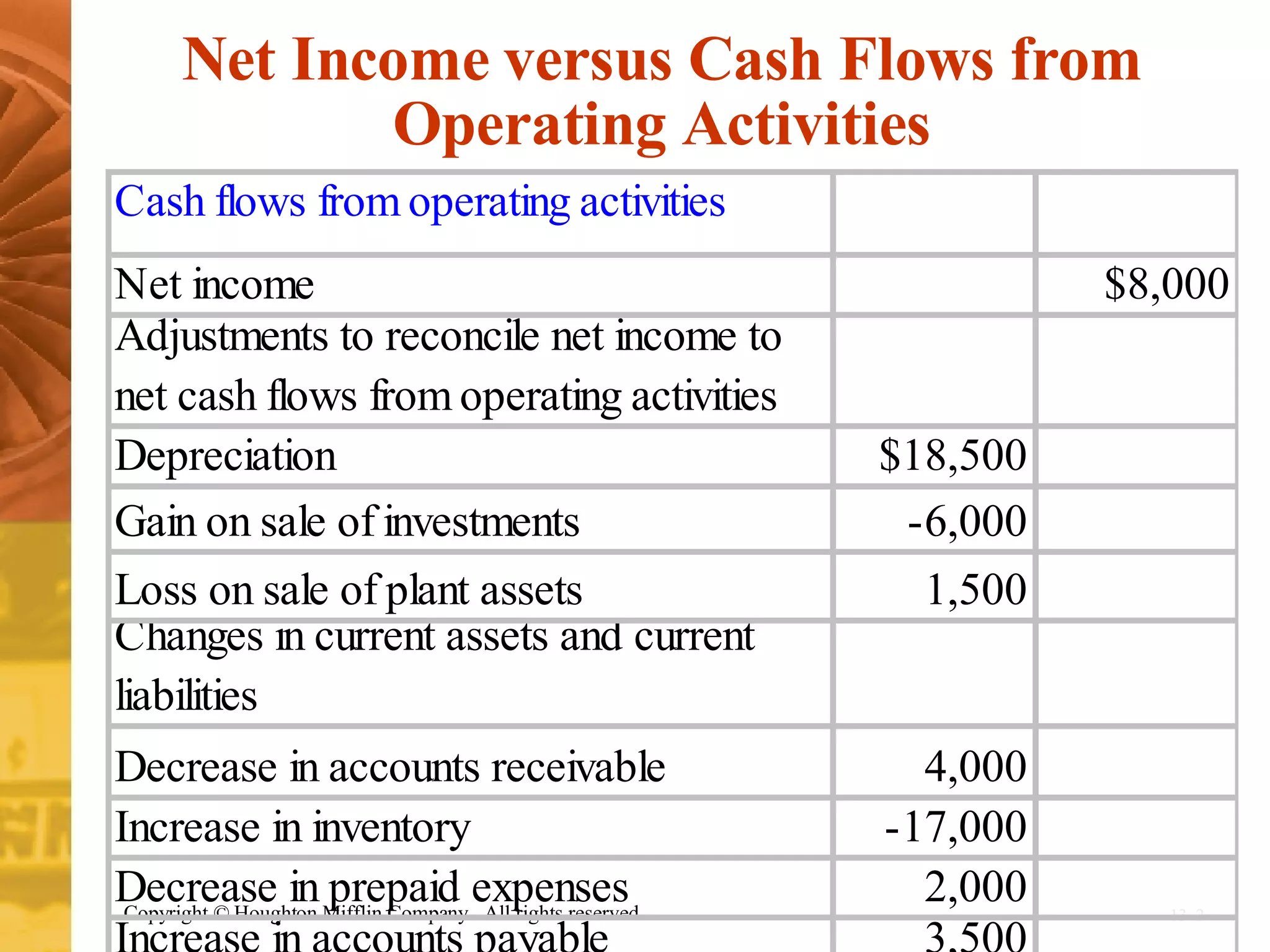
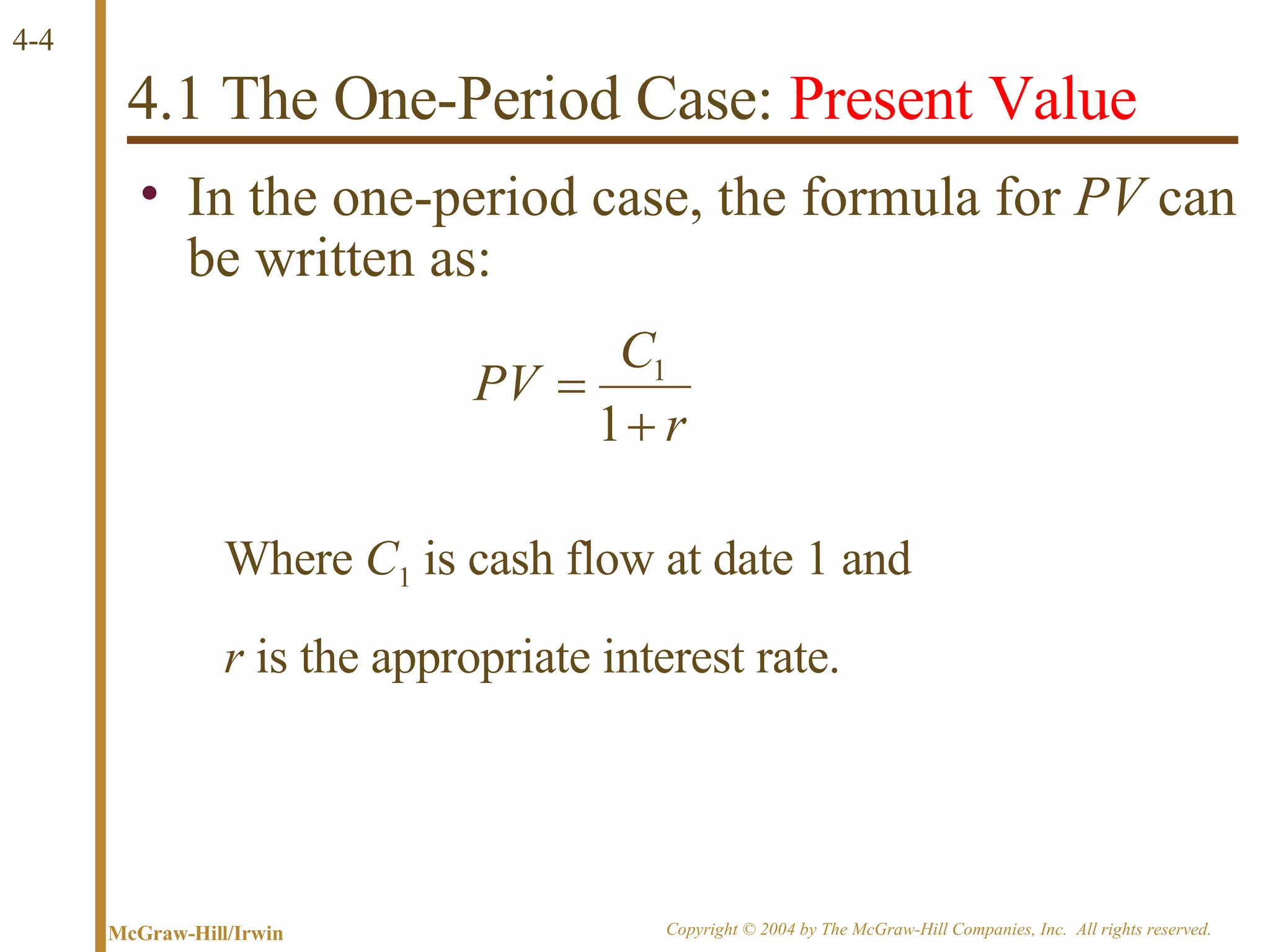
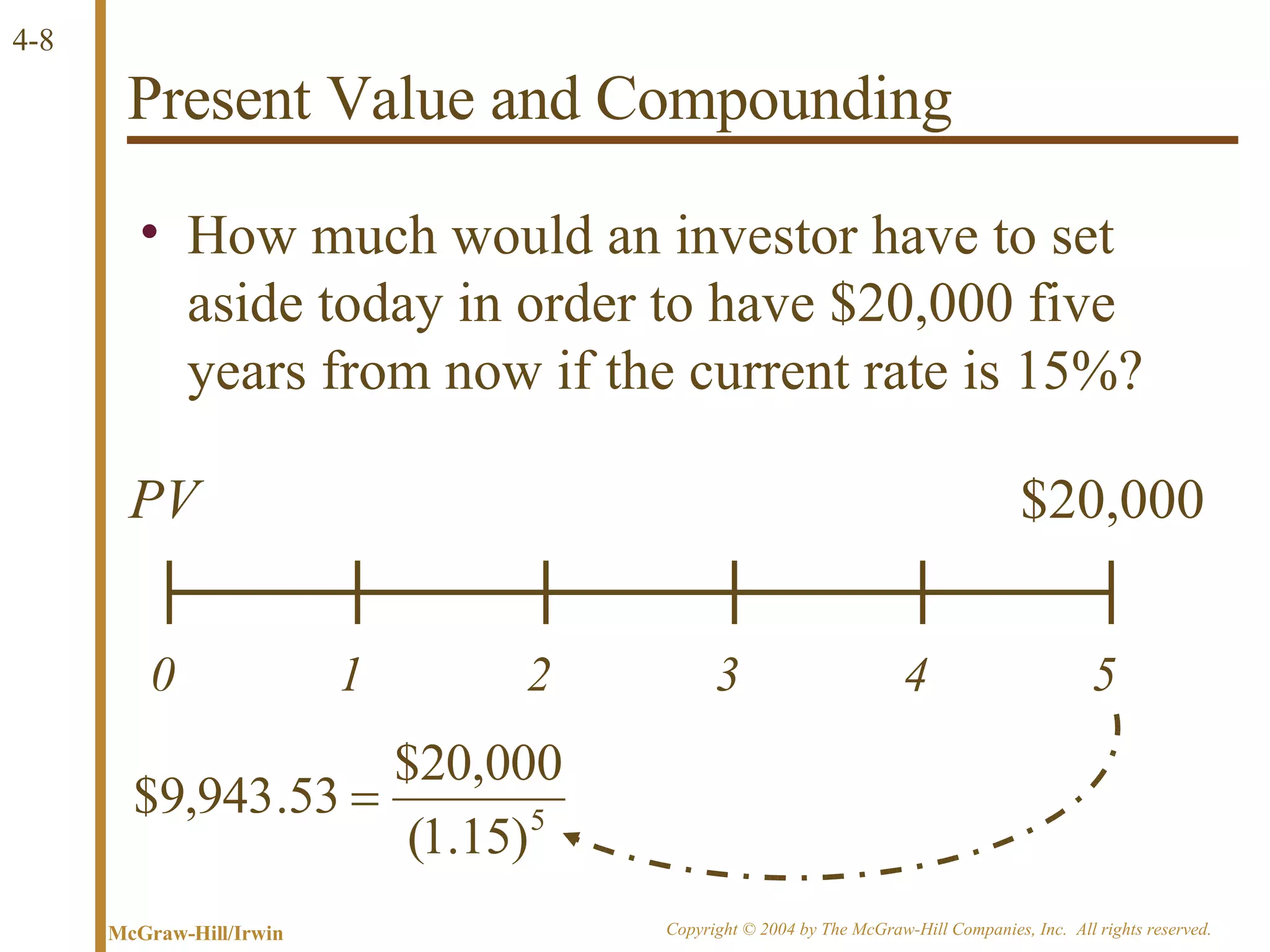
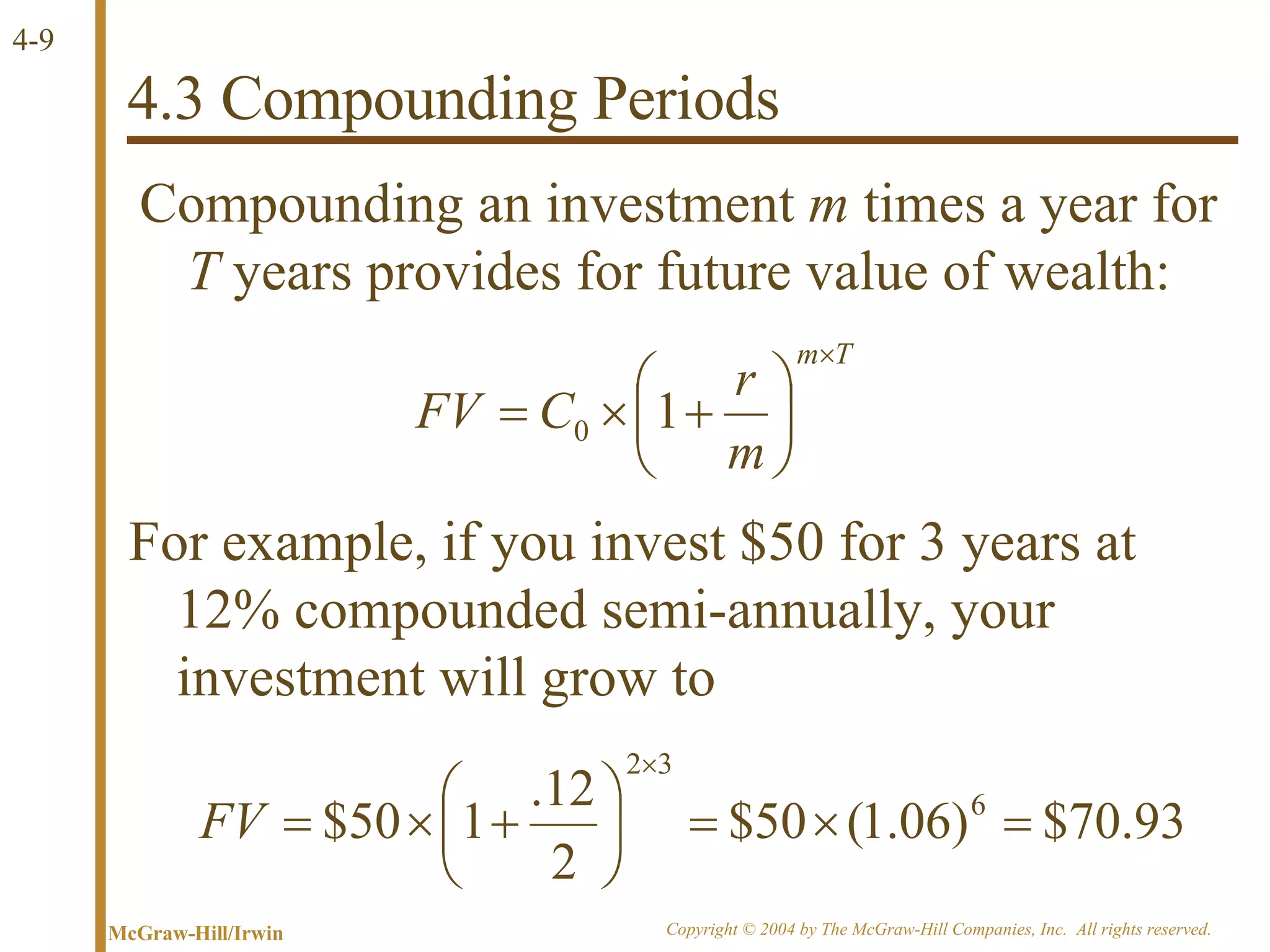
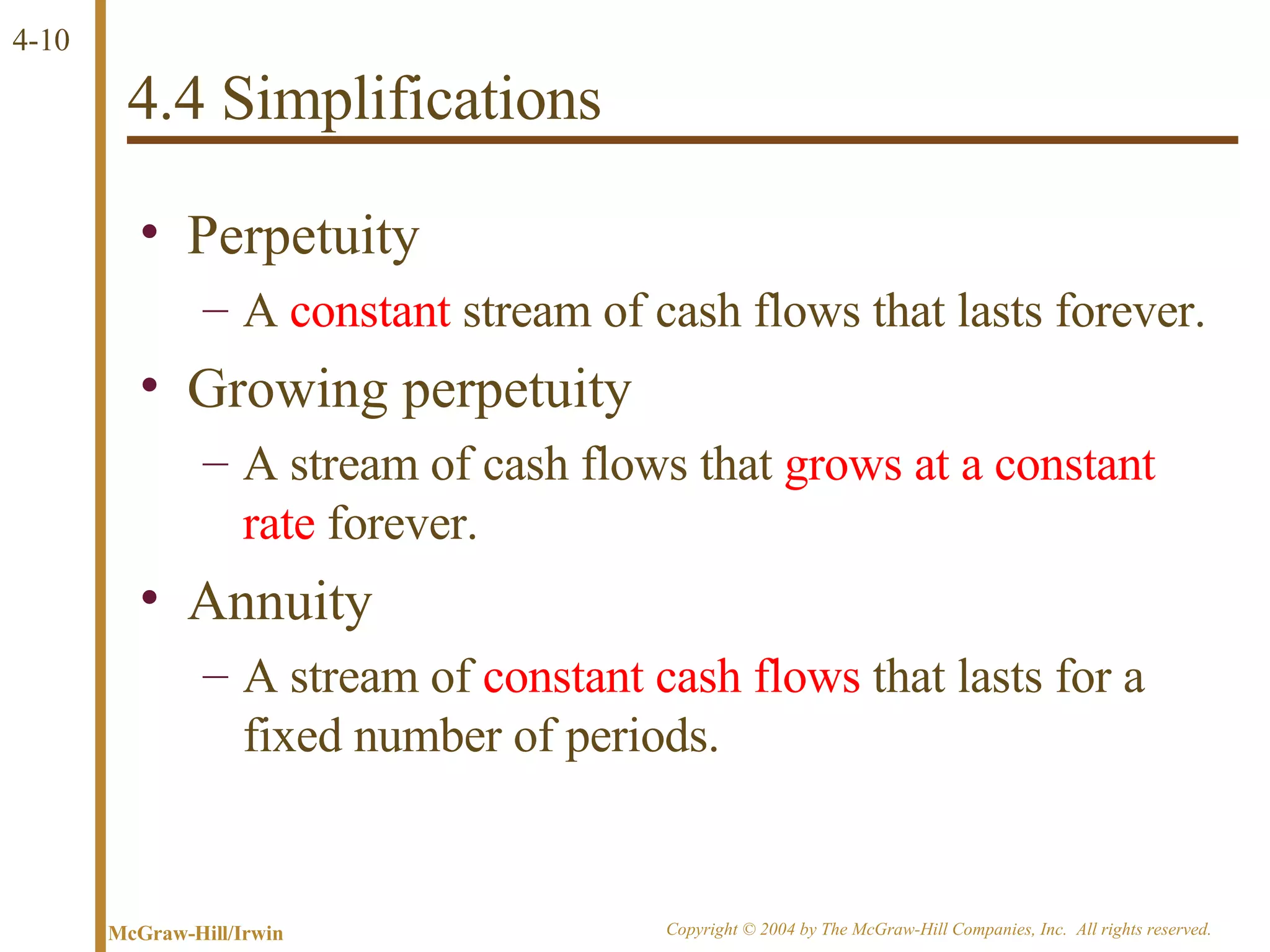
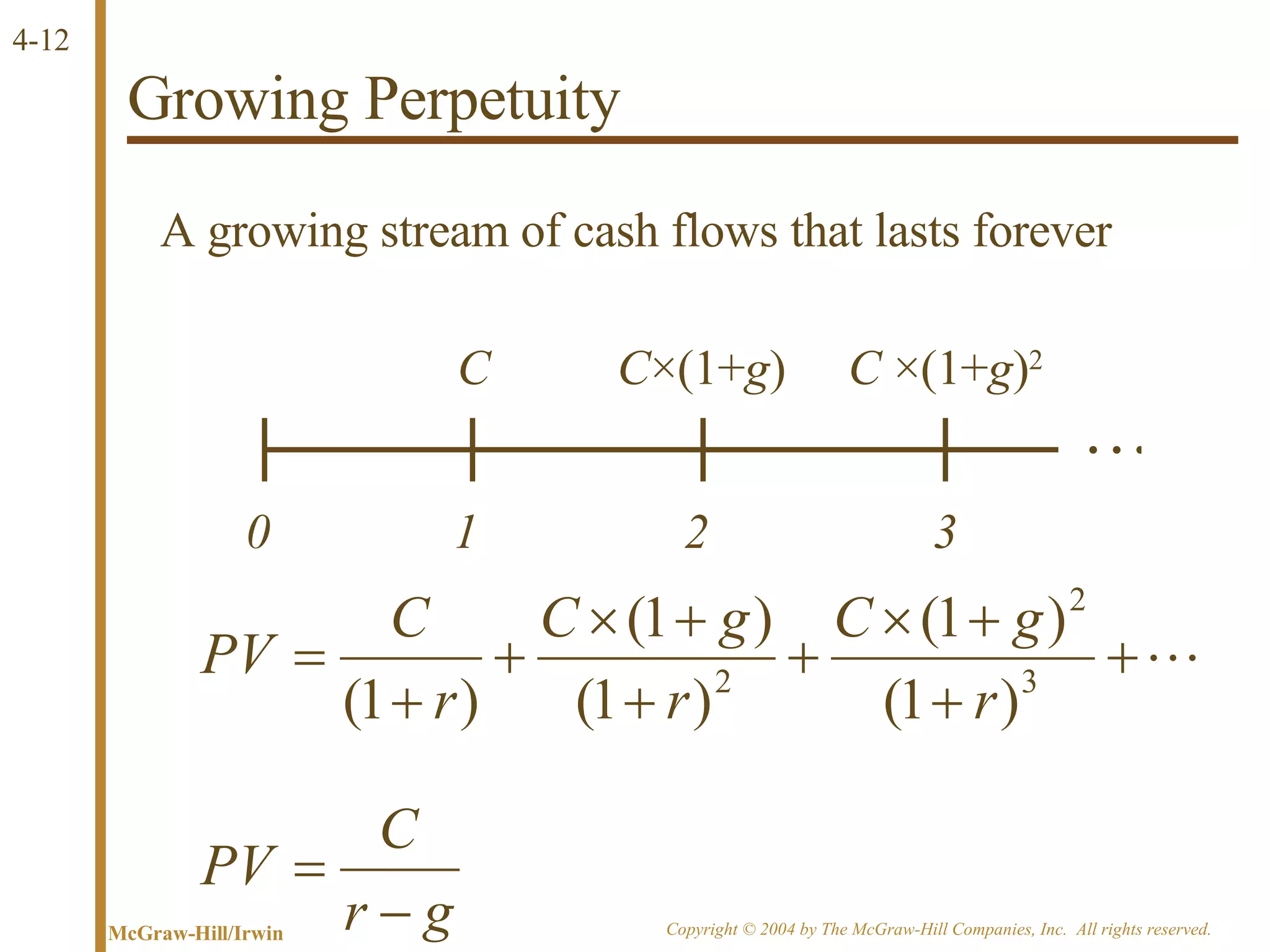
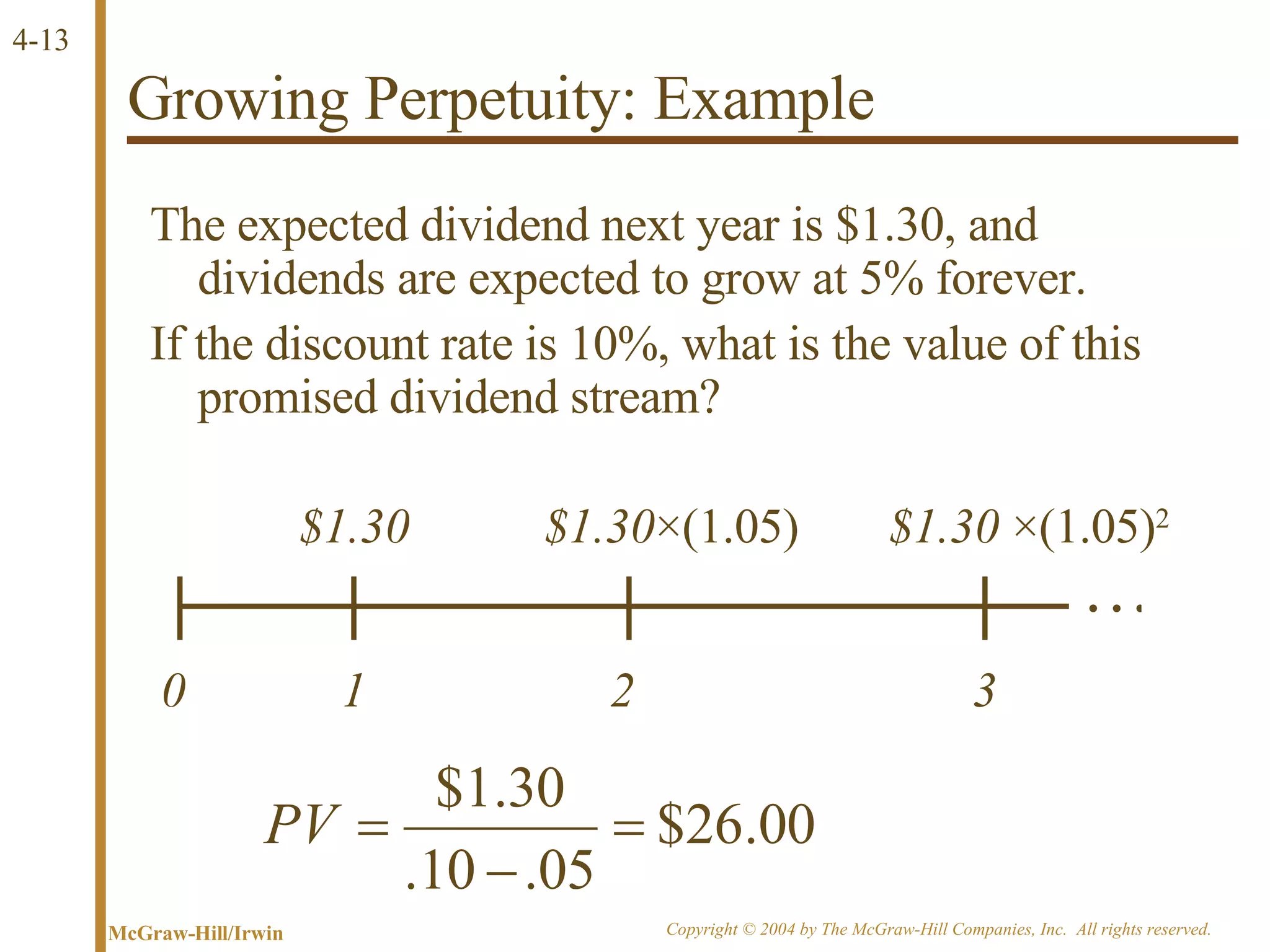
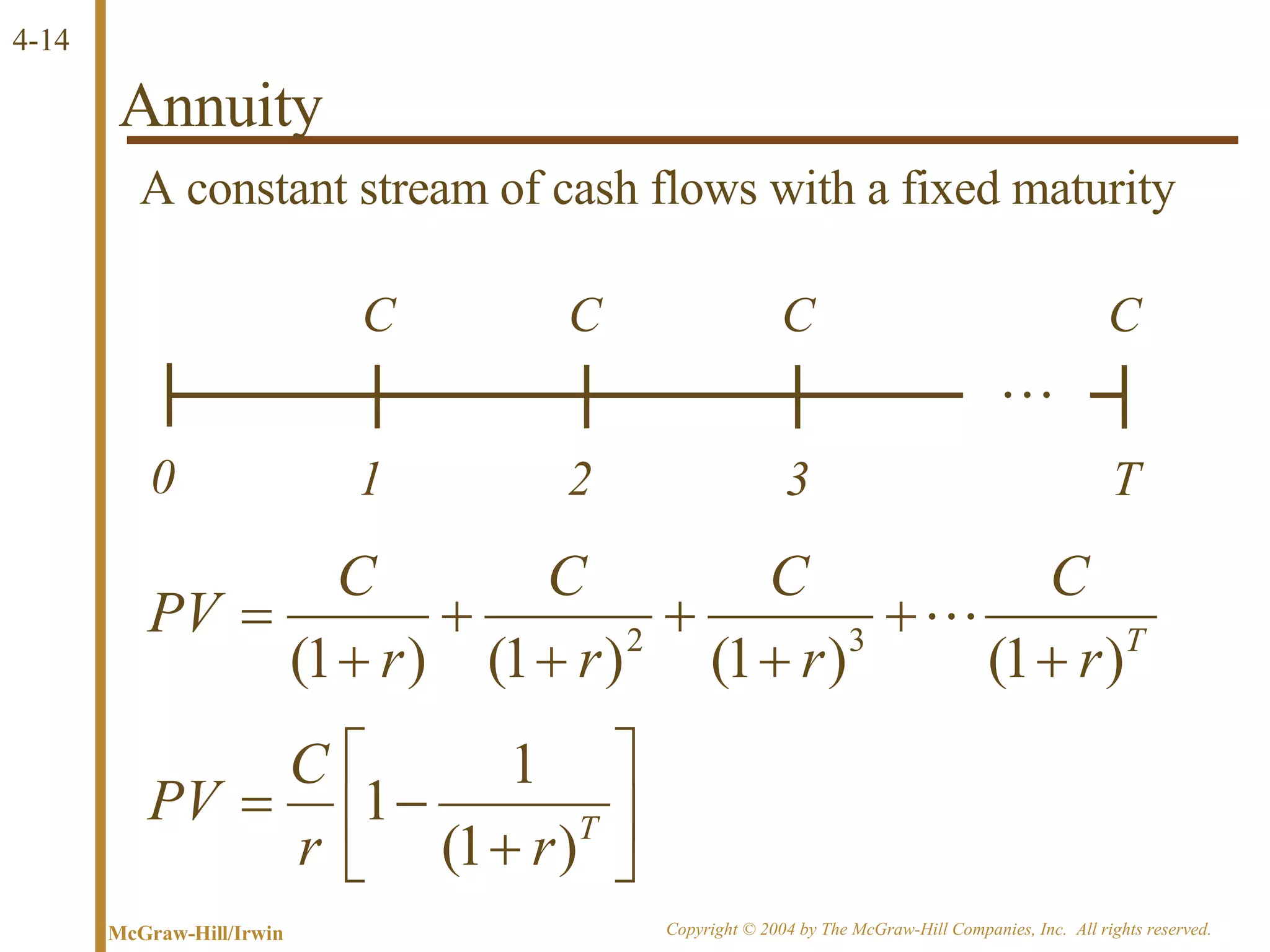
The document discusses discounted cash flow valuation and various cash flow concepts. It defines net present value as the present value of expected cash flows less the cost of investment. It provides the formulas for future value and present value in single-period and multi-period cases. It also discusses compounding periods, perpetuities, growing perpetuities, and annuities.