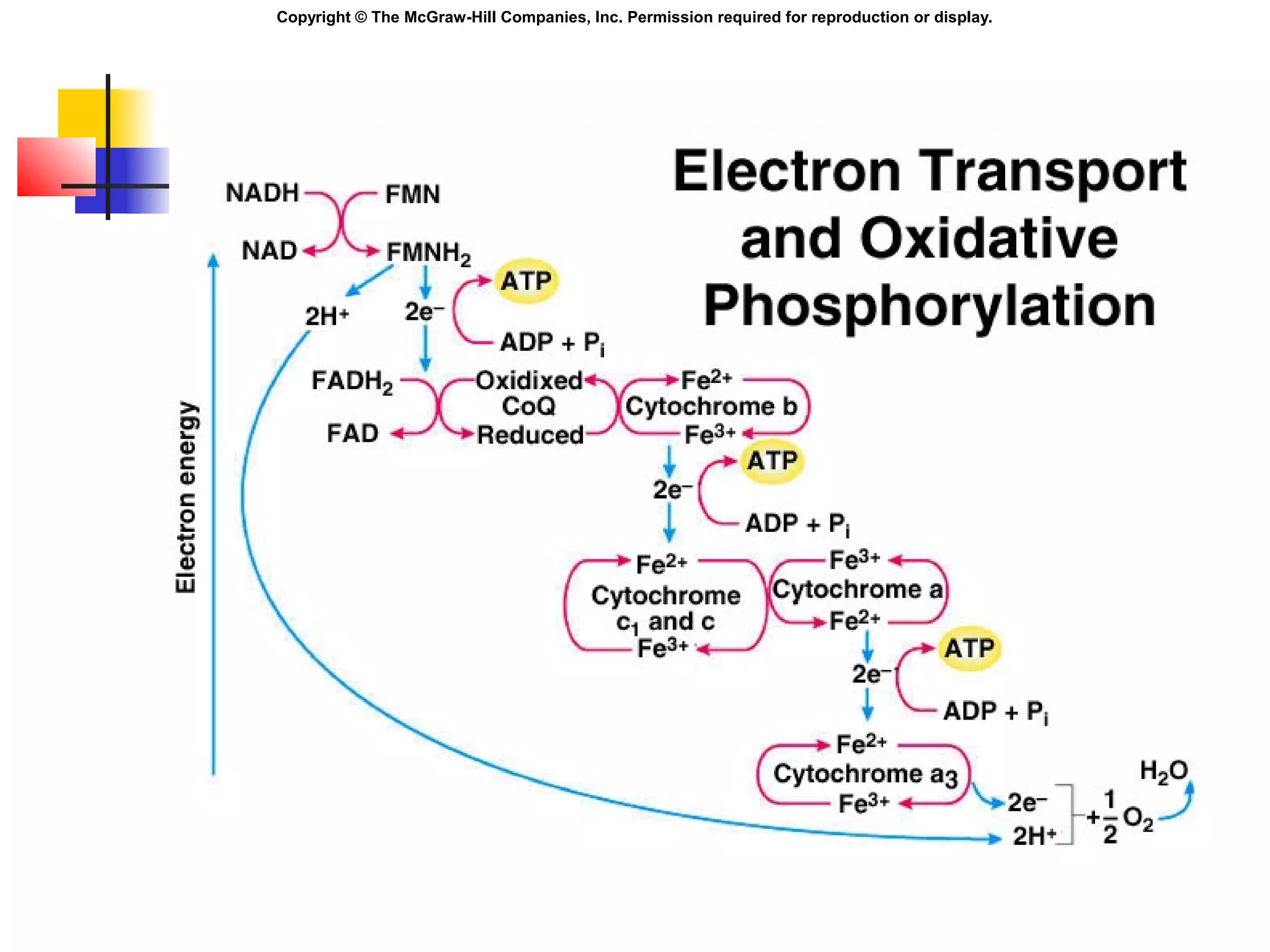
Metabolism involves energy transformations through catabolic and anabolic reactions. Aerobic cell respiration uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor in oxidation-reduction reactions to break down glucose and release energy. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate then undergoes either aerobic respiration through the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain, or anaerobic respiration through lactic acid fermentation. Glycogen and lipids can also provide energy through breakdown.














![Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
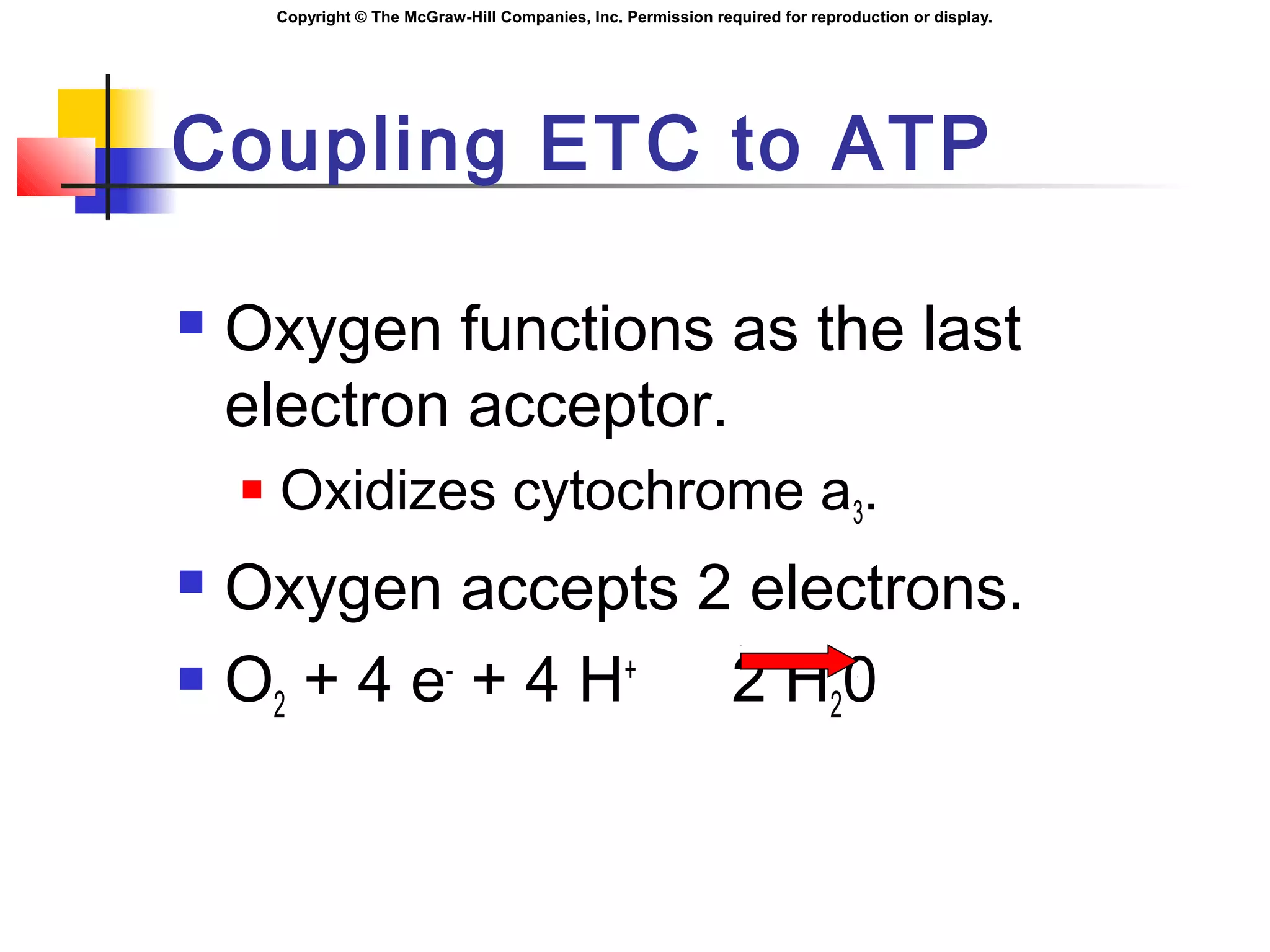
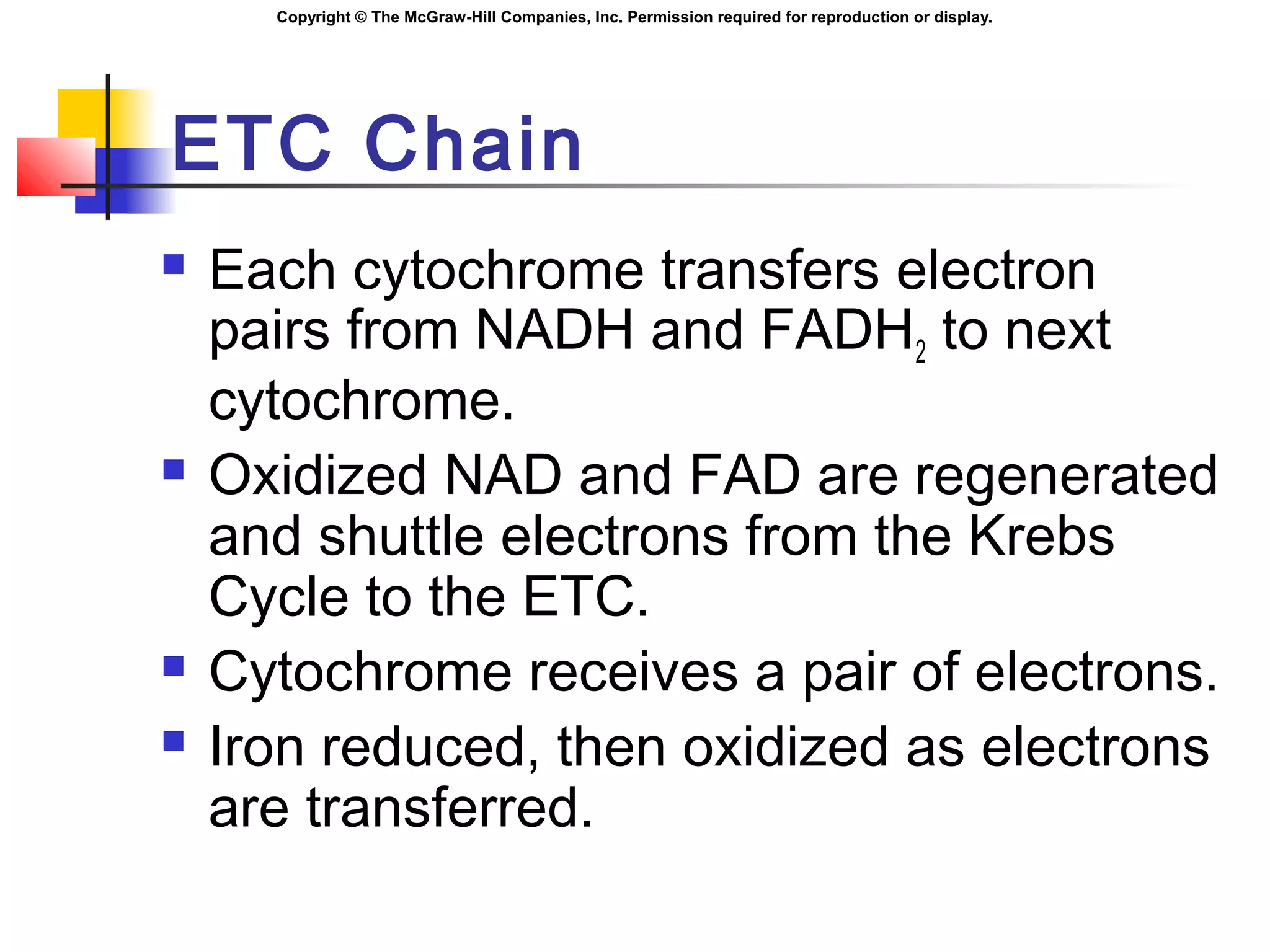
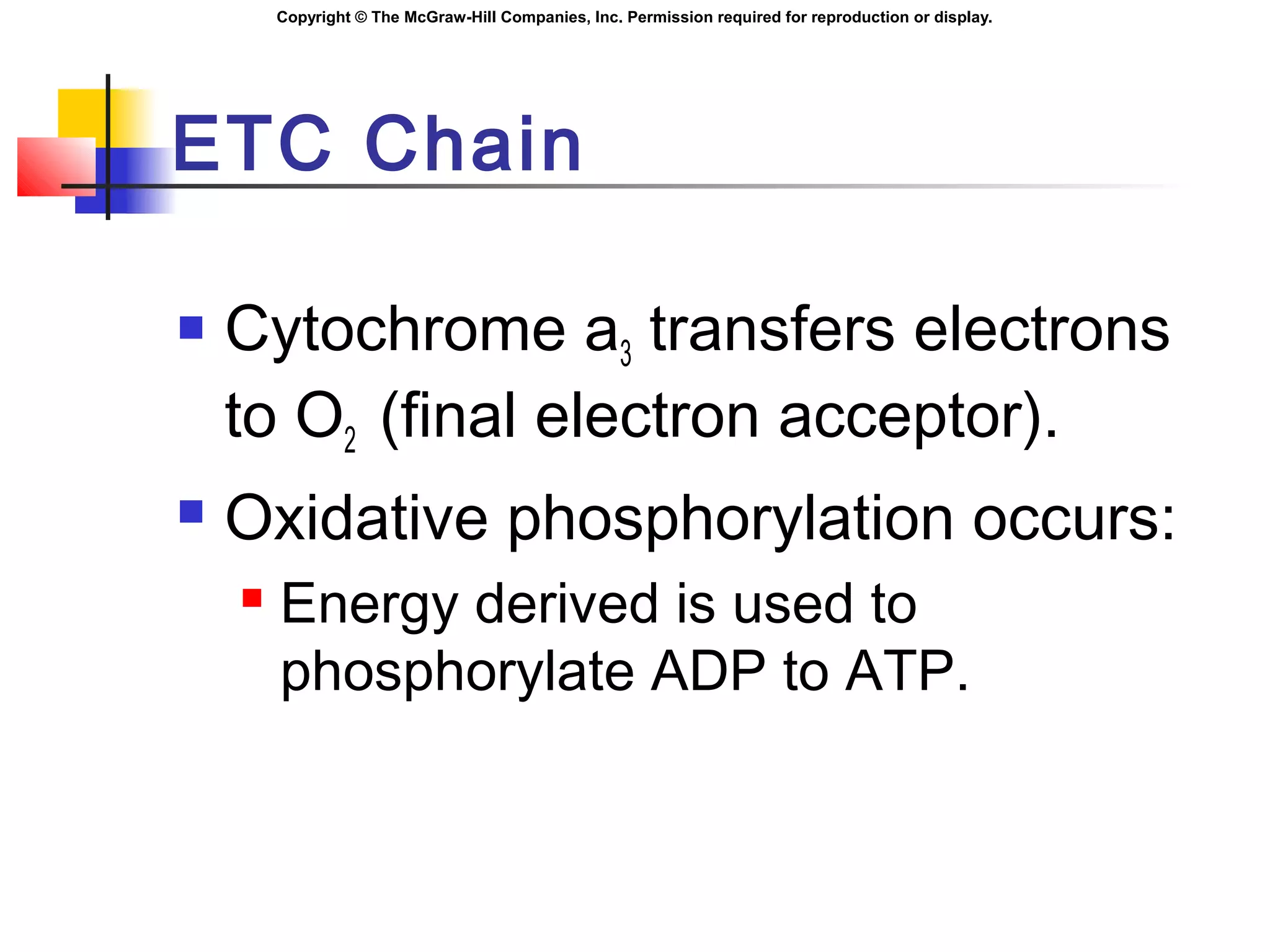
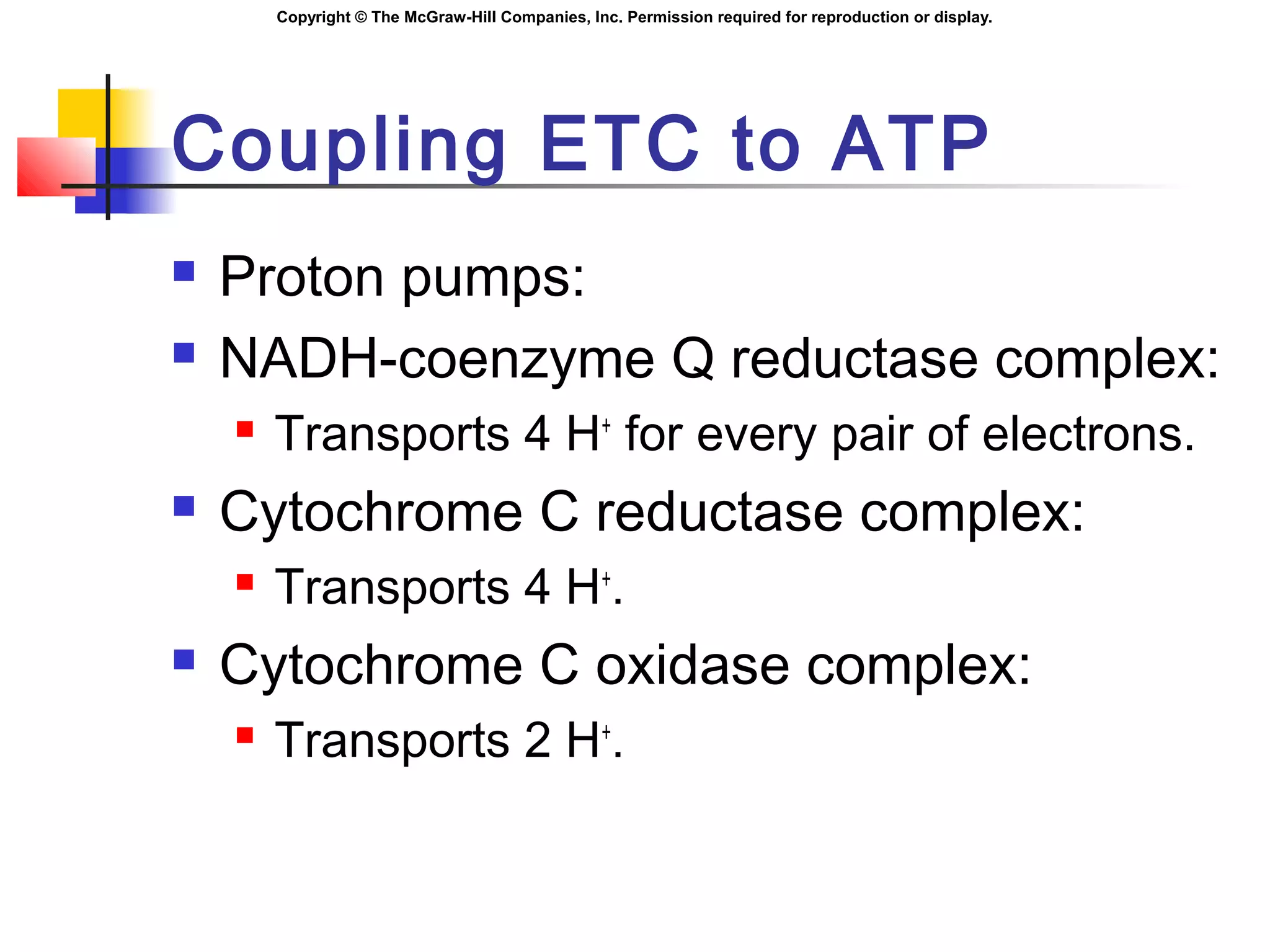
Coupling ETC to ATP
Higher [H+
] in inter-membrane space.
Respiratory assemblies:
Permit the passage of H+
.
Phosphorylation is coupled to oxidation,
when H+
diffuse through the respiratory
assemblies:
ADP and Pi ATP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter05cellrespirationandmetabolism-140825021030-phpapp02/75/Chapter05-cell-respiration-and-metabolism-32-2048.jpg)