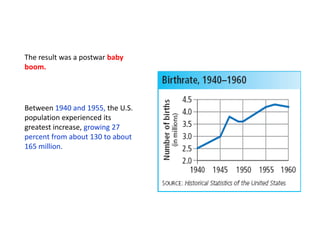
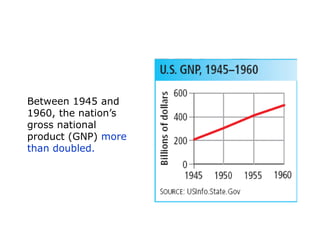
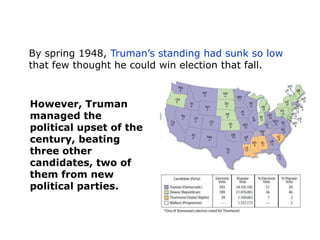
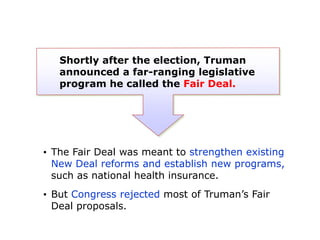
The post-WWII US economy experienced strong growth fueled by increased consumer demand, the GI Bill, and federal spending on defense and infrastructure. The GI Bill provided education and unemployment benefits for veterans, contributing to a boom in higher education and home construction. A postwar baby boom also increased the population. President Truman faced challenges like inflation, labor unrest, and civil rights issues. His Fair Deal proposals were mostly rejected. President Eisenhower continued economic growth through infrastructure spending while moderating political tensions. The 1950s saw rising prosperity across the US.