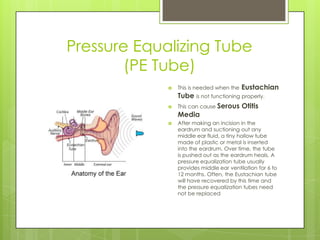
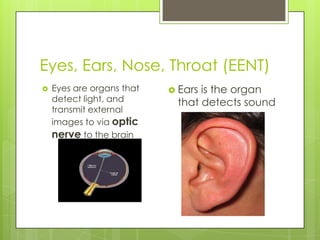
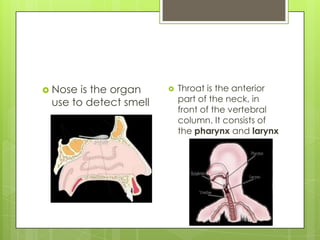
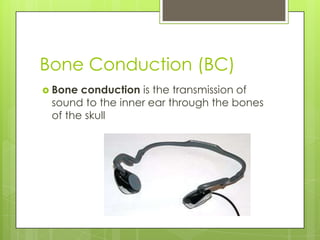
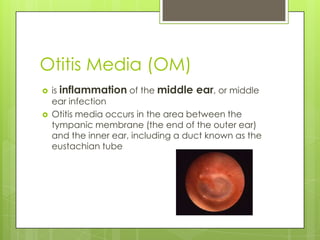
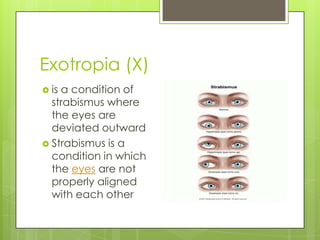
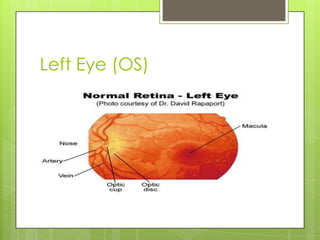
The document discusses various topics related to the eye and ear. It defines a pressure equalizing tube that can be inserted into the eardrum to help with middle ear ventilation when the Eustachian tube is not functioning properly. It also briefly describes the eyes, ears, nose and throat. Additional topics covered include bone conduction, otitis media, emmetropia, exotropia, extraocular movement, and visual acuity. References used include medical textbooks and websites.