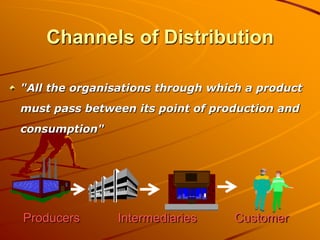
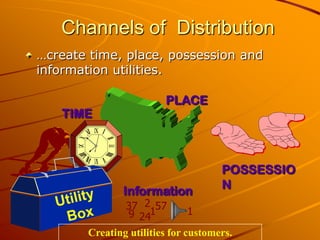
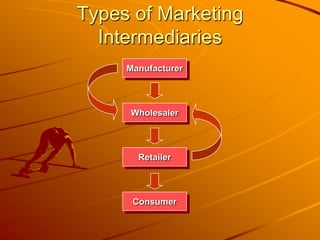
Channels of distribution refer to all organizations involved in moving a product from production to consumption. They create time, place, possession, and information utilities for customers. The key functions of distribution channels are to facilitate selling, provide distribution efficiency, and break bulk. Factors affecting the choice of distribution channel include effective market coverage, cost efficiency, minimizing customer exertion, and partnering with the firm on tasks like financing and sub-distribution. Common types of marketing intermediaries are manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers.