This document provides an overview of philosophy and discusses key concepts such as:
- Philosophy is the study of fundamental problems regarding existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language.
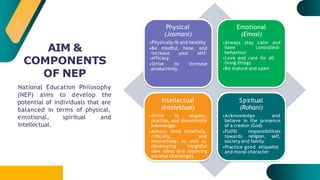
- The National Education Philosophy of Malaysia aims to develop students holistically in their physical, emotional, intellectual, and spiritual dimensions.
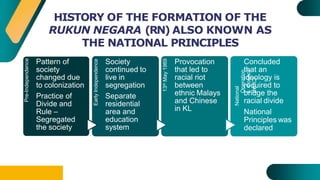
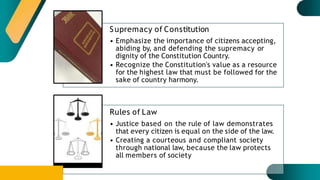
- The Rukun Negara, or National Principles of Malaysia, were established in 1970 following racial riots to foster unity. The five principles are belief in God, loyalty to king and country, supremacy of the constitution, rule of law, and courtesy and morality.