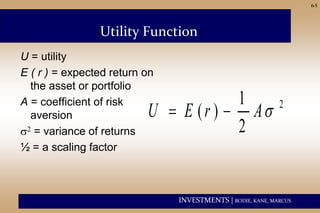
This document discusses risk aversion and how it impacts an investor's allocation of assets between risky and risk-free investments. It introduces the concept of a utility function which captures an investor's preferences over different expected returns and levels of risk. The utility function is used to determine the optimal allocation between a risky portfolio and risk-free asset that maximizes the investor's utility. The document provides examples and tables to illustrate how an investor's degree of risk aversion determines the optimal allocation between risky and risk-free assets. It also discusses how leverage can extend the capital allocation line, showing portfolios with allocations greater than 100% to the risky asset are possible through borrowing.