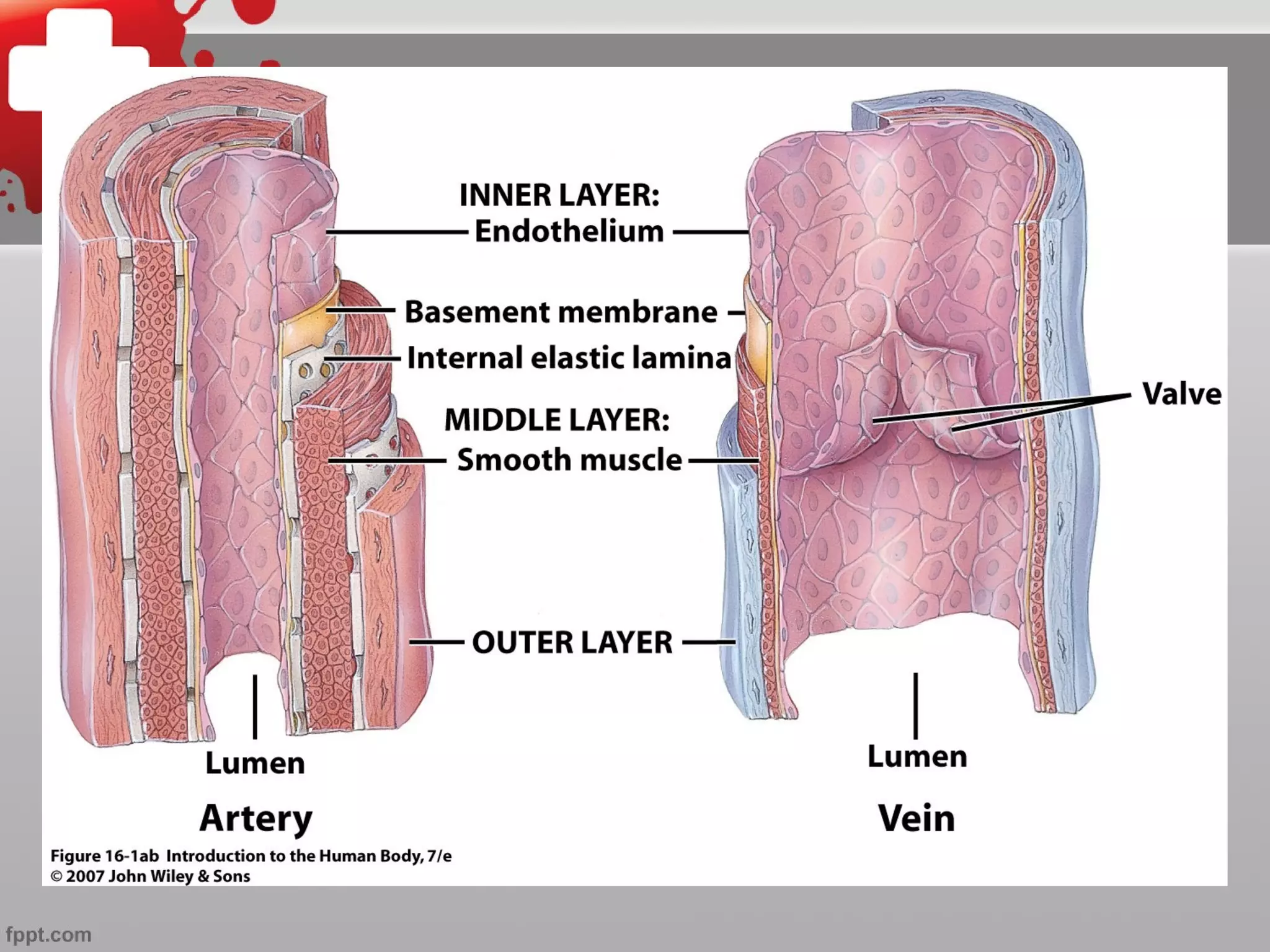
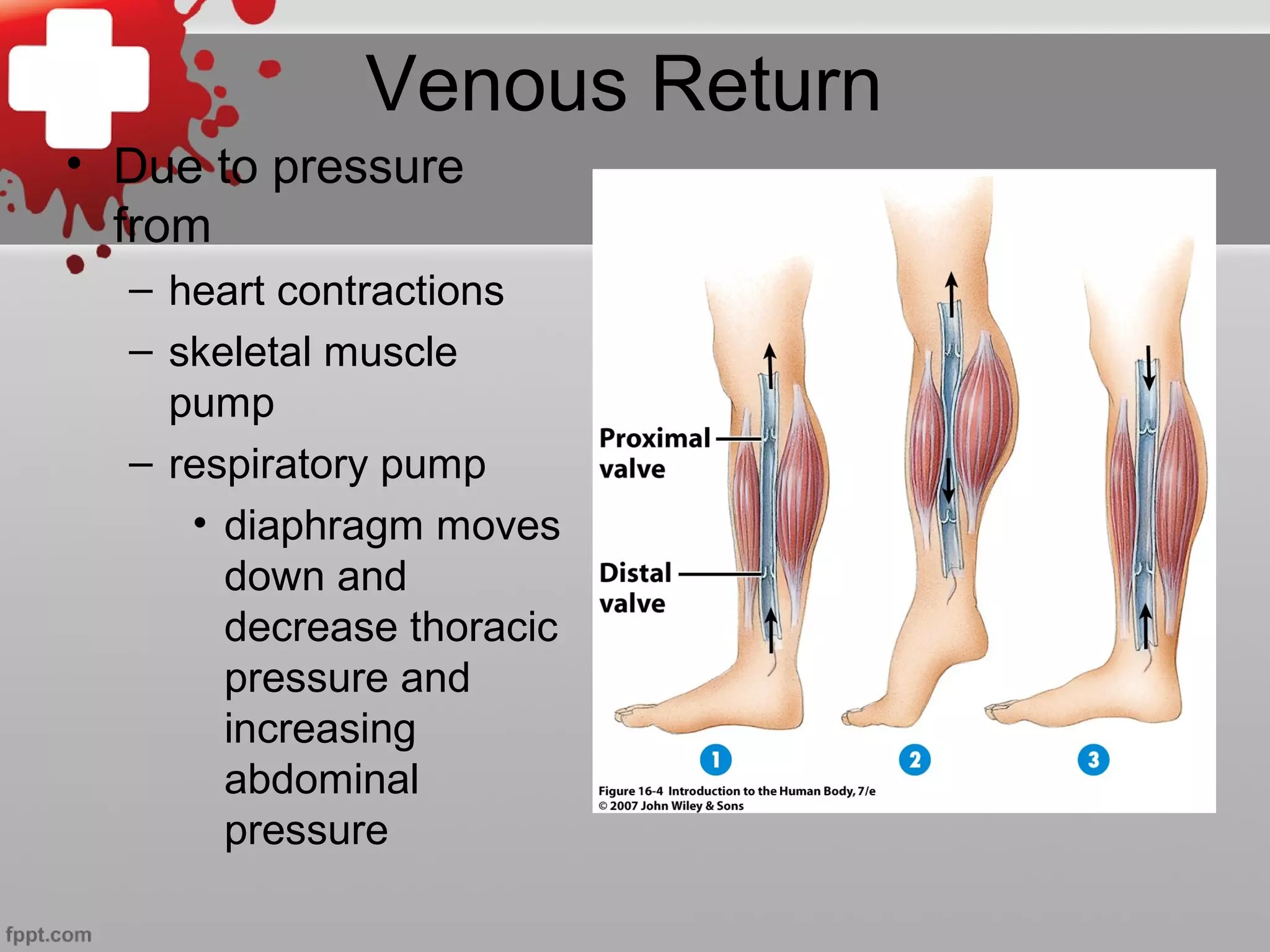
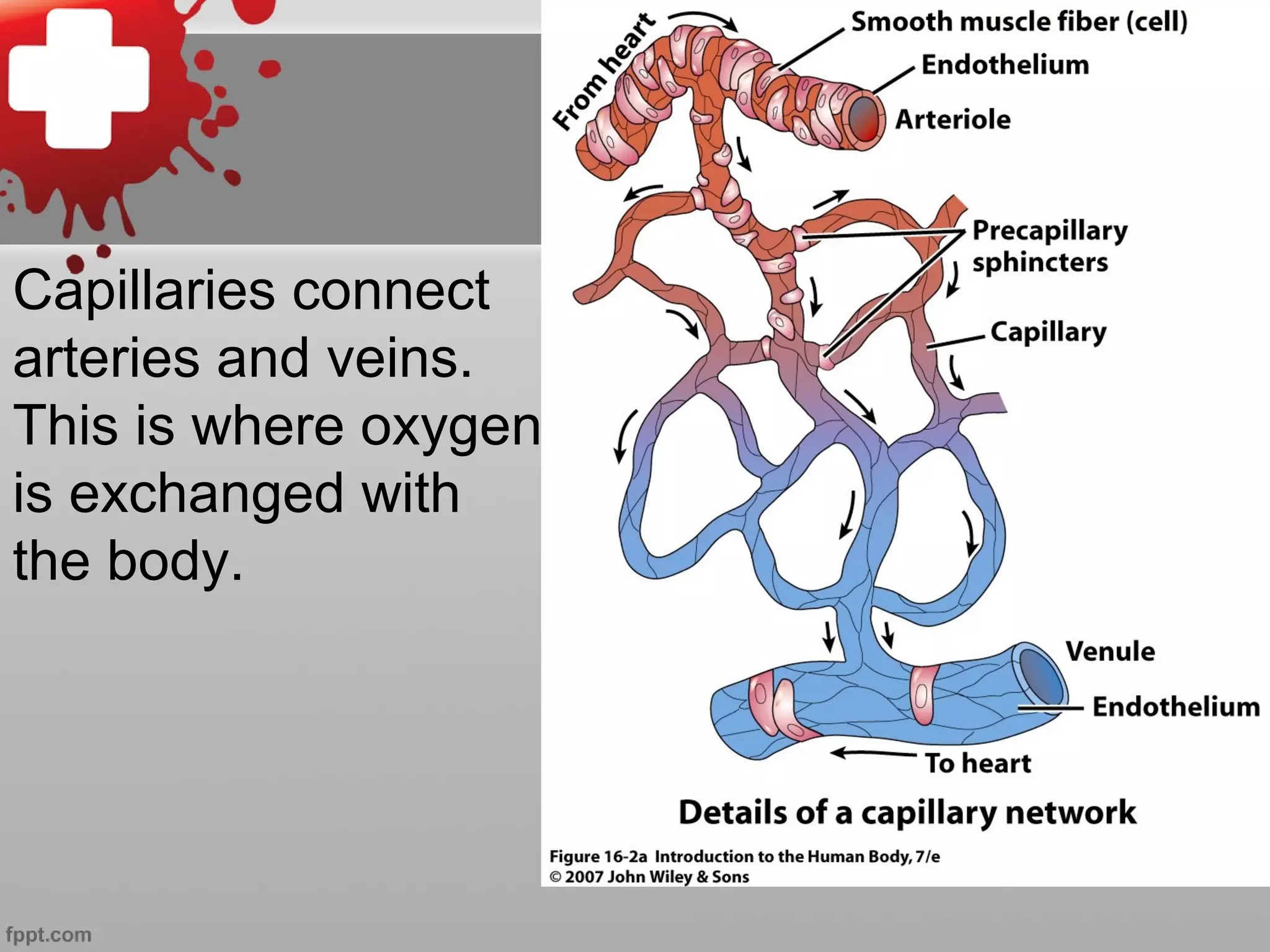
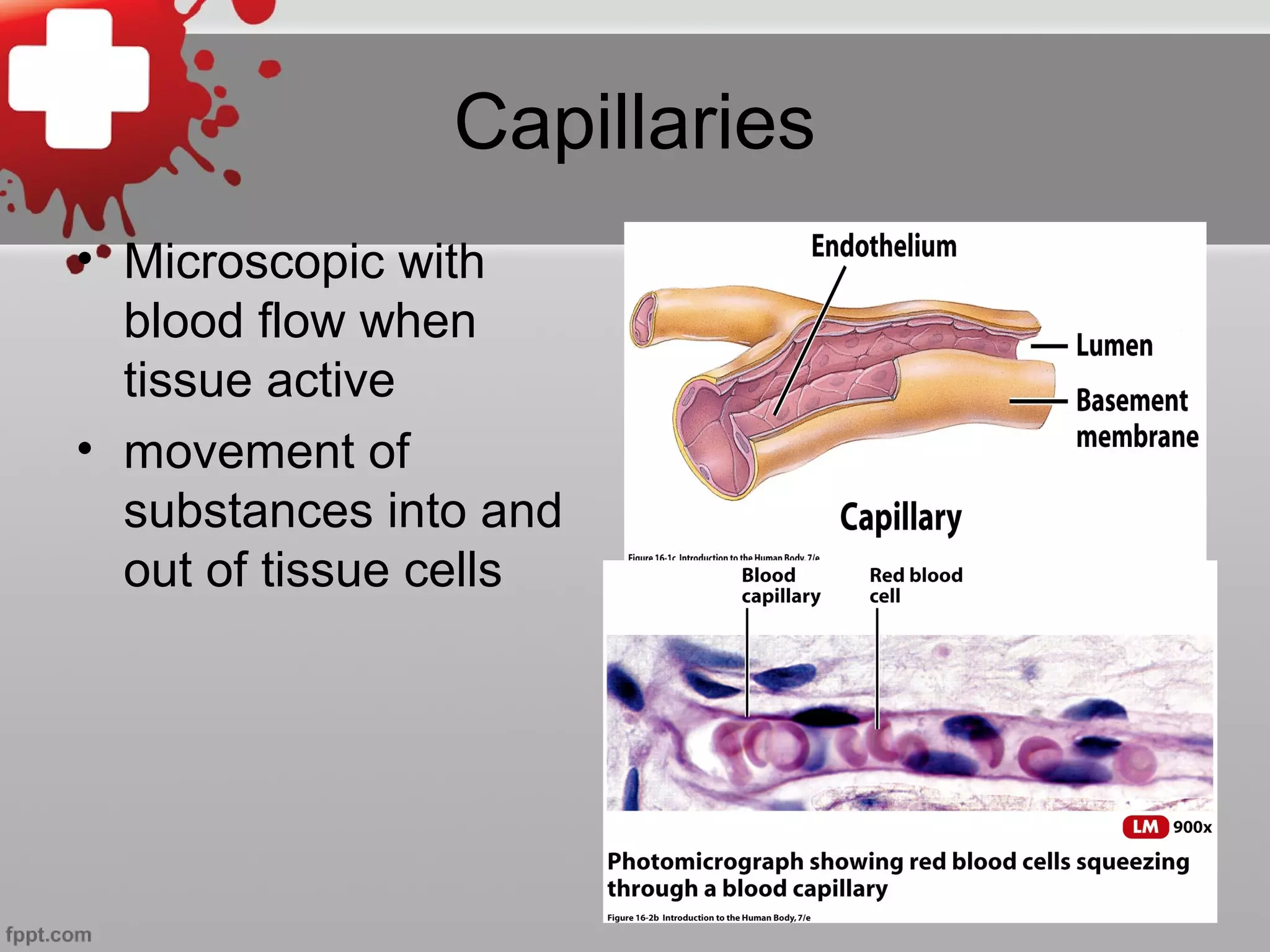
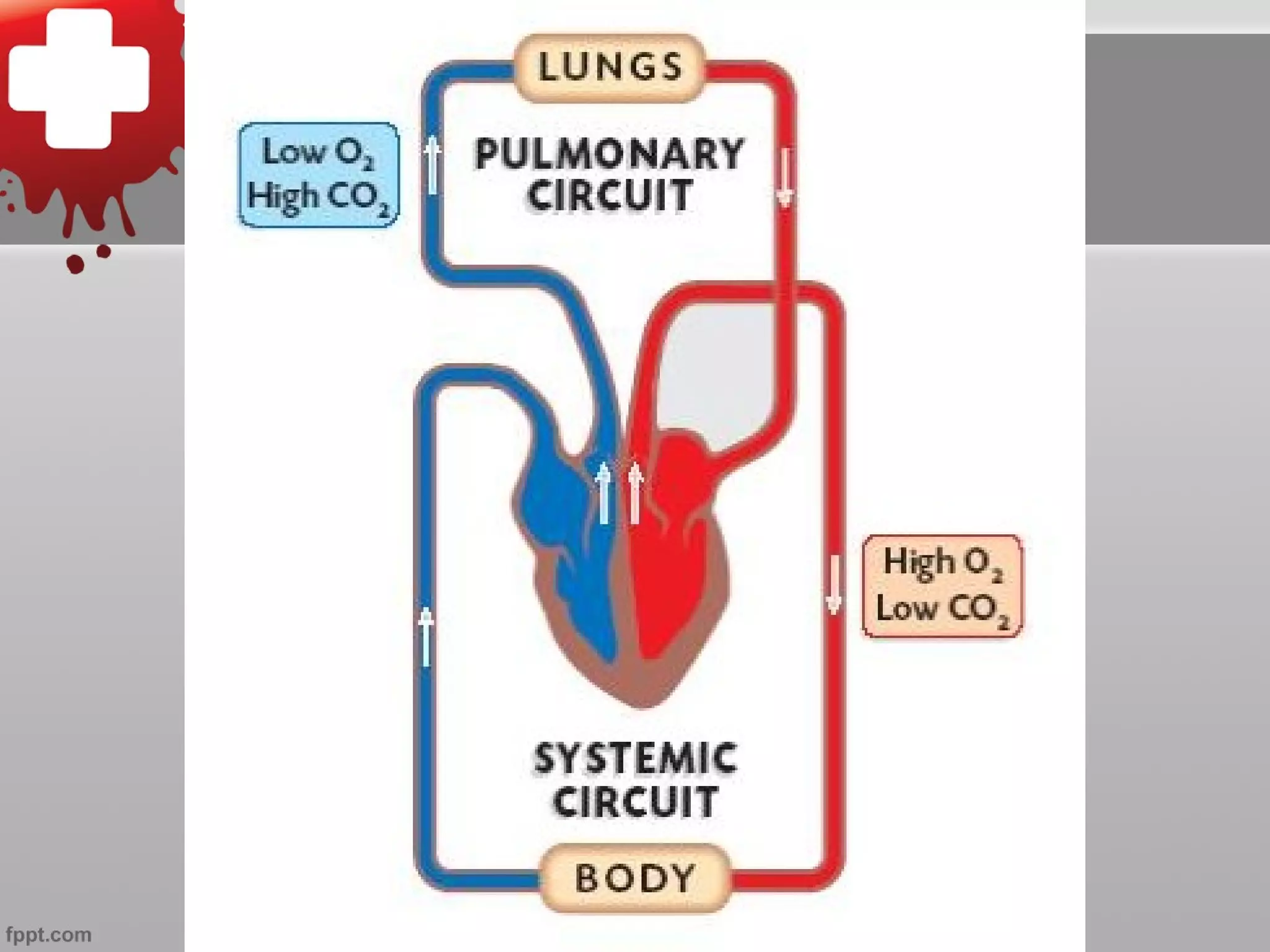
The document summarizes the cardiovascular system, including the five types of blood vessels - arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. It describes how blood flows from the heart through arteries and arterioles to capillaries, then through venules and veins back to the heart. It also discusses how certain veins function as blood reservoirs and how the circulatory system is regulated through nervous system control and blood pressure.