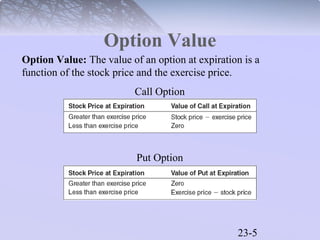
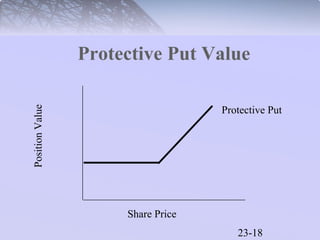
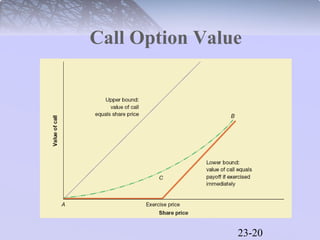
This document discusses various types of options and their payoff structures. It explores call options, which give the right to buy an asset, and put options, which give the right to sell an asset. It provides examples of how option values are calculated based on the underlying asset price and exercise price. The key concepts covered include the payoff limits and profits for option buyers and sellers. Hedging strategies using options are also briefly discussed.


















![Black-Scholes Option
23-22
Pricing Model
OptionC = Ps[N(d1)] - S[N(d2)]e-rt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap023-140918123057-phpapp02/85/Chap023-22-320.jpg)

