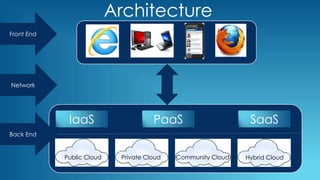
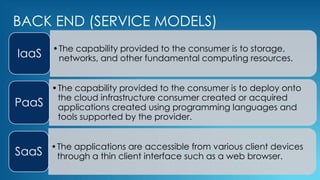
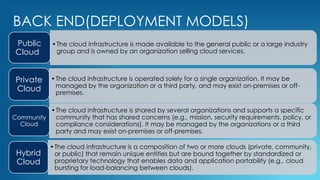
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, architecture, deployment models, and why it is used. It defines cloud computing as using the internet to access software and hardware resources owned by cloud providers. The architecture consists of front-end clients, a network, and back-end servers and storage. It describes infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) deployment models, as well as public, private, hybrid and community clouds. In conclusion, the document states that cloud computing provides ubiquitous access to data and applications from any device, is agile in nature, offers security benefits, reduces costs by minimizing infrastructure needs, and