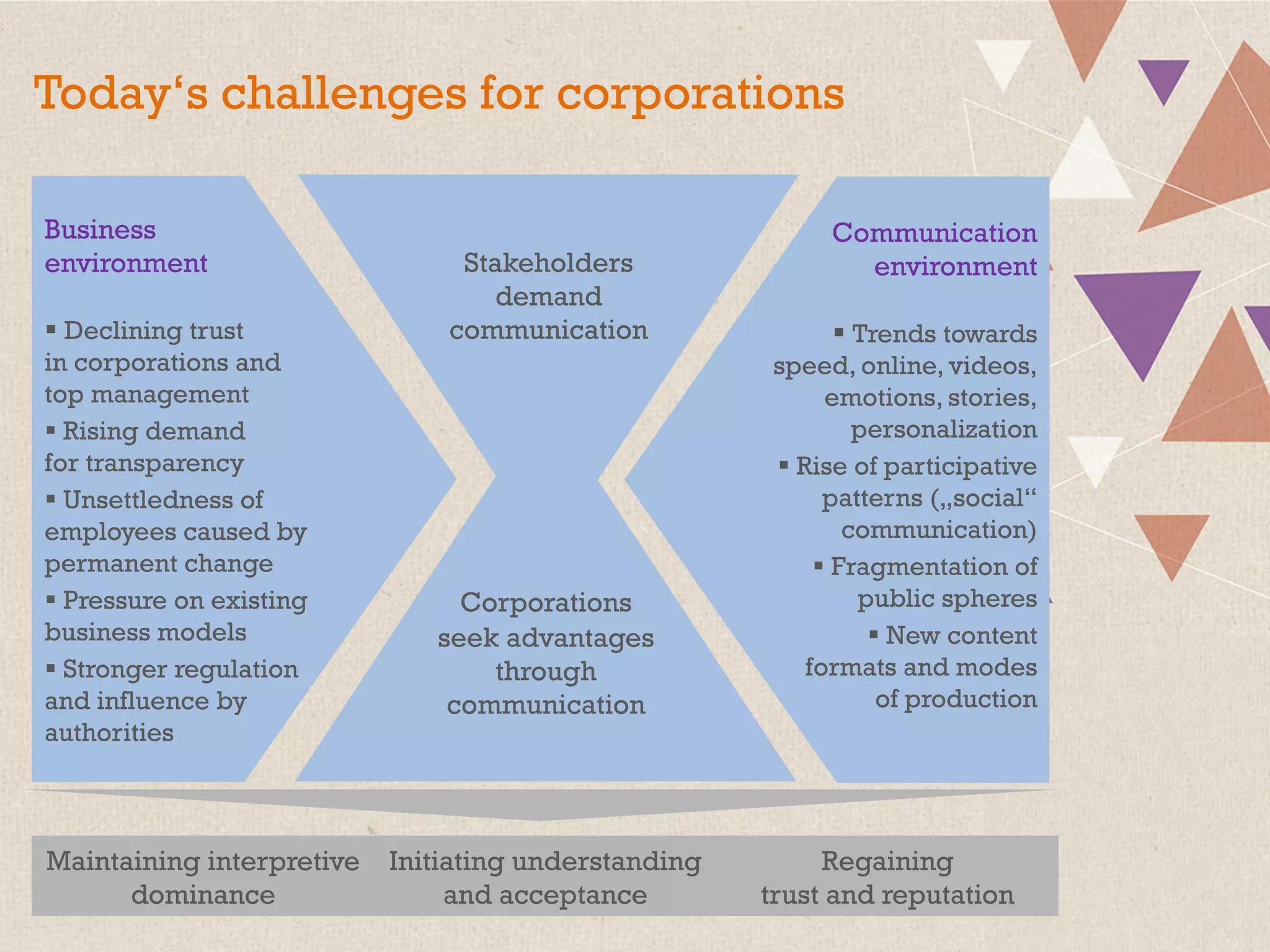
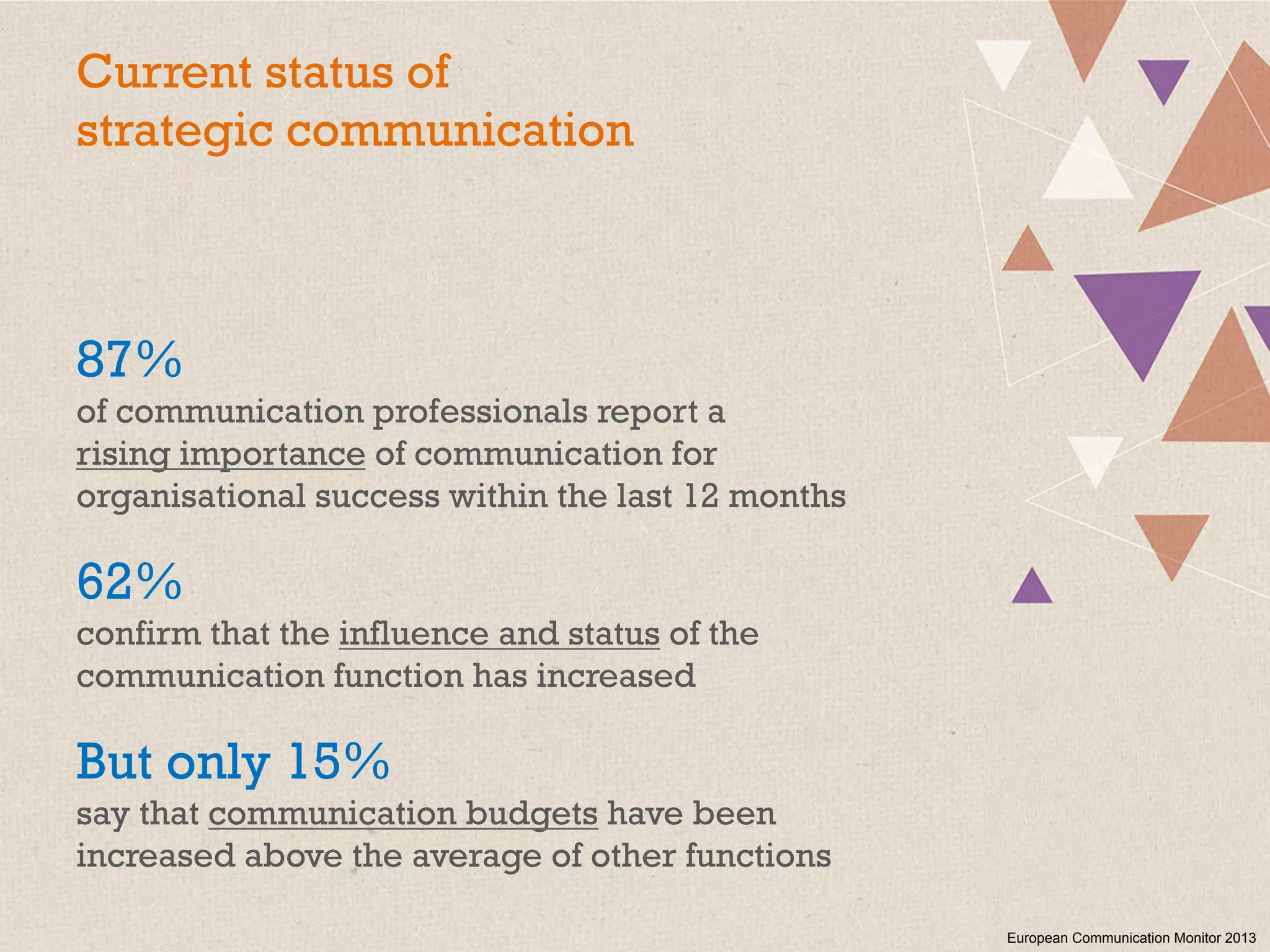
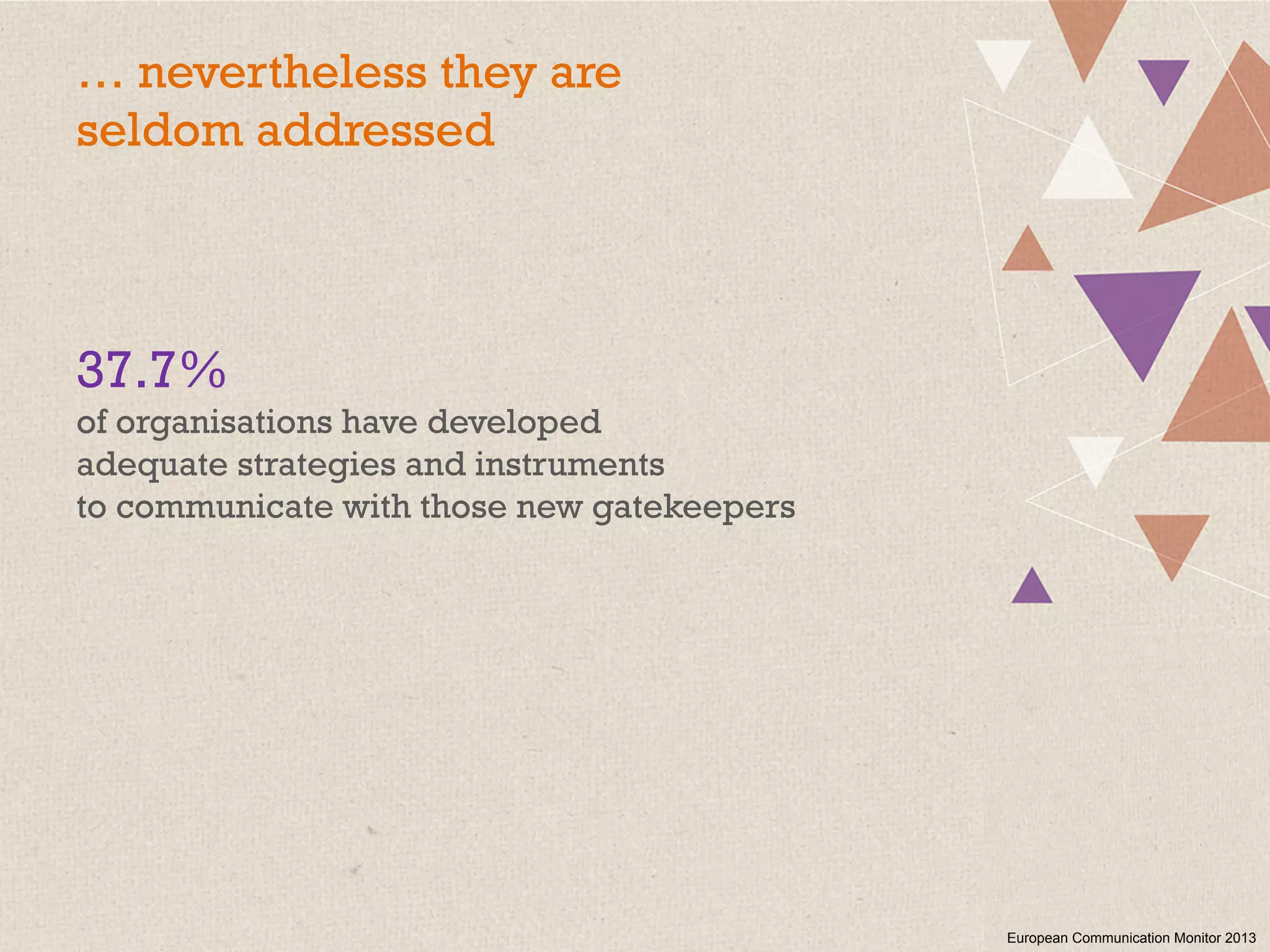
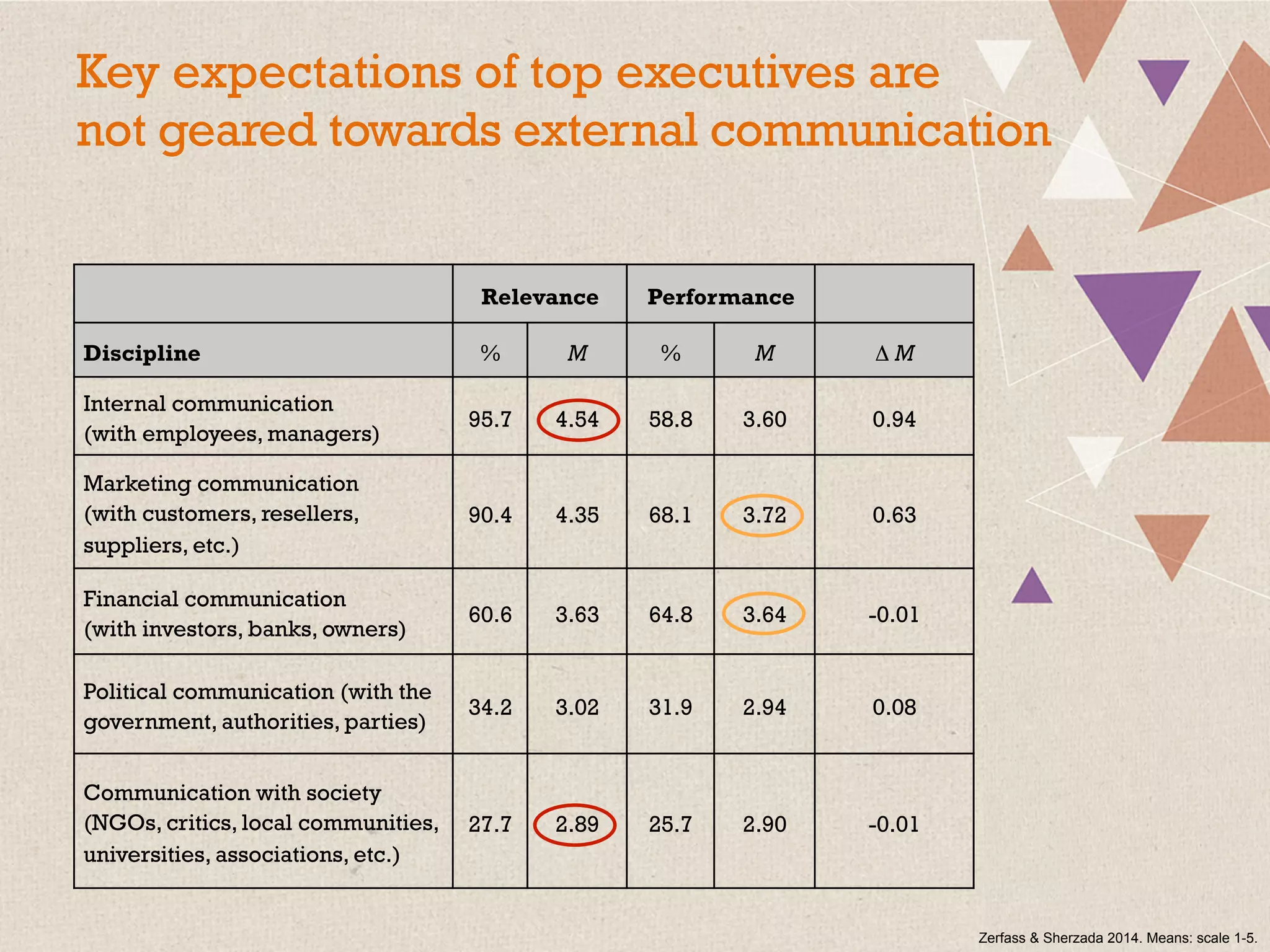
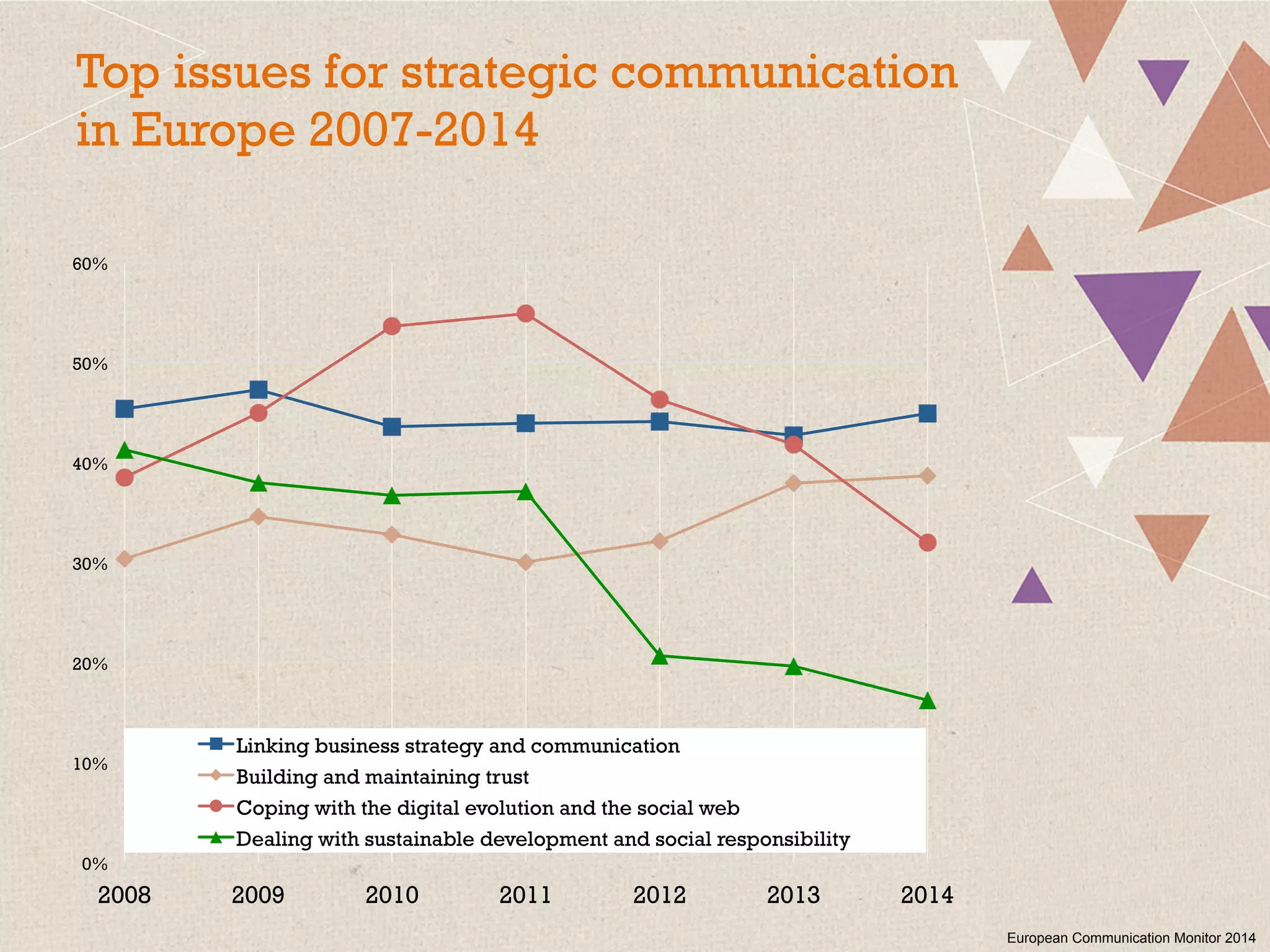
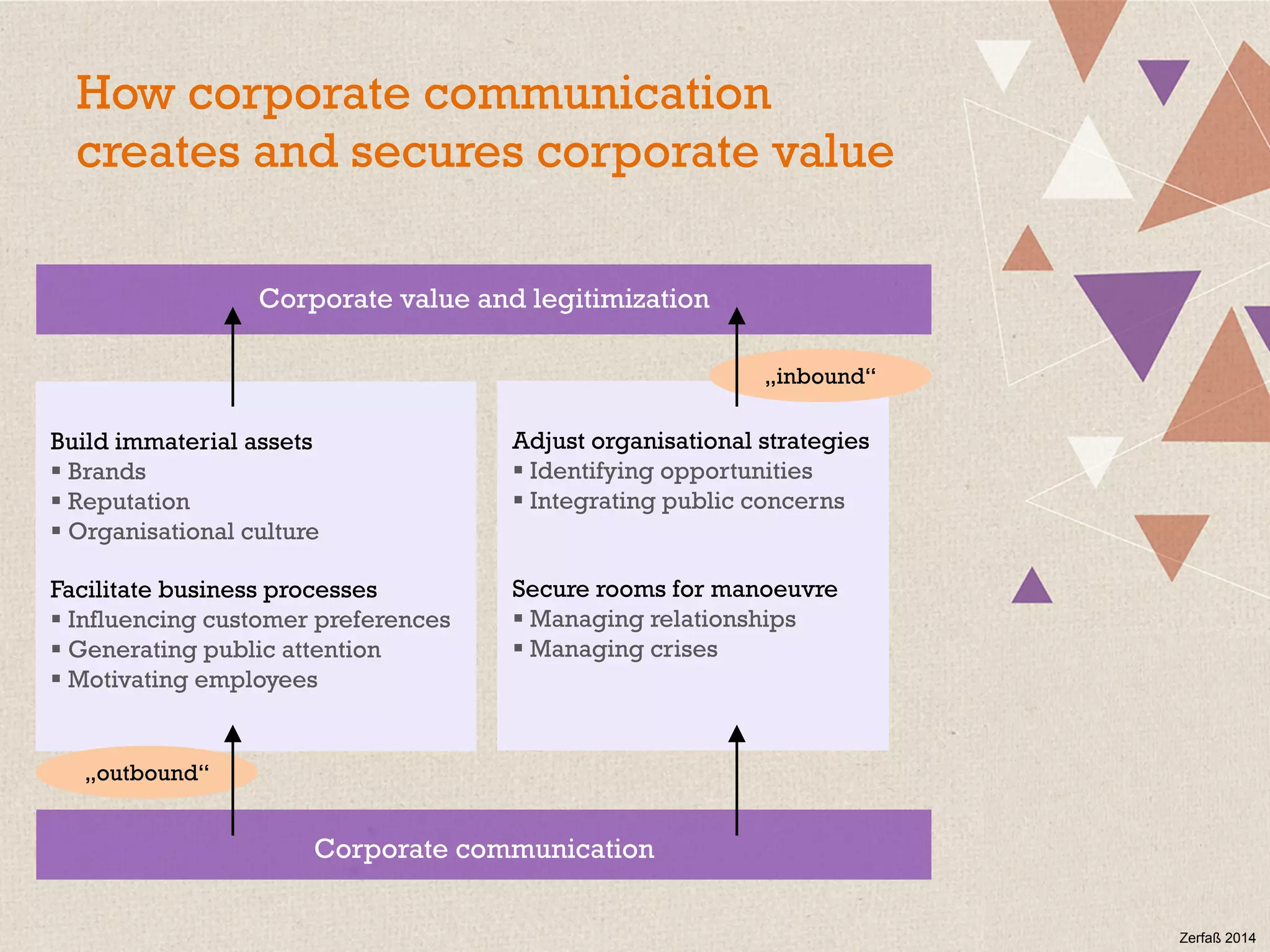
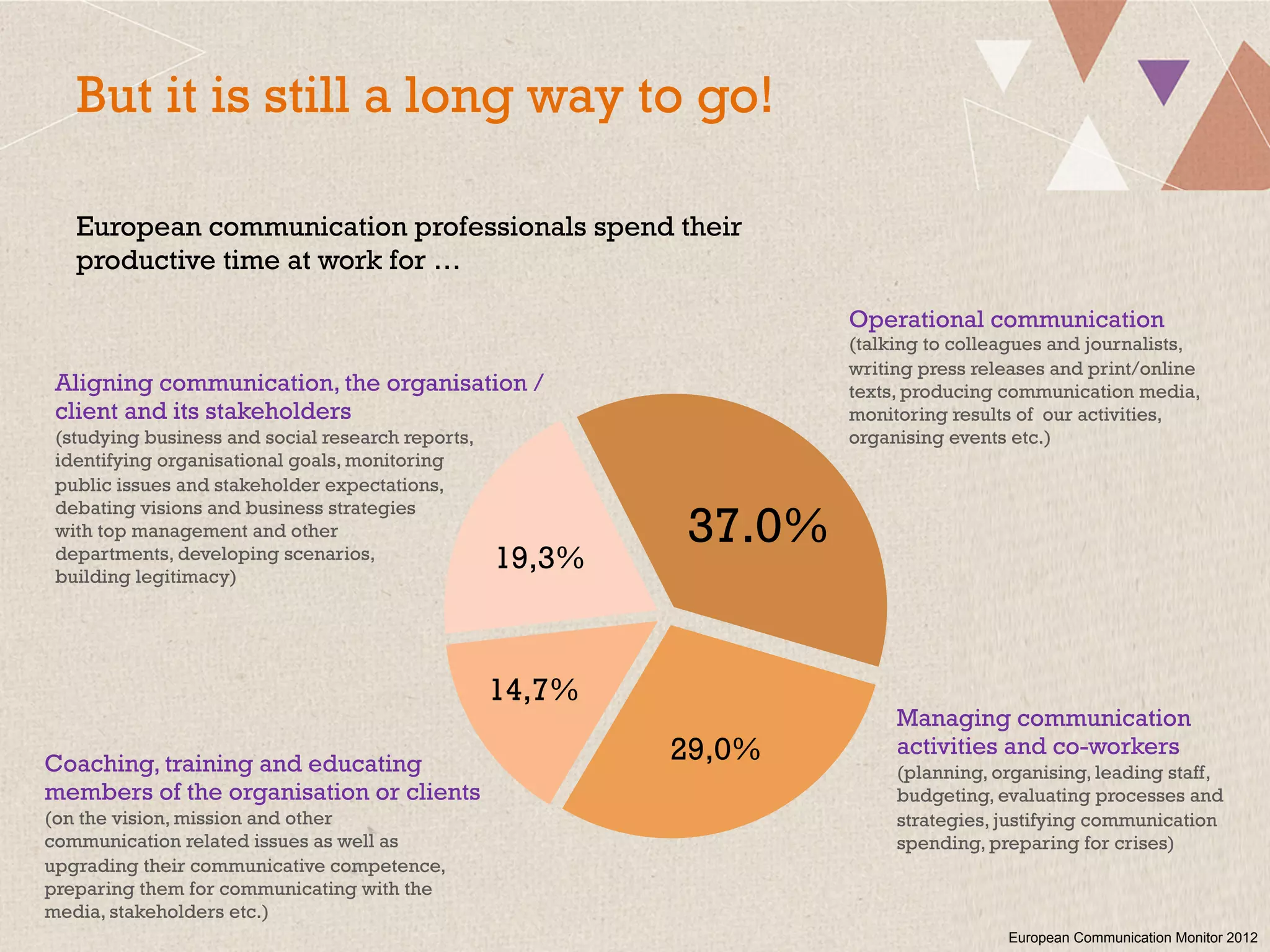
This document summarizes a presentation on the challenges of corporate communications in the digital age. It notes that while communication is increasingly important for organizational success, communication budgets have not increased at the same rate. It also finds that CEOs value their own communication over professional communication functions. Additionally, most corporate communication focuses internally and on marketing, rather than external stakeholders like NGOs. Finally, it argues that corporate communication needs to move beyond outbound messaging to developing communication skills across the organization and having a holistic view of inbound and outbound communication to create long-term value.