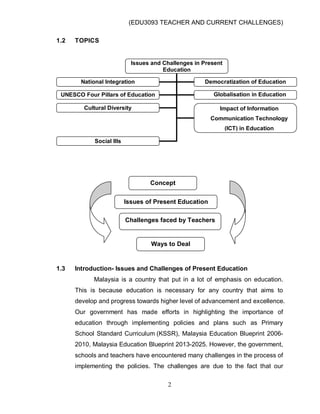
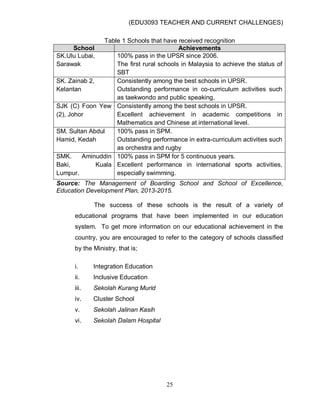
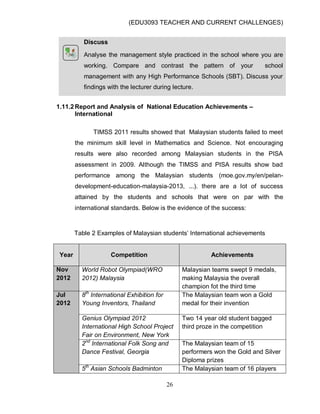
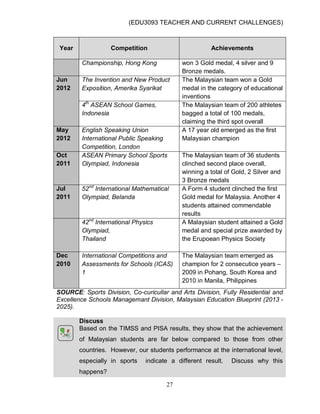
This document discusses issues and challenges in current education in Malaysia. It addresses topics like national integration, democratization of education, UNESCO's four pillars of education, globalization in education, cultural diversity, the influence of ICT, and social ills. Teachers face challenges in dealing with these issues, such as ensuring equal access to education for all students regardless of their backgrounds. The document outlines government policies and programs aimed at promoting national unity and an equitable education system. It also discusses the roles and responsibilities of teachers in implementing these goals.



























![(EDU3093 TEACHER AND CURRENT CHALLENGES)
32
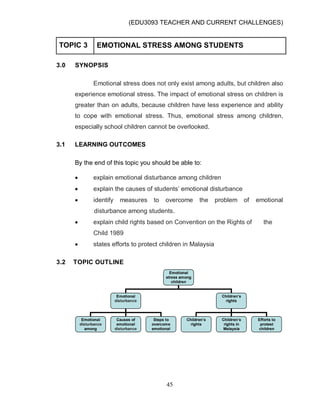
RULE 4 (2)
An officer is not allowed to:
prioritize personal interest to public duty
behave in such a manner that may cause personal interests
conflicting with public duties
behave in any manner that is likely to cause reasonable suspicion
behave in a way that can worsen / discredit the public service
be inefficient or having lack of effort
be dishonest
be irresponsible
take or attempt to take any form of outside influence or pressure
disobey or against the superiors
negligent in performing its duties
RULE 7: Drug abuse, officer can be terminated for public interest
[Rule 49]
If the officer has reached Retirement Age Options. Example; the violation
of Rule 7 is taking marijuana, morphine, heroin or drugs.
RULE 9 : Providing and receiving gifts
A civil servant can not receive / provide any forms of gifts that can be in
any way affect the official duties as it is conflicting with Rule 4. Examples
of violation of Rule 9 is like a contractor celebrating the head of
department that has become the member of the tender board
[entertainment = meals, hotels, airfares and others].
RULE 11 : Maintain living standards over emoluments / valid income
An officer is not allowed to:
maintain living standards over emoluments / valid income
acquire / own any financial resources or property disproportionate
or unreasonable to emoluments / legitimate income](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moduledu3093versibi-160829162500/85/Modul-edu3093-versi-bi-32-320.jpg)





















![(EDU3093 TEACHER AND CURRENT CHALLENGES)
55
There are no guardians willing to take care of the abandoned
children ; no other person qualified to take care of.
Neglect performed on children in need of inspection, investigation or
treatment.
Children‟s behavior that could hurt himself or someone else or
no one is willing to take care or improve the situation.
There is conflict between children and guardian or between
guardians. The dispute resulted in the affected family relationships
and caused emotional disorders in children.
Children who are involved with any of the offenses in Chapter XVI
of the Penal Code.
3.6.2 The Park Childcare 1984 [Act 308]
The Act is related to the registration, regulation and inspection of
child care or nursery
The Act provides protection to children under the age of 4 years.
This Act is to assure health, safety and education of children under
4 years.
Control, supervision and inspection can be carried out by
enforcement gardens registration for childcare
Related parties have the authority to enter and examine the
childcare parks for the health, safety and education of
children.
3.6.3 Adoption Act 1952 (Act 257)
To protect children from being abused, neglected and exploited.
The Act is designed to regulate the procedures of adoption and
ensure the welfare of children.
Legal provisions of this act is as enacted in Ordinance to adopt
a child in 1960.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moduledu3093versibi-160829162500/85/Modul-edu3093-versi-bi-55-320.jpg)