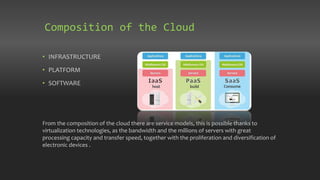
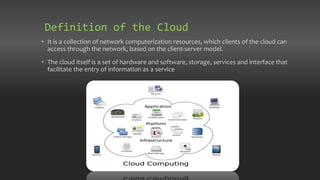
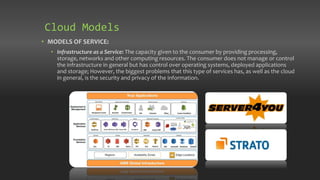
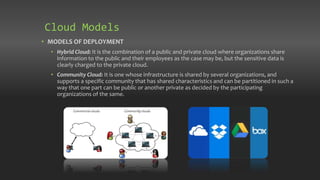
Chapter 7 discusses the origins and architecture of cloud computing, tracing its roots back to concepts introduced by John McCarthy in 1961. It outlines various service models, including Software as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Infrastructure as a Service, as well as deployment models like public, private, hybrid, and community clouds. The chapter emphasizes the significant role of data centers in supporting cloud services and compares the evolution of cloud computing to that of electricity in the industrial age.