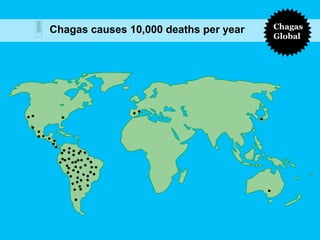
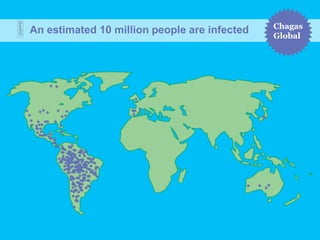
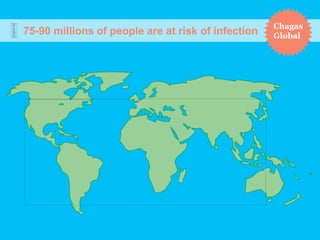
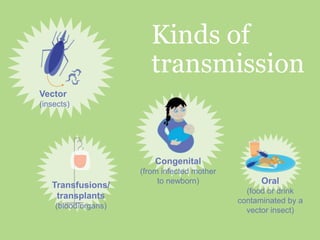
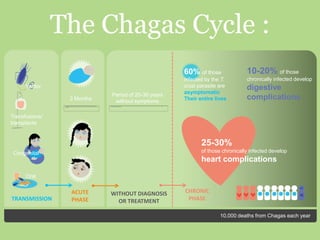
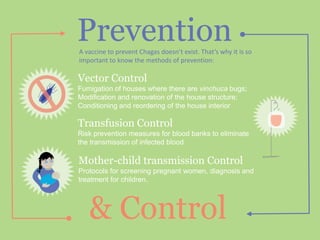
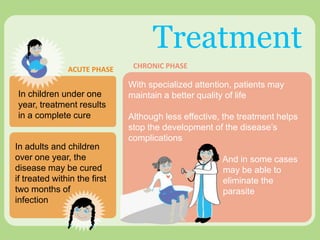
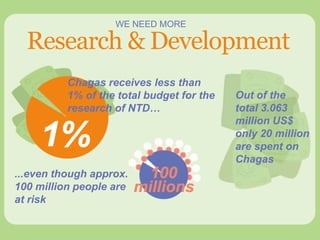
Chagas disease, a neglected tropical disease caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, affects over 10 million people globally and results in around 10,000 deaths annually. It is primarily transmitted by the vinchuca bug and has significant economic impacts in Latin America, with losses due to absenteeism and decreased productivity. Effective prevention and treatment methods are limited, highlighting the need for increased research and funding to combat this public health issue.