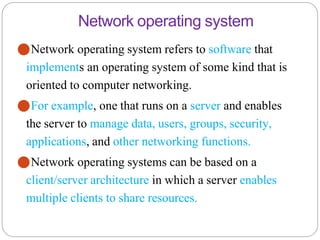
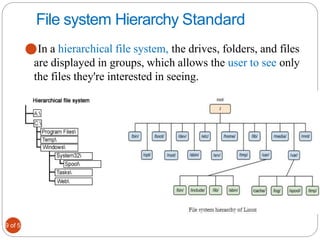
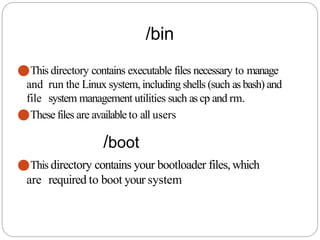
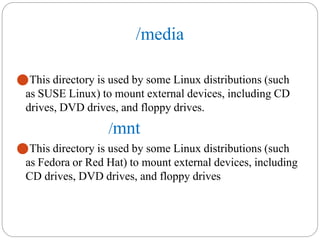
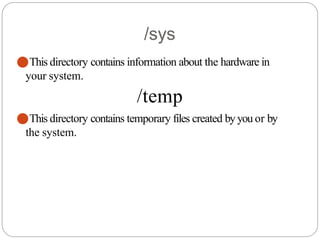
The document provides an overview of system and network administration, detailing the roles and responsibilities of network and system administrators, as well as the differences between various network operating systems, particularly Unix-like and Windows systems. It outlines key concepts such as network administration tasks, system performance monitoring, security policies, and the ethical standards required in the profession. Additionally, it discusses file systems including FAT, NTFS, and their applications in different operating environments.