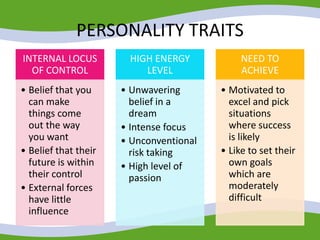
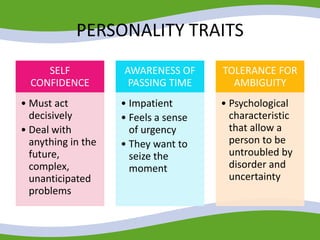
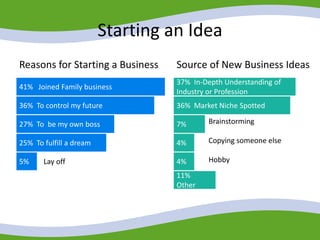
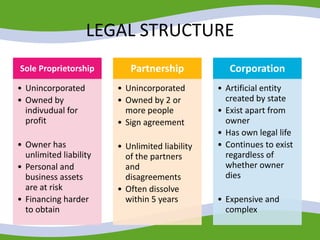
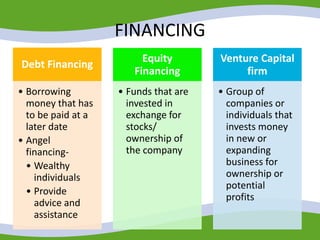
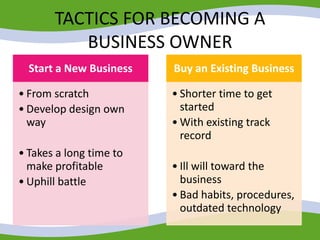
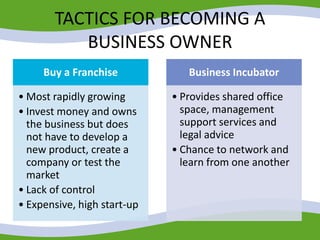
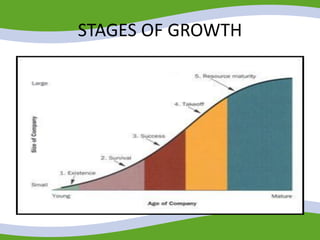
This document discusses managing small business start-ups. It outlines the stages of entrepreneurial start-ups from developing an idea to managing growth. It defines entrepreneurship and small businesses. It also discusses writing business plans, choosing legal structures, obtaining financing, and considering options like franchising or business incubators. The document also outlines the stages of business growth from start-up to maturity and managing aspects like planning, organizing, leading and controlling as a business expands.