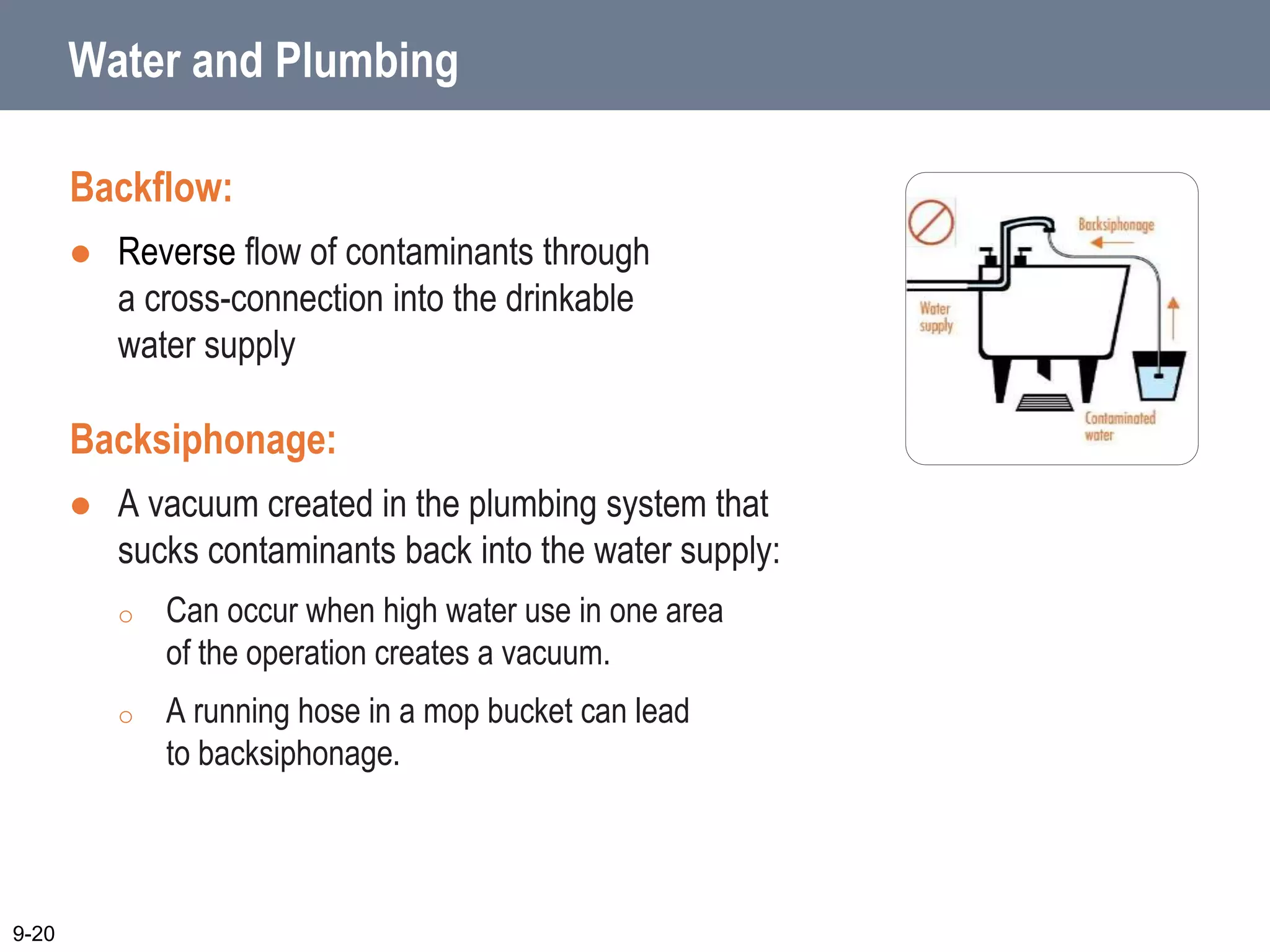
This document discusses safe facilities and pest management in foodservice operations. It covers selecting and installing equipment that is easy to clean and maintain, properly designing and installing plumbing and ensuring clean water sources. Facilities must be kept clean and well-maintained, and have proper lighting, ventilation and garbage handling. Emergencies like power outages require an approved plan. Pests are prevented by denying them access, food, water and shelter through sanitary practices like cleaning up spills and storing supplies off the floor. A licensed pest control operator can help with any pest issues.