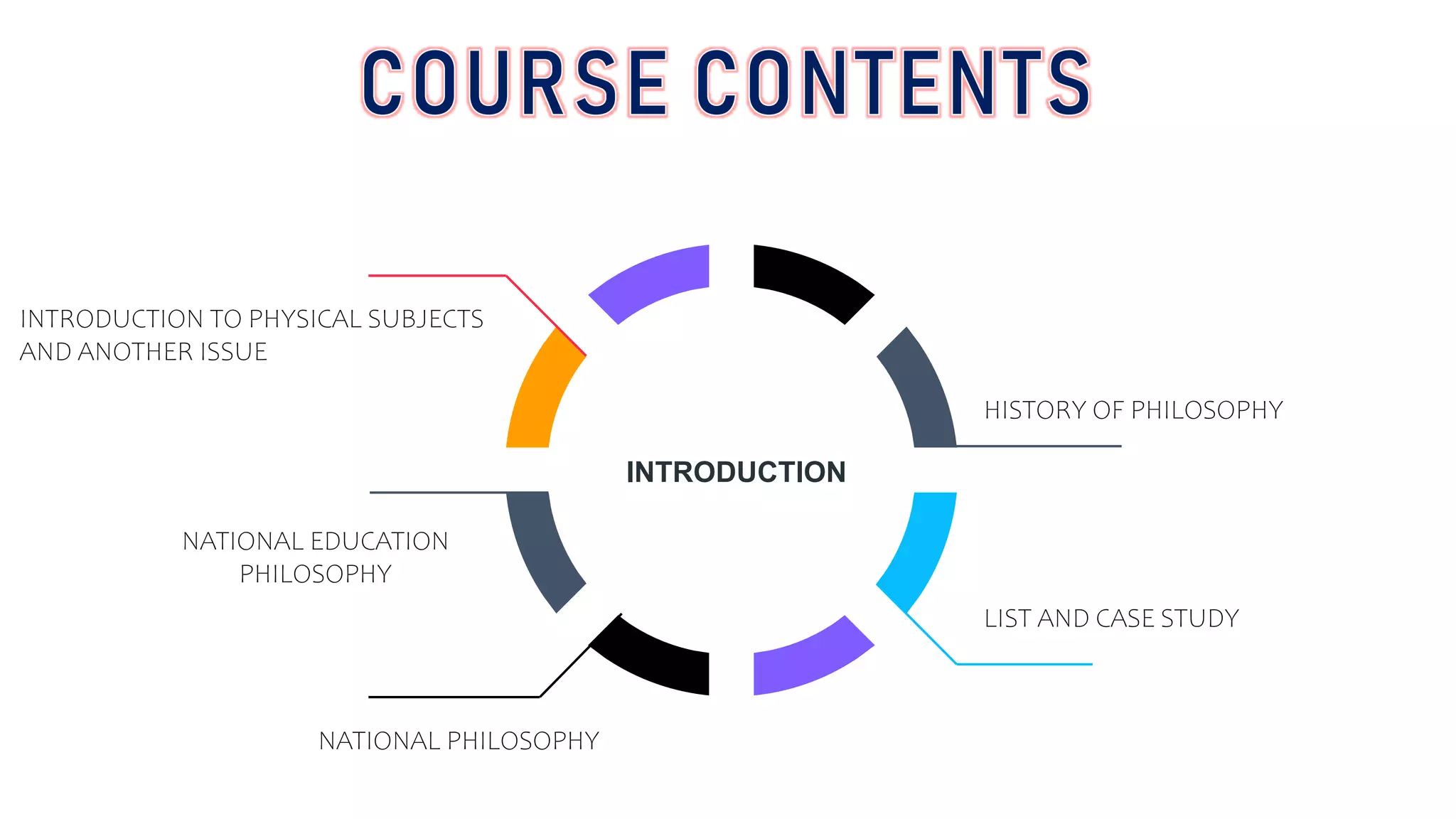
The document discusses Malaysia's National Philosophy of Education and the country's pillars. It explains that the philosophy aims to produce balanced, knowledgeable, skilled, virtuous and responsible citizens through education based on faith in God. It also outlines the history of developing social harmony in Malaysia, from the colonial era of racial segregation to the 1969 riots and subsequent establishment of policies and principles to foster unity. The country's five pillars of belief in God, loyalty to king and country, supremacy of the constitution, rule of law, and courtesy and morality are introduced as guiding principles for unity.



















![Wisdom1 - National Education philosophy
Education in Malaysia is an ongoing (lifelong) effort
towards furthering the holistic potential of
individuals (holistic) and integrated ...
1>
Quality
The whole is greater than the sums
of its part = “complete person.”
DEMAND FOR SCIENCE
(eg. Martial arts)
[ ]
Appreciate
This term of wisdom has been used by
Tan Sri Prof. Dr. Dzulkifli Abdul Razak in
his dissemination of the National
Philosophy of Education on December
10, 2019 in Putrajaya.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter01-introduction1-230323044955-a2014bc3/75/Chapter-01-Introduction-1-pptx-22-2048.jpg)





























