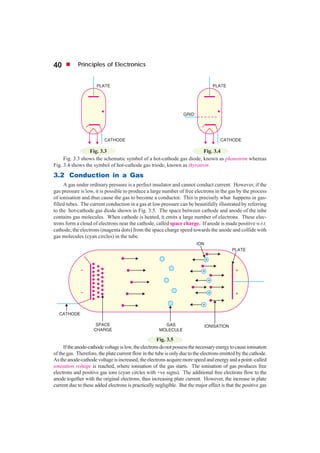
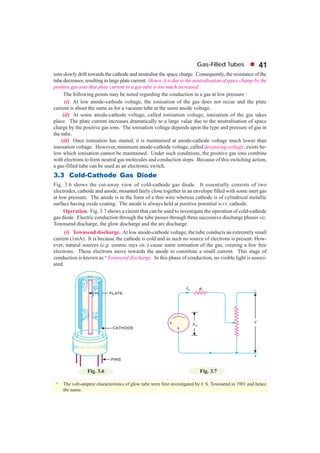
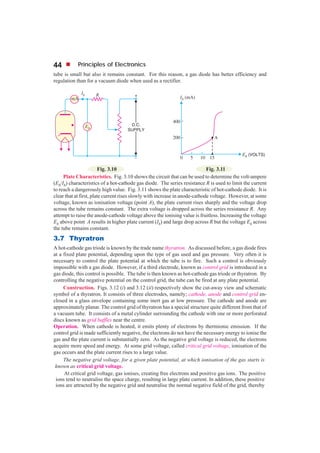
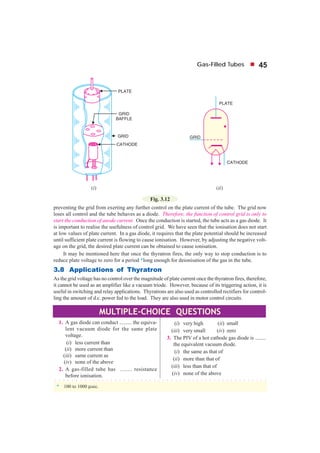
This document discusses gas-filled tubes, which contain a small amount of inert gas at low pressure. There are two main types: cold-cathode tubes, which use natural electron emission, and hot-cathode tubes, which have a heated cathode. Gas-filled tubes can conduct more current than vacuum tubes because electron collisions ionize gas molecules, increasing the number of charge carriers. They also have less control over electron flow than vacuum tubes. Common applications include voltage regulation, rectification, switching, and radio frequency detection.