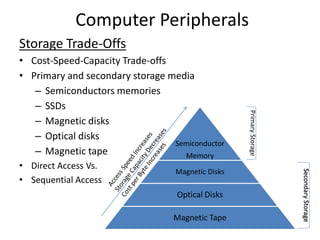
This document provides an overview of computer hardware and peripherals. It discusses the history of computing from early pioneers like Pascal and Babbage to modern developments like integrated circuits. It describes different types of computer systems from microcomputers to supercomputers. It also covers various input technologies like mice, touchscreens, and biometric scanners. Output technologies like printers and displays are examined. Finally, it discusses storage options and tradeoffs between technologies like semiconductor memory, magnetic disks, optical disks, and magnetic tape.