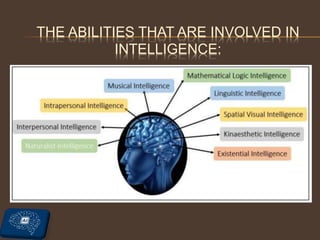
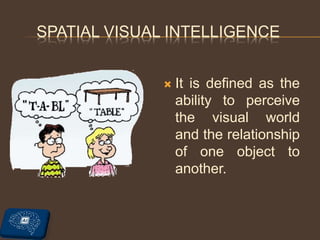
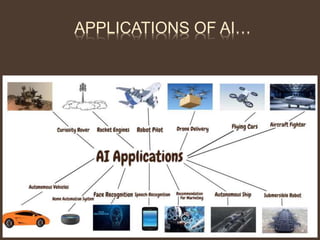
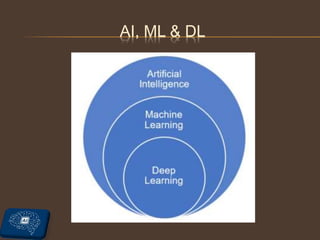
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its definitions, types of intelligence, and applications. It further discusses the distinctions between AI, machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL), while highlighting various domains within AI such as data science, computer vision, and natural language processing. Additionally, it addresses ethical concerns related to AI, including data privacy, AI bias, and access to technology.