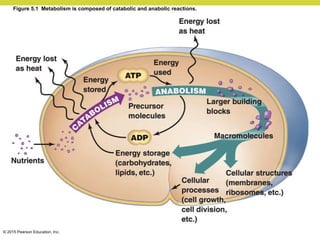
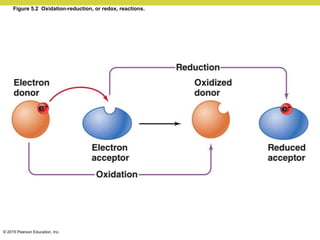
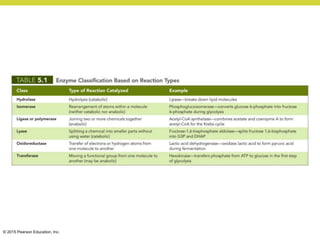
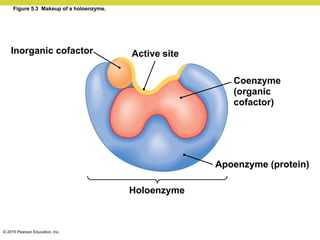
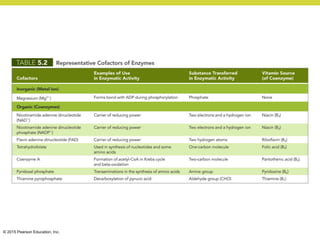
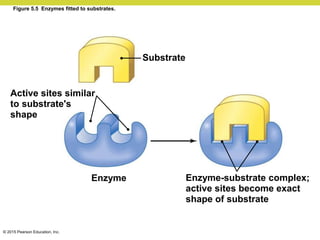
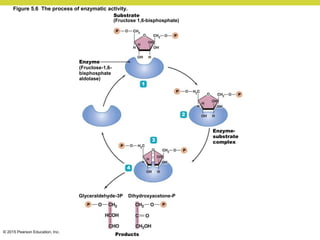
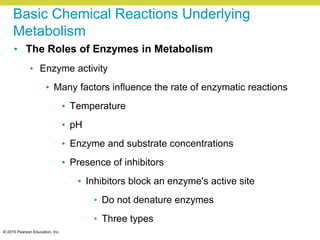
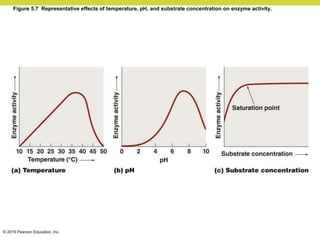
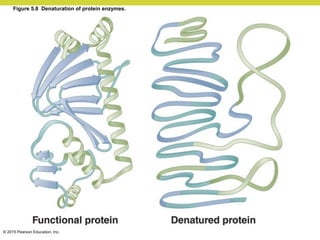
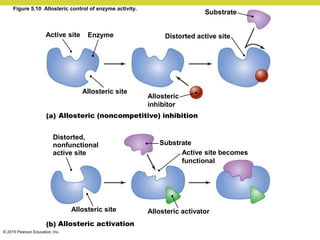
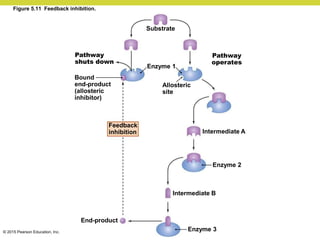
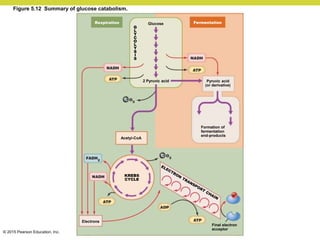
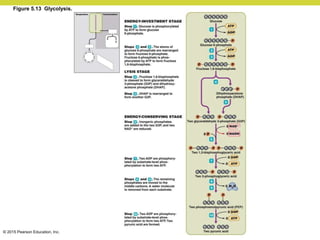
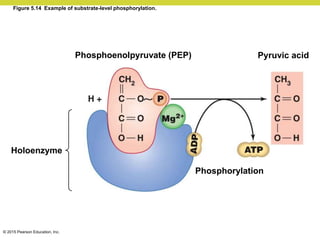
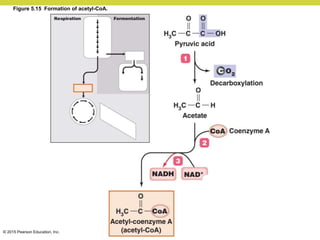
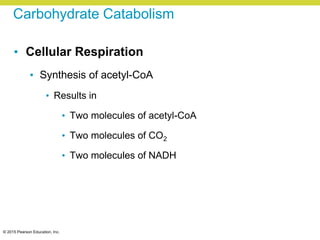
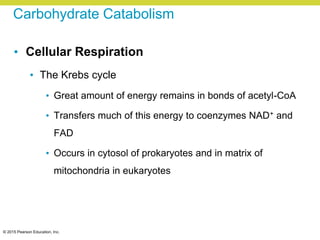
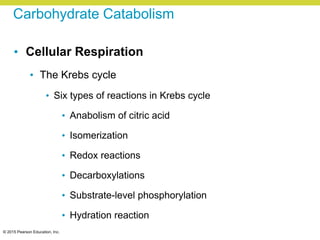
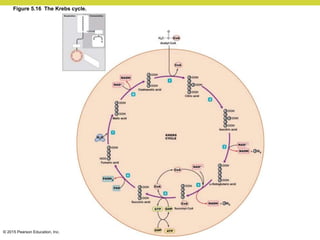
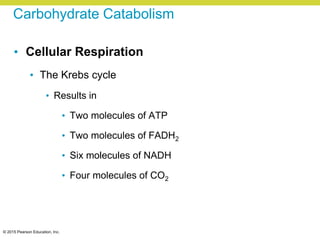
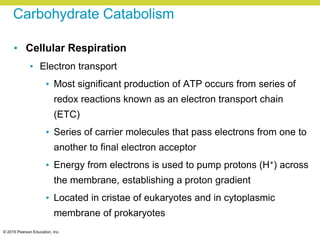
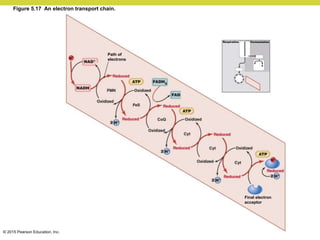
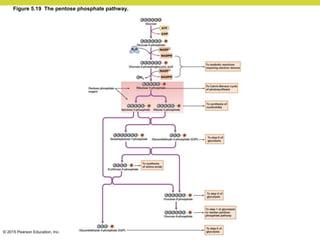
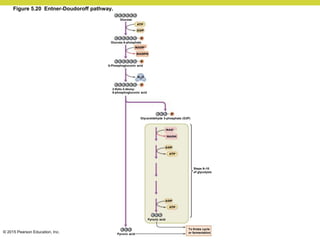
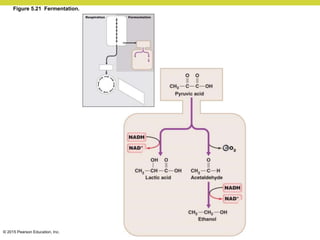
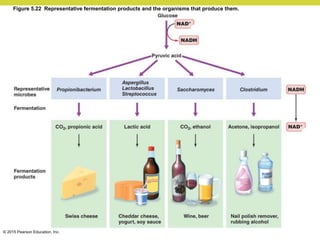
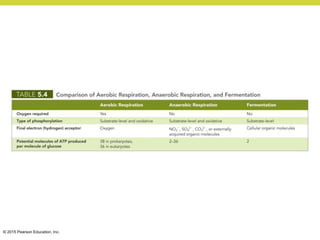
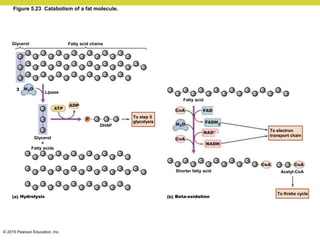
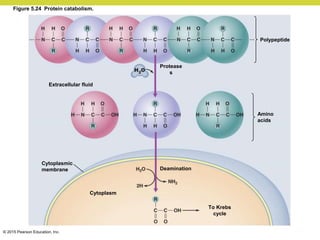
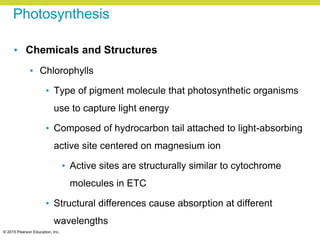
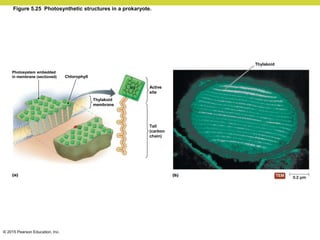
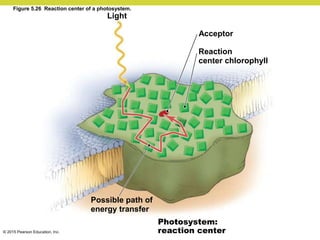
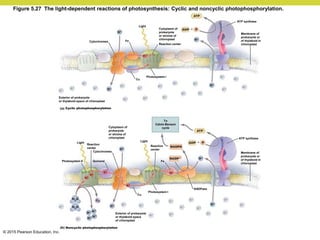
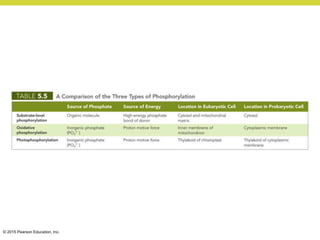
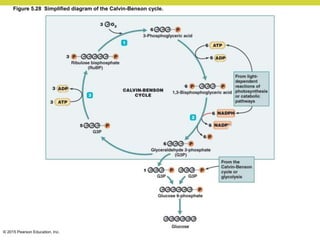
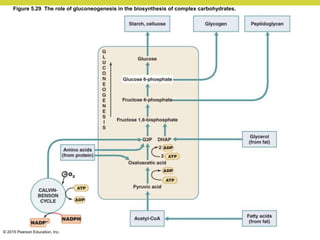
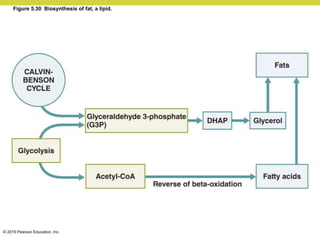
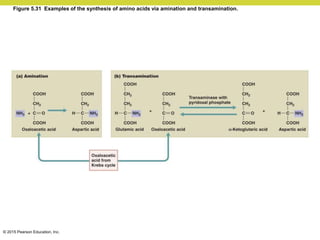
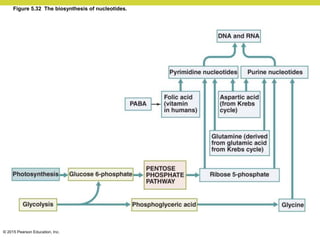
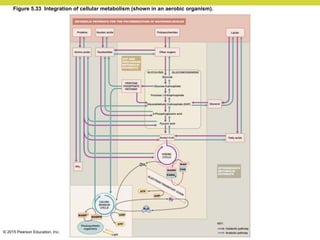
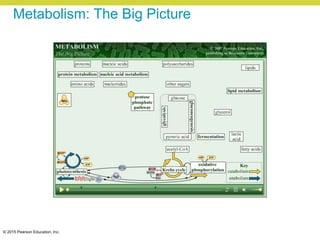
Metabolism involves catabolic reactions that break down molecules and anabolic reactions that build them up. Catabolic pathways are exergonic and release energy, while anabolic pathways are endergonic and require energy. Central to metabolism are oxidation-reduction reactions in which electrons are transferred between molecules. Cells harness this redox energy to produce ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, or photophosphorylation. Enzymes catalyze metabolic reactions and allow organisms to precisely regulate biochemical pathways. Anaerobic organisms can perform oxidation using electron acceptors other than oxygen such as during fermentation.