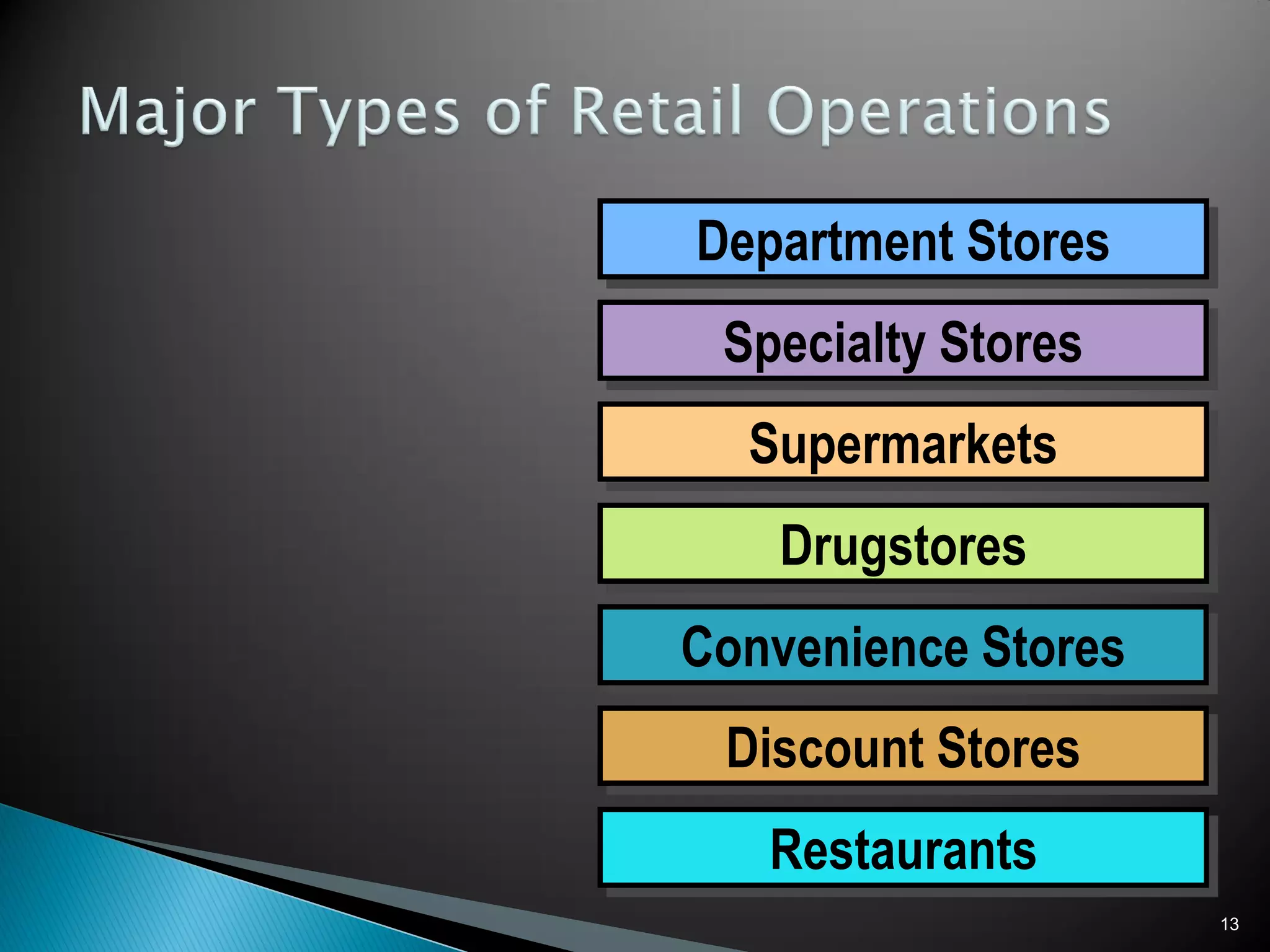
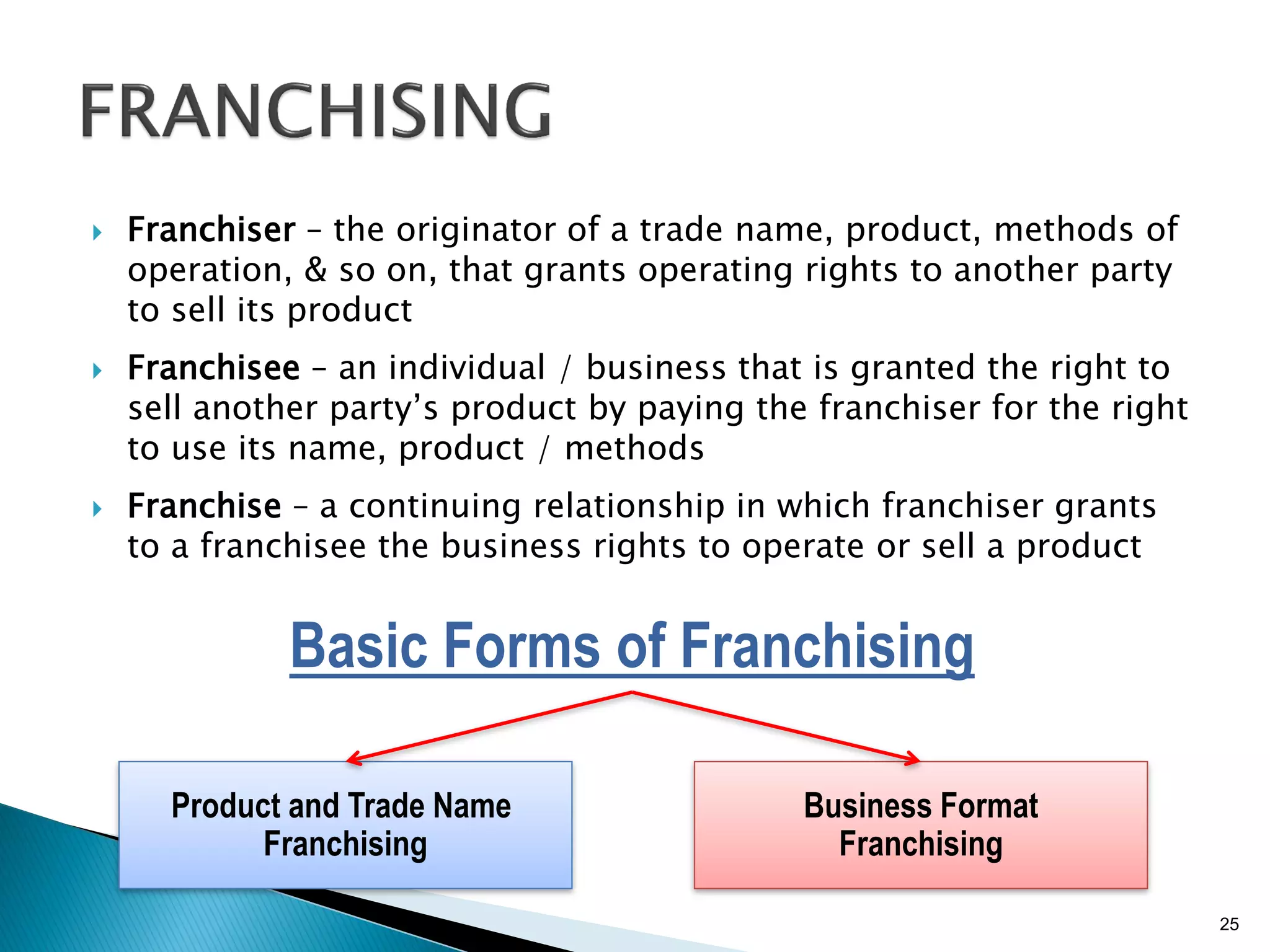
The document discusses various aspects of retailing including defining retailing, classifying retail operations, types of retail operations, non-store retailing, and franchising. It classifies retail operations based on ownership, level of service, product assortment, and price. The major types of retail operations discussed are department stores, specialty stores, supermarkets, drugstores, convenience stores, discount stores, and restaurants. Non-store retailing includes various direct marketing approaches. Franchising involves a franchiser granting a franchisee the right to sell its products or services in exchange for fees and agreement to the franchiser's way of doing business.