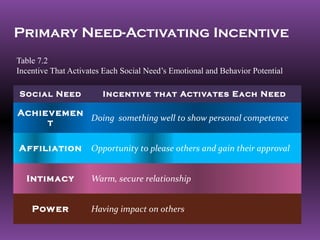
This document discusses social needs, including the needs for achievement, affiliation, intimacy, and power.
1. It describes the incentives that activate each social need, such as doing something well to show competence for achievement or having impact on others for power.
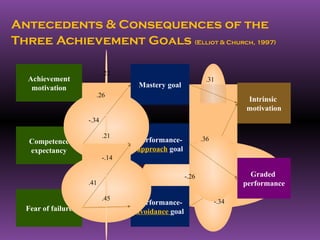
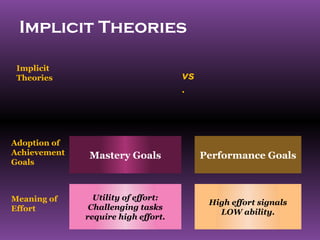
2. For achievement, it discusses Atkinson's model of achievement motivation and how factors like the motive to succeed and avoid failure influence behavior. It also discusses how adopting mastery goals over performance goals can benefit learning.
3. For affiliation and intimacy, it provides a profile of high intimacy motivation including thoughts of relationships and interaction styles.
4. It briefly mentions that certain conditions can involve and satisfy social needs as well as discussing leadership as a variant