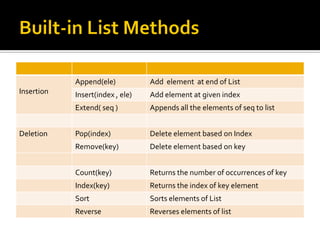
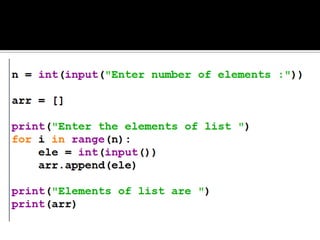
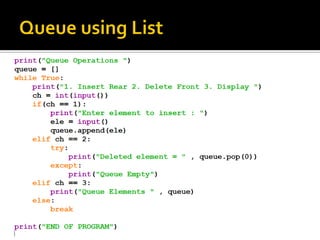
The document discusses lists in Python, including how to create, access, modify, loop through, slice, sort, and perform other operations on list elements. Lists can contain elements of different data types, are indexed starting at 0, and support methods like append(), insert(), pop(), and more to manipulate the list. Examples are provided to demonstrate common list operations and functions.


![ A list is a compound data type, you can group values
together
A list contains items separated by commas and enclosed
within square brackets ([]).
Lists are similar to arrays in C.
One difference between them is that the items belonging
to a list can be of different data type.
The values stored in a list can be accessed using the [ ]
operator
Index starts at 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-3-320.jpg)


![ What is the result of this code?
nums = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
print(nums[-2])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-6-320.jpg)
![>>> math = 45
>>> science = 23
>>> social = 28
>>> marksList = [math, science, social]
>>>
>>> print(marksList)
[45, 23, 28]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-7-320.jpg)






![ We can add elements to list.
To add one element, use append method.
This adds an item to the end of an existing list.
mylist = []
mylist.append(5)
mylist.append(8)
mylist.append(12)
#prints [5,8,12]
print(mylist)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-15-320.jpg)



![ a = [1,2,3]
b = [4,5,6]
Understand the difference between
a.append(b) and
a.extend(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-20-320.jpg)






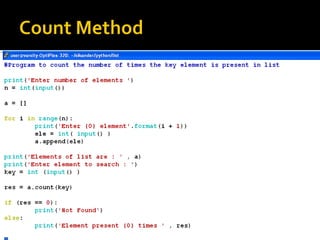


![ The index method finds the first occurrence of a list item and
returns its index.
If the item isn't in the list, it raises aValueError.
letters = ['p', 'q', 'r', 's', 'p', 'u']
print(letters.index('r'))
print(letters.index('p'))
print(letters.index('z'))
2
0
ValueError: 'z' is not in list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-31-320.jpg)


![ mylist = [5 , 8 , 12 , 20 , 25, 50]
mylist[startIndex : endIndex]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-38-320.jpg)

![ Mylist[startIndex : endIndex : step]
mylist = [5 , 8 , 12 , 20 , 25, 50]
print('Full list elements' , mylist)
print('printing alternate elements', mylist[ : : 2])
print('printing in reverse order ', mylist[ : : -1])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-40-320.jpg)

![ # area variables (in square meters)
hall = 11.25
kit = 18.0
liv = 20.0
bed = 10.75
bath = 9.50
# house information as list of lists
house = [["hallway", hall],
["kitchen", kit],
["living room", liv],
["bedroom",bed],
["bathroom",bath]]
# Print out house
print(house)
print(house[0])
print(house[1][0]) [['hallway', 11.25], ['kitchen', 18.0], ['living room', 20.0], ['bedroom', 10.75], ['bathroom', 9.5]]
['hallway', 11.25]
kitchen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-45-320.jpg)
![ BMI = weight/height2
height = [ 1.87, 1.87, 1.82, 1.91, 1.90, 1.85]
weight = [81.65, 97.52, 95.25, 92.98, 86.18, 88.45]
bmi = weight / (height ** 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-46-320.jpg)
![ BMI = weight/height2
height = [ 1.87, 1.87, 1.82, 1.91, 1.90, 1.85]
weight = [81.65, 97.52, 95.25, 92.98, 86.18, 88.45]
bmi = []
n = len(height)
for i in range(0,n):
bmi.append(weight[i] / (height[i] ** 2))
print (bmi)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-47-320.jpg)

![ Given a list of elements, create a new list which
has elements with one added to every element
of old list.
nums = [12, 8, 21, 3, 16]
new_nums = [13, 9, 22, 4, 17]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-49-320.jpg)




![ Conditionals on the iterable
[num ** 2 for num in range(10) if num % 2 == 0]
Conditionals on the output expression
[num ** 2 if num % 2 == 0 else 0 for num in
range(10)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlist-190211124701/85/Python-list-55-320.jpg)



