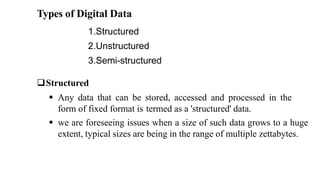
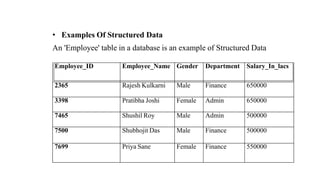
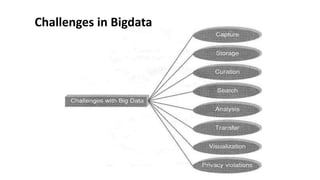
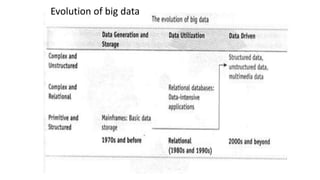
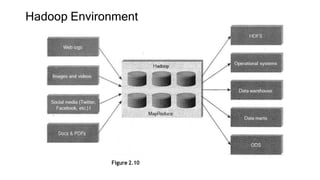
This document provides an overview of a course on fundamentals of big data. It outlines 5 course outcomes related to identifying big data characteristics, implementing Hadoop and MapReduce, analyzing structured and semi-structured data using Hive and Pig, using MongoDB for CRUD operations, and exploring visualization techniques. It also describes 2 course units, the first of which covers characteristics of big data like volume, velocity, and variety, as well as challenges. Traditional business intelligence is contrasted with big data approaches.