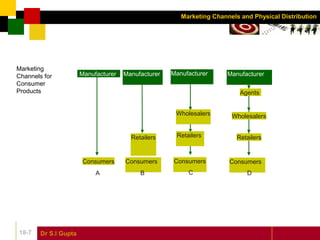
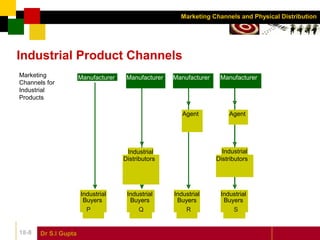
This document discusses marketing channels and physical distribution. It defines key terms like marketing channel and distribution. It describes the different types of channels as direct or indirect. It also outlines the functions of marketing channels and factors to consider when selecting and evaluating alternative channels.