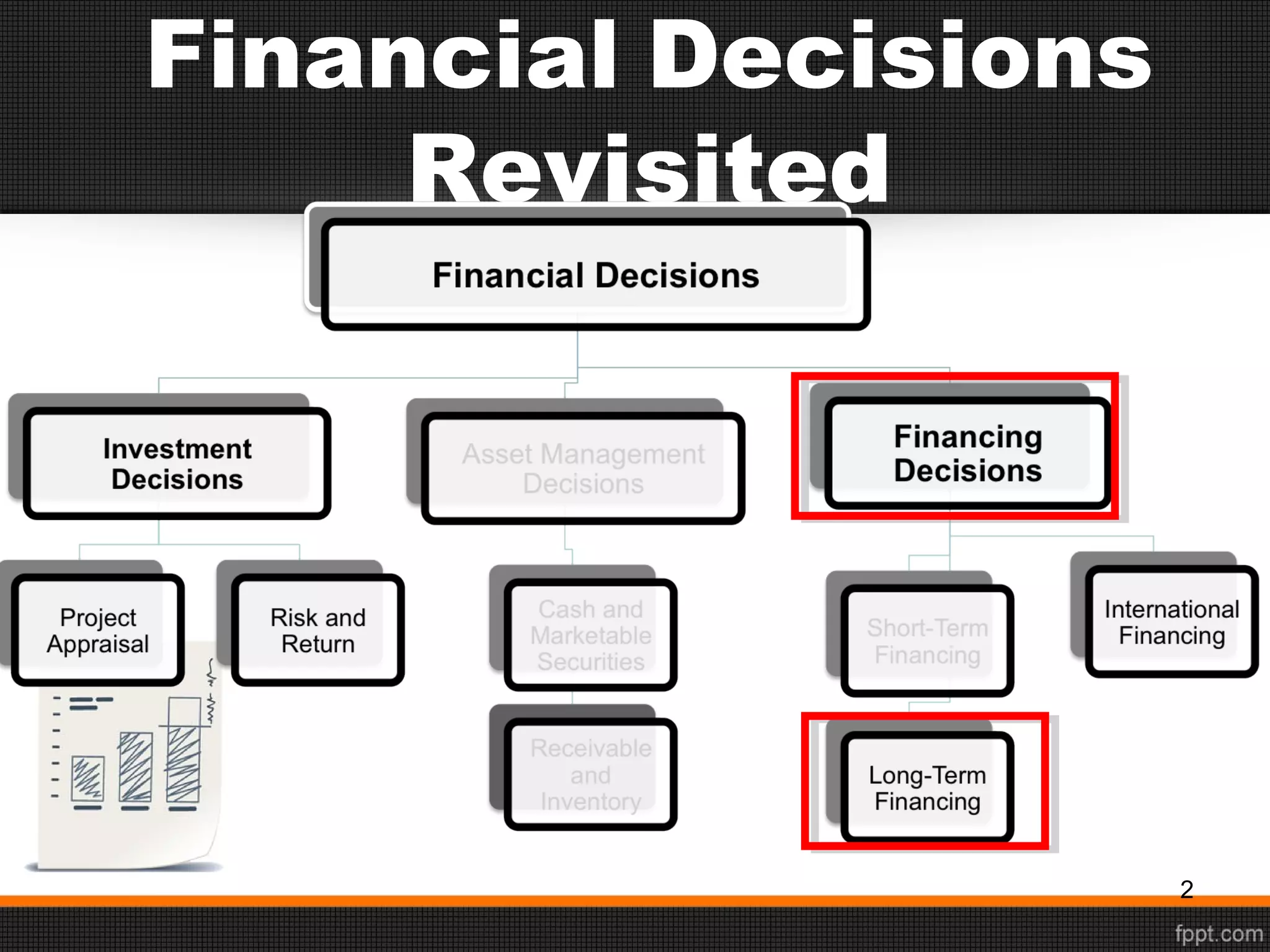
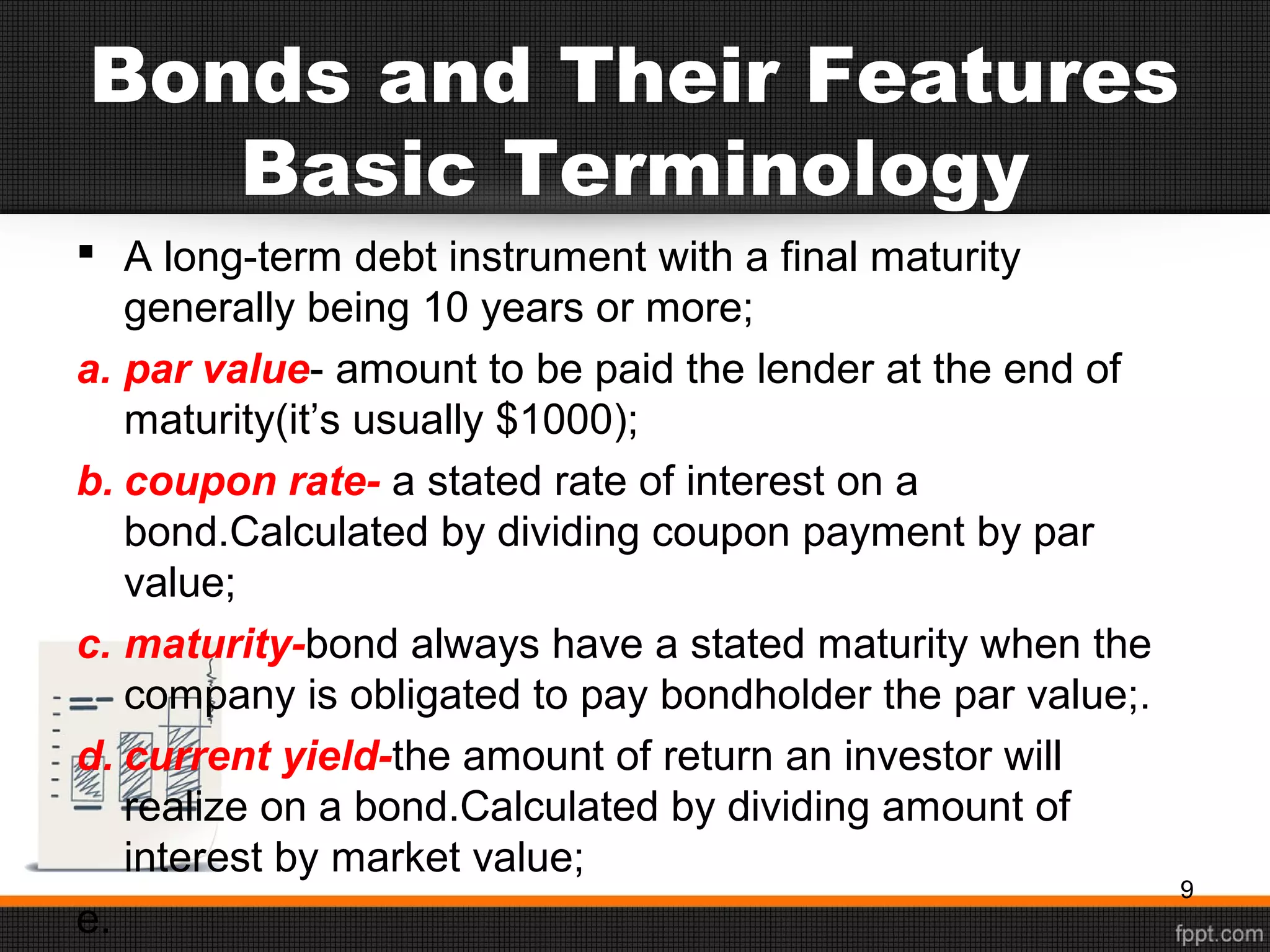
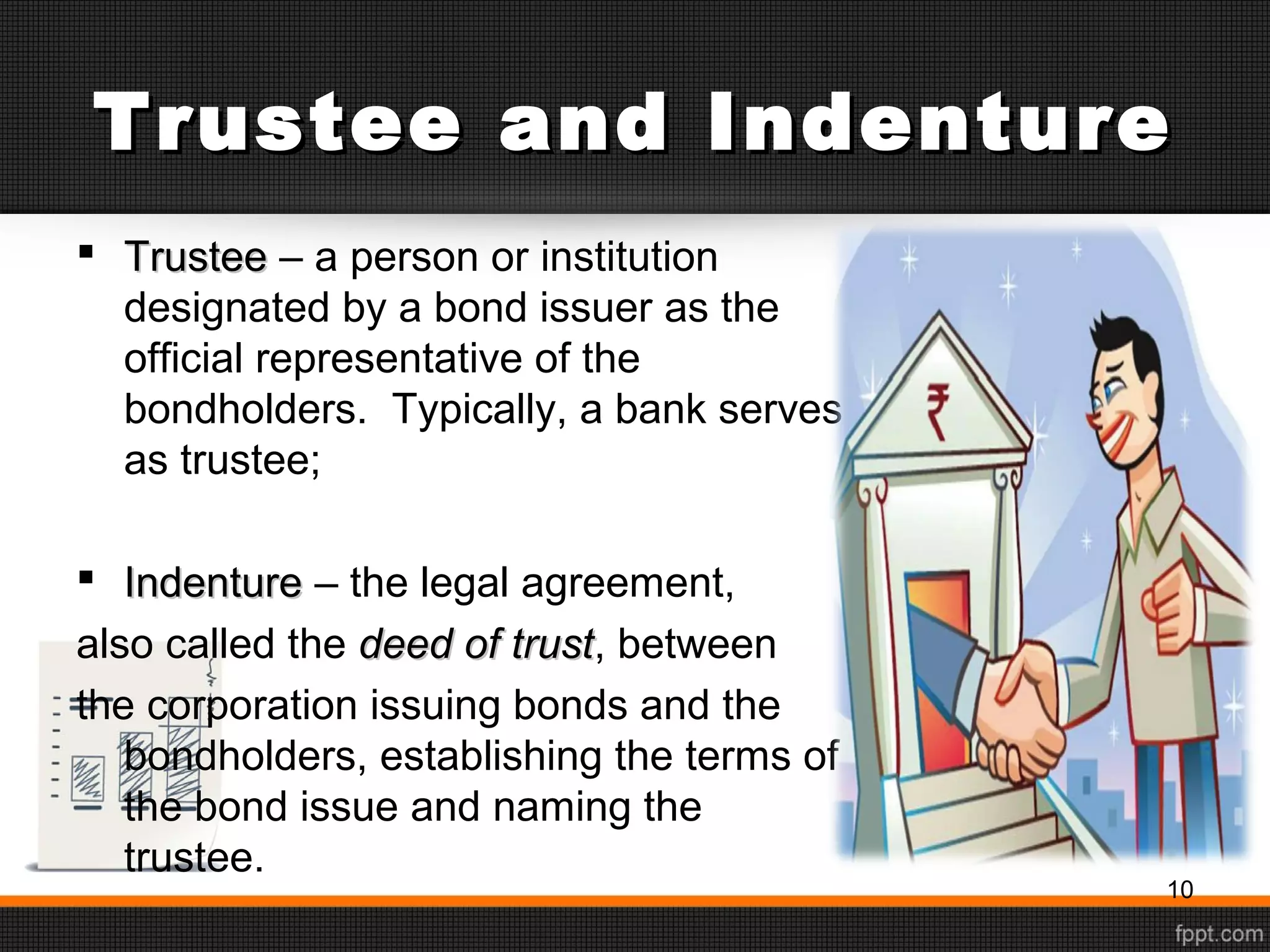
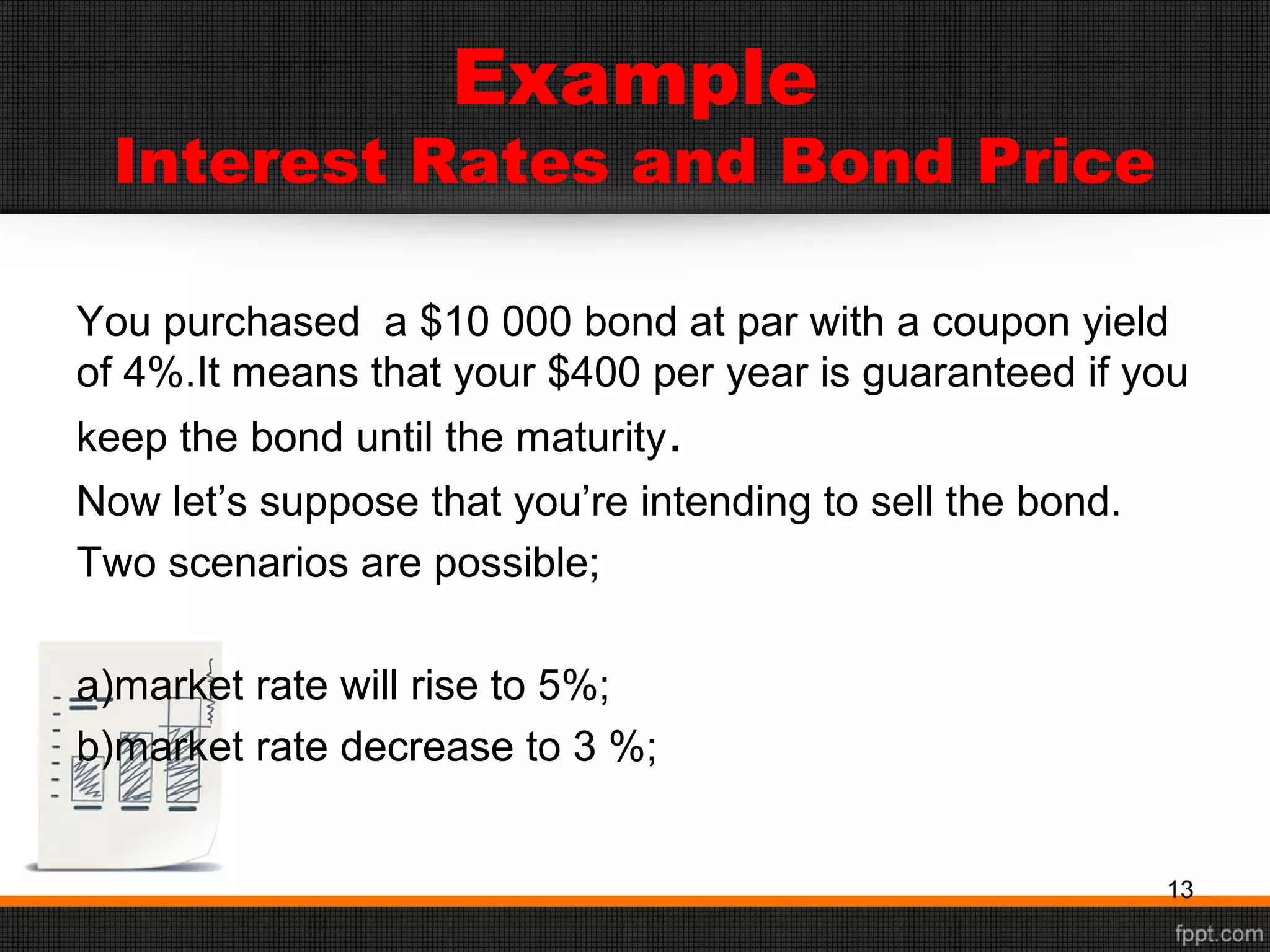
This document discusses sources of long-term financing for businesses. It focuses on debt financing through the issuance of bonds. It describes the basic features of bonds, including par value, coupon rate, maturity date, and current yield. It outlines the roles of trustees and indentures in bond issuances. It also discusses the risks associated with bonds, such as interest rate risk, reinvestment risk, default risk, inflation risk, and liquidity risk. Finally, it covers various types of bonds like zero-coupon bonds, floating-rate notes, junk bonds, convertible bonds, and Eurobonds.