A computer is more than just another household appliance. The vast amount of information and possibilities can be overwhelming. But you can accomplish a lot with a computer, and using one can be a good experience. Let's walk through getting started with your first computer.












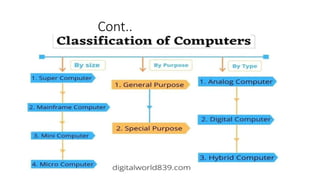
![Computer Classification
We can classify the computers into the following 3
categories:
• On the basis of Size and Capacity, [Super Computer, Mainframe,
Mini, and Micro Computer].
• On the basis of Purposes, [General and Special Purpose].
• On the Basis of Hardware Design and Type[Analog, Digital,
and Hybrid Computer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/connectinghardwareperipherals-250224115502-d529890e/85/Connecting-Hardware-Peripheralmskk-pptx-13-320.jpg)





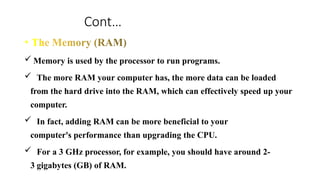
![Cont.….
• Tertiary storage (tertiary memory) provides a third level
of storage.
• Typically it involves a robotic mechanism which will
mount (insert) and dismount removable mass storage
media into a storage device according to the system's
demands; this data is often copied to secondary storage
before use. [Removable Disks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/connectinghardwareperipherals-250224115502-d529890e/85/Connecting-Hardware-Peripheralmskk-pptx-20-320.jpg)